Efficacy of Bifidobacterium breve Fermented Milk in Maintaining Remission of Ulcerative Colitis - PubMed (original) (raw)
Randomized Controlled Trial
. 2018 Jul;63(7):1910-1919.
doi: 10.1007/s10620-018-4946-2. Epub 2018 Feb 15.
Affiliations
- PMID: 29450747
- PMCID: PMC6015104
- DOI: 10.1007/s10620-018-4946-2
Randomized Controlled Trial
Efficacy of Bifidobacterium breve Fermented Milk in Maintaining Remission of Ulcerative Colitis
Katsuyoshi Matsuoka et al. Dig Dis Sci. 2018 Jul.
Abstract
Background: Fermented milk products containing Bifidobacterium breve strain Yakult (BFM) may improve clinical status in ulcerative colitis (UC) patients.
Aims: To assess efficacy of BFM in maintaining remission in Japanese patients with quiescent UC.
Methods: This double-blind study (B-FLORA) enrolled 195 patients with quiescent UC, randomized to receive one pack of BFM fermented milk per day [Bifidobacterium breve strain Yakult (10 billion bacteria) and Lactobacillus acidophilus (1 billion bacteria)] (n = 98) or matching placebo (n = 97) for 48 weeks. The primary efficacy endpoint was relapse-free survival (relapse: rectal bleeding score ≥ 2 on Sutherland disease activity index scale for 3 consecutive days and/or initiation of remission induction therapy for worsening of UC).
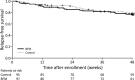
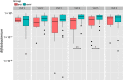
Results: An interim analysis was conducted after inclusion and follow-up of one-third of patients for the first phase of the study (n = 195). Relapse-free survival was not significantly different between the BFM and placebo groups (P = 0.643; hazard ratio 1.16; 95% CI 0.63-2.14, log-rank test), nor was the incidence of relapse. Therefore, the study was discontinued for lack of efficacy. An exploratory analysis of fecal samples from a subgroup of patients revealed no effects of either study beverage on intestinal microbiota, but there was a significant decrease in Bifidobacterium species before relapse, regardless of treatment group. Three mild adverse events occurred for which a causal relationship with the study beverage could not be ruled out (placebo: abdominal bloating and stress in one patient; BFM: body odor in one patient).
Conclusions: BFM had no effect on time to relapse in UC patients compared with placebo.
Study registration: UMIN000007593.
Keywords: Bifidobacterium breve; Probiotics; Randomized controlled trial; Ulcerative colitis.
Conflict of interest statement
Takanori Kanai received a financial donation from Yakult. Yasuo Suzuki, Toshifumi Hibi, Yukari Uemura, Kaoru Yokoyama, Naoki Yoshimura, Reiko Kunisaki, and Katsuyoshi Matsuoka have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
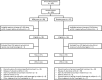
Fig. 1
Study flowchart. Some patients discontinued for more than one reason. 5-ASA 5-aminosalicylic acid, BFM Bifidobacterium breve strain Yakult fermented milk, FAS full analysis set, PPS per-protocol set
Fig. 2
Relapse-free survival rate during the study period (48 weeks after enrollment). BFM Bifidobacterium breve strain Yakult fermented milk
Fig. 3
Bifidobacterium levels in the relapse (exa) versus remission (remi) groups. †P < 0.063, **P = 0.006 by Mann–Whitney U test
Comment in
- A Probiotic for Ulcerative Colitis: The Culture Wars Continue.
Abraham BP, Quigley EMM. Abraham BP, et al. Dig Dis Sci. 2018 Jul;63(7):1678-1680. doi: 10.1007/s10620-018-5097-1. Dig Dis Sci. 2018. PMID: 29785650 No abstract available.
Similar articles
- Randomized placebo-controlled trial assessing the effect of bifidobacteria-fermented milk on active ulcerative colitis.
Kato K, Mizuno S, Umesaki Y, Ishii Y, Sugitani M, Imaoka A, Otsuka M, Hasunuma O, Kurihara R, Iwasaki A, Arakawa Y. Kato K, et al. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2004 Nov 15;20(10):1133-41. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2004.02268.x. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2004. PMID: 15569116 Clinical Trial. - Effects of synbiotic fermented milk containing Lactobacillus acidophilus La-5 and Bifidobacterium animalis ssp. lactis BB-12 on the fecal microbiota of adults with irritable bowel syndrome: A randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.
Bogovič Matijašić B, Obermajer T, Lipoglavšek L, Sernel T, Locatelli I, Kos M, Šmid A, Rogelj I. Bogovič Matijašić B, et al. J Dairy Sci. 2016 Jul;99(7):5008-5021. doi: 10.3168/jds.2015-10743. Epub 2016 May 4. J Dairy Sci. 2016. PMID: 27157575 Clinical Trial. - A randomised double-blind placebo-controlled trial with Lactobacillus acidophilus La-5 and Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis BB-12 for maintenance of remission in ulcerative colitis.
Wildt S, Nordgaard I, Hansen U, Brockmann E, Rumessen JJ. Wildt S, et al. J Crohns Colitis. 2011 Apr;5(2):115-21. doi: 10.1016/j.crohns.2010.11.004. Epub 2011 Jan 8. J Crohns Colitis. 2011. PMID: 21453880 Clinical Trial. - Probiotics for maintaining remission of ulcerative colitis in adults.
Do VT, Baird BG, Kockler DR. Do VT, et al. Ann Pharmacother. 2010 Mar;44(3):565-71. doi: 10.1345/aph.1M498. Epub 2010 Feb 2. Ann Pharmacother. 2010. PMID: 20124461 Review. - Systematic Review and Meta-analysis: Fecal Microbiota Transplantation for Treatment of Active Ulcerative Colitis.
Narula N, Kassam Z, Yuan Y, Colombel JF, Ponsioen C, Reinisch W, Moayyedi P. Narula N, et al. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2017 Oct;23(10):1702-1709. doi: 10.1097/MIB.0000000000001228. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2017. PMID: 28906291 Review.
Cited by
- The Effectiveness of Probiotics in the Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)-A Critical Review.
Jakubczyk D, Leszczyńska K, Górska S. Jakubczyk D, et al. Nutrients. 2020 Jul 2;12(7):1973. doi: 10.3390/nu12071973. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32630805 Free PMC article. Review. - Probiotics as a Coadjuvant Factor in Active or Quiescent Inflammatory Bowel Disease of Adults-A Meta-Analytical Study.
Pabón-Carrasco M, Ramirez-Baena L, Vilar-Palomo S, Castro-Méndez A, Martos-García R, Rodríguez-Gallego I. Pabón-Carrasco M, et al. Nutrients. 2020 Aug 28;12(9):2628. doi: 10.3390/nu12092628. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32872272 Free PMC article. - Side Effects Associated with Probiotic Use in Adult Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.
Dore MP, Bibbò S, Fresi G, Bassotti G, Pes GM. Dore MP, et al. Nutrients. 2019 Dec 2;11(12):2913. doi: 10.3390/nu11122913. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31810233 Free PMC article. - Efficacy and Safety of Probiotics Combined With Traditional Chinese Medicine for Ulcerative Colitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.
Hu Y, Ye Z, She Y, Li L, Wu M, Qin K, Li Y, He H, Hu Z, Yang M, Lu F, Ye Q. Hu Y, et al. Front Pharmacol. 2022 Mar 7;13:844961. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.844961. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35321324 Free PMC article. Review. - Adhesion mechanisms mediated by probiotics and prebiotics and their potential impact on human health.
Monteagudo-Mera A, Rastall RA, Gibson GR, Charalampopoulos D, Chatzifragkou A. Monteagudo-Mera A, et al. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019 Aug;103(16):6463-6472. doi: 10.1007/s00253-019-09978-7. Epub 2019 Jul 2. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 31267231 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical