Overweight in adult cats: a cross-sectional study - PubMed (original) (raw)
Overweight in adult cats: a cross-sectional study
Malin Öhlund et al. Acta Vet Scand. 2018.
Abstract
Background: Overweight in cats is a major risk factor for diabetes mellitus and has also been associated with other disorders. Overweight and obesity are believed to be increasing problems in cats, as is currently seen in people, with important health consequences. The objectives of the present study were to determine the prevalence of overweight in cats from two different cohorts in a cross-sectional study design and to assess associations between overweight and diagnoses, and between overweight and demographic and environmental factors. Data were obtained from medical records for cats (n = 1072) visiting an academic medical center during 2013-2015, and from a questionnaire on insured cats (n = 1665). From the medical records, information on body condition score, breed, age, sex, neutering status, and diagnosis was obtained. The questionnaire included questions relating to the cat's body condition, breed, age, sex, neutering status, outdoor access, activity level, and diet. Data were analyzed by multivariable logistic regression.
Results: The prevalence of overweight was 45% in the medical records cohort and 22% in the questionnaire cohort, where owners judged their pet's body condition. Overweight cats in the medical records cohort were more likely to be diagnosed with lower urinary tract disease, diabetes mellitus, respiratory disease, skin disorders, locomotor disease, and trauma. Eating predominantly dry food, being a greedy eater, and inactivity were factors associated with an increased risk of overweight in the final model in the questionnaire cohort. In both cohorts, the Birman and Persian breeds, and geriatric cats, were less likely to be overweight, and male cats were more likely to be overweight.
Conclusions: The prevalence of overweight cats (45%) as assessed by trained personnel was high and in the same range as previously reported. Birman and Persian cats had a lower risk of overweight. The association with dry food found in adult, neutered cats is potentially important because this type of food is commonly fed to cats worldwide, and warrants further attention. Drawbacks related to the study design need to be acknowledged when interpreting the results, such as a potential for selection bias for cats visiting an animal hospital, and an information bias for questionnaire data. The high occurrence of overweight in cats needs to be addressed because it negatively affects their health.
Keywords: Dry food; Epidemiology; Feline; Logistic regression; Obesity; Type 2 diabetes.
Figures
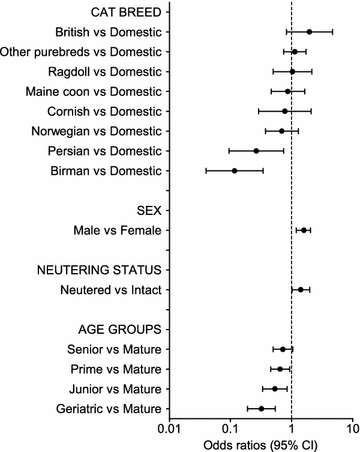
Fig. 1
Multivariable logistic regression on the medical records cohort—demographic factors. Odds ratios for overweight in the medical records cohort (overweight cats n = 479, not overweight n = 593) from the multivariable logistic regression analysis depending on demographic risk factors (breed, sex, neutering status, and age groups). Error bars represent 95% confidence intervals (CI)
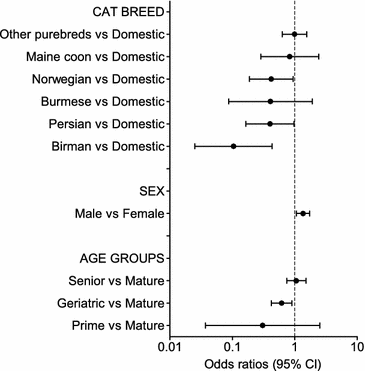
Fig. 2
Multivariable logistic regression on the questionnaire cohort—demographic factors. Odds ratios for overweight in the questionnaire cohort (overweight cats n = 369, not overweight n = 1296) from the multivariable logistic regression analysis depending on demographic risk factors (breed, sex, and age groups). Error bars represent 95% confidence intervals (CI)
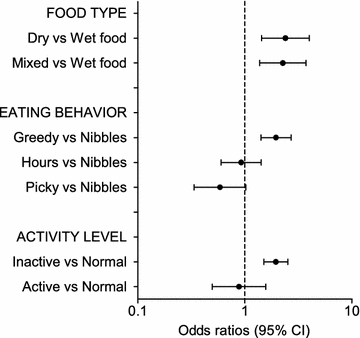
Fig. 3
Multivariable logistic regression on the questionnaire cohort—environmental factors. Odds ratios for overweight in the questionnaire cohort (overweight cats n = 369, not overweight n = 1296) from the multivariable logistic regression analysis depending on environmental risk factors (food type, eating behavior, and activity level). Error bars represent 95% confidence intervals (CI)
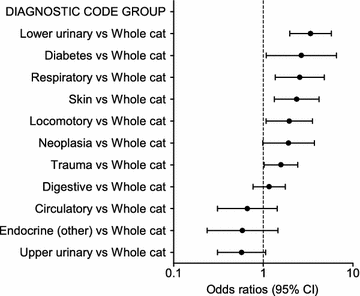
Fig. 4
Multivariable logistic regression on the medical records cohort—diagnostic code groups. Odds ratios for overweight in the medical records cohort (overweight cats n = 479, not overweight n = 593) from the multivariable logistic regression analysis depending on diagnostic code group. Error bars represent 95% confidence intervals (CI)
Similar articles
- Risk factors identified for owner-reported feline obesity at around one year of age: Dry diet and indoor lifestyle.
Rowe E, Browne W, Casey R, Gruffydd-Jones T, Murray J. Rowe E, et al. Prev Vet Med. 2015 Oct 1;121(3-4):273-81. doi: 10.1016/j.prevetmed.2015.07.011. Epub 2015 Jul 31. Prev Vet Med. 2015. PMID: 26265631 - Environmental Risk Factors for Diabetes Mellitus in Cats.
Öhlund M, Egenvall A, Fall T, Hansson-Hamlin H, Röcklinsberg H, Holst BS. Öhlund M, et al. J Vet Intern Med. 2017 Jan;31(1):29-35. doi: 10.1111/jvim.14618. Epub 2016 Dec 1. J Vet Intern Med. 2017. PMID: 27906456 Free PMC article. - Prevalence and risk factors of obesity in an urban population of healthy cats.
Colliard L, Paragon BM, Lemuet B, Bénet JJ, Blanchard G. Colliard L, et al. J Feline Med Surg. 2009 Feb;11(2):135-40. doi: 10.1016/j.jfms.2008.07.002. Epub 2008 Sep 5. J Feline Med Surg. 2009. PMID: 18774325 Free PMC article. - An investigation into the epidemiology of feline obesity in Great Britain: results of a cross-sectional study of 47 companion animal practises.
Courcier EA, Mellor DJ, Pendlebury E, Evans C, Yam PS. Courcier EA, et al. Vet Rec. 2012 Dec 1;171(22):560. doi: 10.1136/vr.100953. Epub 2012 Oct 18. Vet Rec. 2012. PMID: 23081976 - From problem to success: feline weight loss programs that work.
Michel K, Scherk M. Michel K, et al. J Feline Med Surg. 2012 May;14(5):327-36. doi: 10.1177/1098612X12444999. J Feline Med Surg. 2012. PMID: 22511475 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Insights into the interplay between gut microbiota and lipid metabolism in the obesity management of canines and felines.
Li K, Xiao X, Li Y, Lu S, Zi J, Sun X, Xu J, Liu HY, Li X, Song T, Cai D. Li K, et al. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2024 Aug 8;15(1):114. doi: 10.1186/s40104-024-01073-w. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39118186 Free PMC article. Review. - Life tables of annual life expectancy and risk factors for mortality in cats in the UK.
Teng KT, Brodbelt DC, Church DB, O'Neill DG. Teng KT, et al. J Feline Med Surg. 2024 May;26(5):1098612X241234556. doi: 10.1177/1098612X241234556. J Feline Med Surg. 2024. PMID: 38714312 Free PMC article. - Body Condition Scores in Cats and Associations with Systolic Blood Pressure, Glucose Homeostasis, and Systemic Inflammation.
Vitor RC, Oliveira JTS, Navarro AWM, Lima ACR, de Oliveira GMS, Munhoz AD, Sevá ADP, Guedes PEB, Carlos RSA. Vitor RC, et al. Vet Sci. 2024 Mar 28;11(4):151. doi: 10.3390/vetsci11040151. Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 38668418 Free PMC article. - One Health: Circadian Medicine Benefits Both Non-human Animals and Humans Alike.
Farag HI, Murphy BA, Templeman JR, Hanlon C, Joshua J, Koch TG, Niel L, Shoveller AK, Bedecarrats GY, Ellison A, Wilcockson D, Martino TA. Farag HI, et al. J Biol Rhythms. 2024 Jun;39(3):237-269. doi: 10.1177/07487304241228021. Epub 2024 Feb 20. J Biol Rhythms. 2024. PMID: 38379166 Free PMC article. Review. - Cat caregivers' perceptions, motivations, and behaviours for feeding treats: A cross sectional study.
Nielson SA, Khosa DK, Verbrugghe A, Clow KM. Nielson SA, et al. PLoS One. 2024 Jan 10;19(1):e0296011. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0296011. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38198455 Free PMC article.
References
- Scarlett JM, Donoghue S. Associations between body condition and disease in cats. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1998;212:1725–1731. - PubMed
- Panciera DL, Thomas CB, Eicker SW, Atkins CE. Epizootiologic patterns of diabetes mellitus in cats: 333 cases (1980–1986) J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1990;197:1504–1508. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous