Phasing in on the cell cycle - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Phasing in on the cell cycle
Steven Boeynaems et al. Cell Div. 2018.
Abstract
Just like all matter, proteins can also switch between gas, liquid and solid phases. Protein phase transition has claimed the spotlight in recent years as a novel way of how cells compartmentalize and regulate biochemical reactions. Moreover, this discovery has provided a new framework for the study of membrane-less organelle biogenesis and protein aggregation in neurodegenerative disorders. We now argue that this framework could be useful in the study of cell cycle regulation and cancer. Based on our work on phase transitions of arginine-rich proteins in neurodegeneration, via combining mass spectroscopy with bioinformatics analyses, we found that also numerous proteins involved in the regulation of the cell cycle can undergo protein phase separation. Indeed, several proteins whose function affects the cell cycle or are associated with cancer, have been recently found to phase separate from the test tube to cells. Investigating the role of this process for cell cycle proteins and understanding its molecular underpinnings will provide pivotal insights into the biology of cell cycle progression and cancer.
Keywords: Cancer; Centrosome; Nucleolus; Oncogenic fusion; Protein aggregation; Protein phase separation; Stress granules.
Figures
Fig. 1
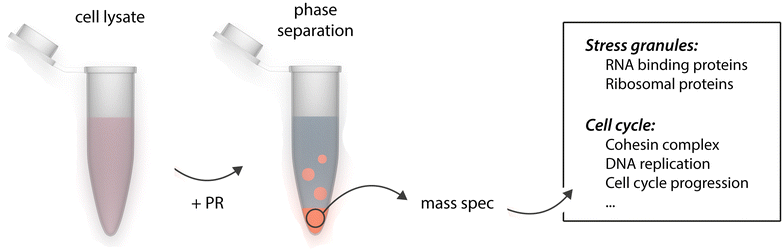
Identification of the phase separating proteome. Cleared cell lysate was incubated with poly-PR peptide to induce phase separation of cellular proteins. Phase separated proteins were precipitated by mild centrifugation and subjected to mass spectrometry. Identified proteins included stress granule factors and other membrane-less organelle components, but surprisingly as well proteins annotated as implicated in the regulation of the cell cycle
Fig. 2
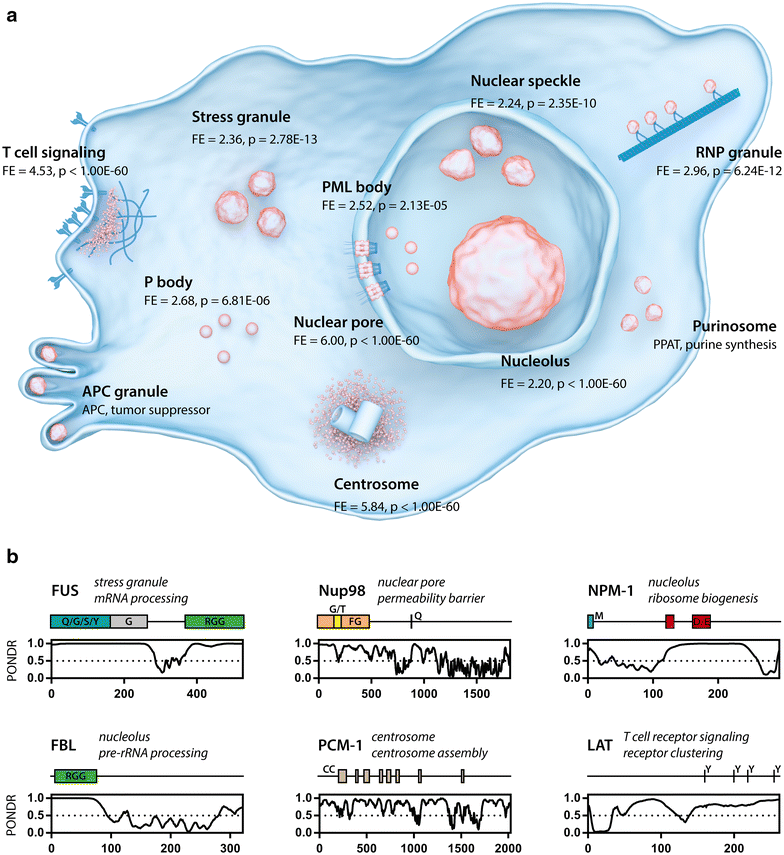
Proteins regulating or affecting the cell cycle are involved in cellular phase separations. a Overview of different membraneless organelles (orange). The fold enrichment of cell cycle proteins (GO:0000278) is shown for each organelle for which the protein content was available. T cell signaling (GO:0050852) [40], stress granule [11], nuclear speckle (GO:0016607), RNP granule (GO:0035770), PML body [73], P body (GO:0000932), nuclear pore (GO:0005643) [74], nucleolus [75], centrosome (GO:0005813) [76]. APC granules and purinosomes were positive for cell cycle proteins APC [77] and PPAT [78] respectively. b Examples of cell cycle proteins found in membrane-less organelles which can undergo phase separation (see Table 1). PONDR disorder prediction plots are shown, indicating prevalence of disordered regions in these proteins (score > 0.5). Coiled coil (CC) and low complexity domains (letters indicate overrepresented amino acids) are also indicated. Phosphotyrosine residues necessary for receptor clustering are indicated for LAT
Similar articles
- Macromolecular crowding: chemistry and physics meet biology (Ascona, Switzerland, 10-14 June 2012).
Foffi G, Pastore A, Piazza F, Temussi PA. Foffi G, et al. Phys Biol. 2013 Aug;10(4):040301. doi: 10.1088/1478-3975/10/4/040301. Epub 2013 Aug 2. Phys Biol. 2013. PMID: 23912807 - Aberrant Phase Transitions: Side Effects and Novel Therapeutic Strategies in Human Disease.
Verdile V, De Paola E, Paronetto MP. Verdile V, et al. Front Genet. 2019 Mar 22;10:173. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.00173. eCollection 2019. Front Genet. 2019. PMID: 30967892 Free PMC article. Review. - Matter over mind: Liquid phase separation and neurodegeneration.
Elbaum-Garfinkle S. Elbaum-Garfinkle S. J Biol Chem. 2019 May 3;294(18):7160-7168. doi: 10.1074/jbc.REV118.001188. Epub 2019 Mar 26. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30914480 Free PMC article. Review. - Phase-to-Phase With Nucleoli - Stress Responses, Protein Aggregation and Novel Roles of RNA.
Latonen L. Latonen L. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019 Apr 26;13:151. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2019.00151. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31080406 Free PMC article. Review. - Friend or foe-Post-translational modifications as regulators of phase separation and RNP granule dynamics.
Hofweber M, Dormann D. Hofweber M, et al. J Biol Chem. 2019 May 3;294(18):7137-7150. doi: 10.1074/jbc.TM118.001189. Epub 2018 Dec 26. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30587571 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Protein Phase Separation: A New Phase in Cell Biology.
Boeynaems S, Alberti S, Fawzi NL, Mittag T, Polymenidou M, Rousseau F, Schymkowitz J, Shorter J, Wolozin B, Van Den Bosch L, Tompa P, Fuxreiter M. Boeynaems S, et al. Trends Cell Biol. 2018 Jun;28(6):420-435. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2018.02.004. Epub 2018 Mar 27. Trends Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 29602697 Free PMC article. Review. - Soft X-ray tomography: virtual sculptures from cell cultures.
Guo J, Larabell CA. Guo J, et al. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2019 Oct;58:324-332. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2019.06.012. Epub 2019 Sep 6. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2019. PMID: 31495562 Free PMC article. Review. - RNA-protein interactions in an unstructured context.
Zagrovic B, Bartonek L, Polyansky AA. Zagrovic B, et al. FEBS Lett. 2018 Sep;592(17):2901-2916. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.13116. Epub 2018 Jun 21. FEBS Lett. 2018. PMID: 29851074 Free PMC article. Review. - Spontaneous driving forces give rise to protein-RNA condensates with coexisting phases and complex material properties.
Boeynaems S, Holehouse AS, Weinhardt V, Kovacs D, Van Lindt J, Larabell C, Van Den Bosch L, Das R, Tompa PS, Pappu RV, Gitler AD. Boeynaems S, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Apr 16;116(16):7889-7898. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1821038116. Epub 2019 Mar 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 30926670 Free PMC article. - Microfluidic characterization of macromolecular liquid-liquid phase separation.
Bremer A, Mittag T, Heymann M. Bremer A, et al. Lab Chip. 2020 Nov 10;20(22):4225-4234. doi: 10.1039/d0lc00613k. Lab Chip. 2020. PMID: 33057557 Free PMC article.
References
- Brangwynne CP, Tompa P, Pappu RV. Polymer physics of intracellular phase transitions. Nat Phys. 2015;11:899–904. doi: 10.1038/nphys3532. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources