Fluoroquinolone use and risk of aortic aneurysm and dissection: nationwide cohort study - PubMed (original) (raw)
Fluoroquinolone use and risk of aortic aneurysm and dissection: nationwide cohort study
Björn Pasternak et al. BMJ. 2018.
Abstract
Objective: To investigate whether oral fluoroquinolone use is associated with an increased risk of aortic aneurysm or dissection.
Design: Nationwide historical cohort study using linked register data on patient characteristics, filled prescriptions, and cases of aortic aneurysm or dissection.
Setting: Sweden, July 2006 to December 2013.
Participants: 360 088 treatment episodes of fluoroquinolone use (78%ciprofloxacin) and propensity score matched comparator episodes of amoxicillin use (n=360 088).
Main outcome measures: Cox regression was used to estimate hazard ratios for a first diagnosis of aortic aneurysm or dissection, defined as admission to hospital or emergency department for, or death due to, aortic aneurysm or dissection, within 60 days from start of treatment.
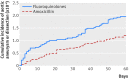
Results: Within the 60 day risk period, the rate of aortic aneurysm or dissection was 1.2 cases per 1000 person years among fluoroquinolone users and 0.7 cases per 1000 person years among amoxicillin users. Fluoroquinolone use was associated with an increased risk of aortic aneurysm or dissection (hazard ratio 1.66 (95% confidence interval 1.12 to 2.46)), with an estimated absolute difference of 82 (95% confidence interval 15 to 181) cases of aortic aneurysm or dissection by 60 days per 1 million treatment episodes. In a secondary analysis, the hazard ratio for the association with fluoroquinolone use was 1.90 (1.22 to 2.96) for aortic aneurysm and 0.93 (0.38 to 2.29) for aortic dissection.
Conclusions: In a propensity score matched cohort, fluoroquinolone use was associated with an increased risk of aortic aneurysm or dissection. This association appeared to be largely driven by aortic aneurysm.
Published by the BMJ Publishing Group Limited. For permission to use (where not already granted under a licence) please go to http://group.bmj.com/group/rights-licensing/permissions.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form at www.icmje.org/coi\_disclosure.pdf and declare: no support from any organisation for the submitted work; no financial relationships with any organisations that might have an interest in the submitted work in the previous three years; no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
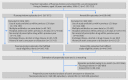
Fig 1
Nationwide cohort of patients in Sweden with treatment episodes of fluoroquinolone use and amoxicillin use, 2006-13. Values for exclusion criteria do not add up to totals because some episodes were excluded for more than one reason
Fig 2
Cumulative incidence of aortic aneurysm or dissection within 60 day risk period from start of study treatment
Comment in
- Fluoroquinolones and the aorta.
Juurlink DN. Juurlink DN. BMJ. 2018 Mar 8;360:k988. doi: 10.1136/bmj.k988. BMJ. 2018. PMID: 29519782 No abstract available.
Similar articles
- Association of Fluoroquinolone Use With Short-term Risk of Development of Aortic Aneurysm.
Newton ER, Akerman AW, Strassle PD, Kibbe MR. Newton ER, et al. JAMA Surg. 2021 Mar 1;156(3):264-272. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2020.6165. JAMA Surg. 2021. PMID: 33404647 Free PMC article. - Association of Fluoroquinolones With the Risk of Aortic Aneurysm or Aortic Dissection.
Gopalakrishnan C, Bykov K, Fischer MA, Connolly JG, Gagne JJ, Fralick M. Gopalakrishnan C, et al. JAMA Intern Med. 2020 Dec 1;180(12):1596-1605. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.4199. JAMA Intern Med. 2020. PMID: 32897307 Free PMC article. - Oral fluoroquinolones and risk of aortic aneurysm or dissection: A nationwide population-based propensity score-matched cohort study.
Garg M, Venugopalan V, Vouri SM, Diaby V, Iovine NM, Park H. Garg M, et al. Pharmacotherapy. 2023 Sep;43(9):883-893. doi: 10.1002/phar.2841. Epub 2023 Jul 11. Pharmacotherapy. 2023. PMID: 37381584 - Fluoroquinolones and the Risk of Aortopathy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.
Latif A, Ahsan MJ, Kapoor V, Lateef N, Malik SU, Patel AD, Khan BA, Bittner M, Holmberg M. Latif A, et al. WMJ. 2020 Sep;119(3):185-189. WMJ. 2020. PMID: 33091293 Review. - Aortic Dissection and Aortic Aneurysms Associated with Fluoroquinolones: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.
Singh S, Nautiyal A. Singh S, et al. Am J Med. 2017 Dec;130(12):1449-1457.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2017.06.029. Epub 2017 Jul 21. Am J Med. 2017. PMID: 28739200 Review.
Cited by
- Delayed Inflammatory Reactions to Hyaluronic Acid Fillers: A Literature Review and Proposed Treatment Algorithm.
Artzi O, Cohen JL, Dover JS, Suwanchinda A, Pavicic T, Landau M, Goodman GJ, Ghannam S, Al Niaimi F, van Loghem JAJ, Goldie K, Sattler S, Cassuto D, Lim TS, Wanitphakdeedecha R, Verner I, Fischer TC, Bucay V, Sprecher E, Shalmon D. Artzi O, et al. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2020 May 18;13:371-378. doi: 10.2147/CCID.S247171. eCollection 2020. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2020. PMID: 32547150 Free PMC article. - Patients at Risk for Aortic Rupture Often Exposed to Fluoroquinolones during Hospitalization.
Frankel WC, Trautner BW, Spiegelman A, Grigoryan L, LeMaire SA. Frankel WC, et al. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019 Jan 29;63(2):e01712-18. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01712-18. Print 2019 Feb. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019. PMID: 30478167 Free PMC article. - The incidence of collagen-associated adverse events in pediatric population with the use of fluoroquinolones: a nationwide cohort study in Taiwan.
Yu PH, Hu CF, Liu JW, Chung CH, Chen YC, Sun CA, Chien WC. Yu PH, et al. BMC Pediatr. 2020 Feb 11;20(1):64. doi: 10.1186/s12887-020-1962-0. BMC Pediatr. 2020. PMID: 32046672 Free PMC article. - The Risk of Clostridioides difficile Infection in Cirrhotic Patients Receiving Norfloxacin for Secondary Prophylaxis of Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis-A Real Life Cohort.
Girleanu I, Trifan A, Huiban L, Muzica C, Nemteanu R, Teodorescu A, Singeap AM, Cojocariu C, Chiriac S, Petrea O, Zenovia S, Nastasa R, Cuciureanu T, Stanciu C. Girleanu I, et al. Medicina (Kaunas). 2021 Sep 13;57(9):964. doi: 10.3390/medicina57090964. Medicina (Kaunas). 2021. PMID: 34577887 Free PMC article. - Current progress of fluoroquinolones-increased risk of aortic aneurysm and dissection.
Jun C, Fang B. Jun C, et al. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2021 Sep 28;21(1):470. doi: 10.1186/s12872-021-02258-1. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2021. PMID: 34583637 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Hicks LA, Bartoces MG, Roberts RM, et al. US outpatient antibiotic prescribing variation according to geography, patient population, and provider specialty in 2011. Clin Infect Dis 2015;60:1308-16. - PubMed
- Cipro (ciprofloxacin product information). Bayer HealthCare. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2016/019537s085,020....
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical