GLP-1 receptor agonists: differentiation within the class - PubMed (original) (raw)
Comment
GLP-1 receptor agonists: differentiation within the class
Simeon I Taylor. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018 Feb.
No abstract available
Figures
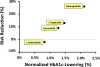
Figure. Magnitude of cardioprotection is correlated with HbA1c-lowering
Hazard ratios from SUSTAIN-6, LEADER, EXSCEL, and ELIXA– are plotted on the vertical axis as a function of ‘normalized’ HbA1c-lowering plotted on the horizontal axis. To account for variation in study design among six head-to-head efficacy studies–, HbA1c-lowering data were normalized as follows:
- Normalized HbA1c-lowering for short-acting exenatide/BYETTA was defined as 1.00%.
- Normalized HbA1c-lowering for lixisenatide was calculated based on head-to-head comparative efficacy data obtained in the GetGoal-X study. Observed HbA1c-lowering was 0.96% for short-acting exenatide/BYETTA and 0.79% for lixisenatide, corresponding to an Efficacy Ratio of 0.82 (=0.79% / 0.96%). A normalized HbA1c-lowering for lixisenatide of **0.82%**was calculated by multiplying the Efficacy Ratio (0.82) times the normalized HbA1c-lowering for short-acting exenatide (1.00%).
- Normalized HbA1c-lowering for long-acting exenatide/BYDUREON was calculated in a similar fashion based on comparative efficacy data in the DURATION-1 study. This yielded a value of1.27% as the normalized HbA1c-lowering for long-acting exenatide [BYETTA].
- The DURATION-6 and SUSTAIN-3 studies reported Efficacy Ratios of 1.16 and 1.67 for liraglutide and semaglutide, respectively, relative to extended-release exenatide/BYDUREON. These calculations yield values for normalized HbA1c-lowering of 1.47% and 2.12% for liraglutide and semaglutide, respectively.
- The AWARD-6 and HARMONY-7 studies reported Efficacy Ratios of 1.04 and 0.79 for dulaglutide and albiglutide, respectively, relative to liraglutide. These calculations yield values for normalized HbA1c-lowering of1.53% and 1.16% for dulaglutide and albiglutide, respectively.
Comment in
- GLP-1 receptor agonists and cardiovascular disease: drug-specific or class effects?
Zweck E, Roden M. Zweck E, et al. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019 Feb;7(2):89-90. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(18)30351-6. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019. PMID: 30683221 No abstract available.
Comment on
- Cardiovascular outcomes with glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists in patients with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis.
Bethel MA, Patel RA, Merrill P, Lokhnygina Y, Buse JB, Mentz RJ, Pagidipati NJ, Chan JC, Gustavson SM, Iqbal N, Maggioni AP, Öhman P, Poulter NR, Ramachandran A, Zinman B, Hernandez AF, Holman RR; EXSCEL Study Group. Bethel MA, et al. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018 Feb;6(2):105-113. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(17)30412-6. Epub 2017 Dec 6. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018. PMID: 29221659
Similar articles
- Glucagon-like peptide-1 analogues for Type 2 diabetes mellitus: current and emerging agents.
Gallwitz B. Gallwitz B. Drugs. 2011 Sep 10;71(13):1675-88. doi: 10.2165/11592810-000000000-00000. Drugs. 2011. PMID: 21902291 Review. - An overview of once-weekly glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists--available efficacy and safety data and perspectives for the future.
Madsbad S, Kielgast U, Asmar M, Deacon CF, Torekov SS, Holst JJ. Madsbad S, et al. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2011 May;13(5):394-407. doi: 10.1111/j.1463-1326.2011.01357.x. Epub 2011 Jan 5. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2011. PMID: 21208359 Review. - Differential effects of GLP-1 receptor agonists on components of dysglycaemia in individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Owens DR, Monnier L, Bolli GB. Owens DR, et al. Diabetes Metab. 2013 Dec;39(6):485-96. doi: 10.1016/j.diabet.2013.09.004. Epub 2013 Oct 22. Diabetes Metab. 2013. PMID: 24156868 Review. - GLP-1 receptor agonists and HBA1c target of <7% in type 2 diabetes: meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.
Esposito K, Mosca C, Brancario C, Chiodini P, Ceriello A, Giugliano D. Esposito K, et al. Curr Med Res Opin. 2011 Aug;27(8):1519-28. doi: 10.1185/03007995.2011.590127. Epub 2011 Jun 13. Curr Med Res Opin. 2011. PMID: 21663496 - GLP-1 receptor agonists: targeting both hyperglycaemia and disease processes in diabetes.
Holst JJ, Seino Y. Holst JJ, et al. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2009 Jul;85(1):1-3. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2009.02.017. Epub 2009 Mar 18. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2009. PMID: 19299027 No abstract available.
Cited by
- The High Cost of Diabetes Drugs: Disparate Impact on the Most Vulnerable Patients.
Taylor SI. Taylor SI. Diabetes Care. 2020 Oct;43(10):2330-2332. doi: 10.2337/dci20-0039. Diabetes Care. 2020. PMID: 32958616 Free PMC article. No abstract available. - Genetics Insights in the Relationship Between Type 2 Diabetes and Coronary Heart Disease.
Goodarzi MO, Rotter JI. Goodarzi MO, et al. Circ Res. 2020 May 22;126(11):1526-1548. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.119.316065. Epub 2020 May 21. Circ Res. 2020. PMID: 32437307 Free PMC article. Review. - Acute pharmacodynamic responses to exenatide: Drug-induced increases in insulin secretion and glucose effectiveness.
Taylor SI, Montasser ME, Yuen AH, Fan H, Yazdi ZS, Whitlatch HB, Mitchell BD, Shuldiner AR, Muniyappa R, Streeten EA, Beitelshees AL. Taylor SI, et al. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2023 Sep;25(9):2586-2594. doi: 10.1111/dom.15143. Epub 2023 Jun 1. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2023. PMID: 37264484 Free PMC article. - Acute pharmacodynamic responses to exenatide: Drug-induced increases in insulin secretion and glucose effectiveness.
Taylor SI, Montasser ME, Yuen AH, Fan H, Yazdi ZS, Whitlatch HB, Mitchell BD, Shuldiner AR, Muniyappa R, Streeten EA, Beitelshees AL. Taylor SI, et al. medRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 May 3:2023.03.15.23287166. doi: 10.1101/2023.03.15.23287166. medRxiv. 2023. PMID: 36993363 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint. - TNF Signaling Impacts Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Expression and Secretion.
Chen S, Wei W, Chen M, Qin X, Qiu L, Zhang L, Zhang Y, Cao Q, Ying Z. Chen S, et al. J Mol Endocrinol. 2018 Oct 15;61(4):153-161. doi: 10.1530/JME-18-0129. J Mol Endocrinol. 2018. PMID: 30021757 Free PMC article.
References
- Bethel MA, Patel RA, Merrill P, et al. Cardiovascular outcomes with GLP-1 receptor agonists: A meta-analysis. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017 in press. - PubMed
- Marso SP, Bain SC, Consoli A, et al. Semaglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:1834–44. - PubMed
- Pfeffer MA, Claggett B, Diaz R, et al. Lixisenatide in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Acute Coronary Syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:2247–57. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources