Coptidis rhizoma and its main bioactive components: recent advances in chemical investigation, quality evaluation and pharmacological activity - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Coptidis rhizoma and its main bioactive components: recent advances in chemical investigation, quality evaluation and pharmacological activity
Fan-Cheng Meng et al. Chin Med. 2018.
Abstract
Background: Coptidis rhizoma (CR) is the dried rhizome of Coptis chinensis Franch., C. deltoidea C. Y. Cheng et Hsiao or C. teeta Wall. (Ranunculaceae) and is commonly used in Traditional Chinese Medicine for the treatment of various diseases including bacillary dysentery, typhoid, tuberculosis, epidemic cerebrospinal meningitis, empyrosis, pertussis, and other illnesses.
Methods: A literature survey was conducted via SciFinder, ScieneDirect, PubMed, Springer, and Wiley databases. A total of 139 selected references were classified on the basis of their research scopes, including chemical investigation, quality evaluation and pharmacological studies.
Results: Many types of secondary metabolites including alkaloids, lignans, phenylpropanoids, flavonoids, phenolic compounds, saccharides, and steroids have been isolated from CR. Among them, protoberberine-type alkaloids, such as berberine, palmatine, coptisine, epiberberine, jatrorrhizine, columamine, are the main components of CR. Quantitative determination of these alkaloids is a very important aspect in the quality evaluation of CR. In recent years, with the advances in isolation and detection technologies, many new instruments and methods have been developed for the quantitative and qualitative analysis of the main alkaloids from CR. The quality control of CR has provided safety for pharmacological applications. These quality evaluation methods are also frequently employed to screen the active components from CR. Various investigations have shown that CR and its main alkaloids exhibited many powerful pharmacological effects including anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, anti-diabetic, neuroprotective, cardioprotective, hypoglycemic, anti-Alzheimer and hepatoprotective activities.
Conclusion: This review summarizes the recent phytochemical investigations, quality evaluation methods, the biological studies focusing on CR as well as its main alkaloids.
Keywords: Coptidis rhizoma; Coptis genus; Pharmacological effects; Phytochemistry; Quality evaluation.
Figures
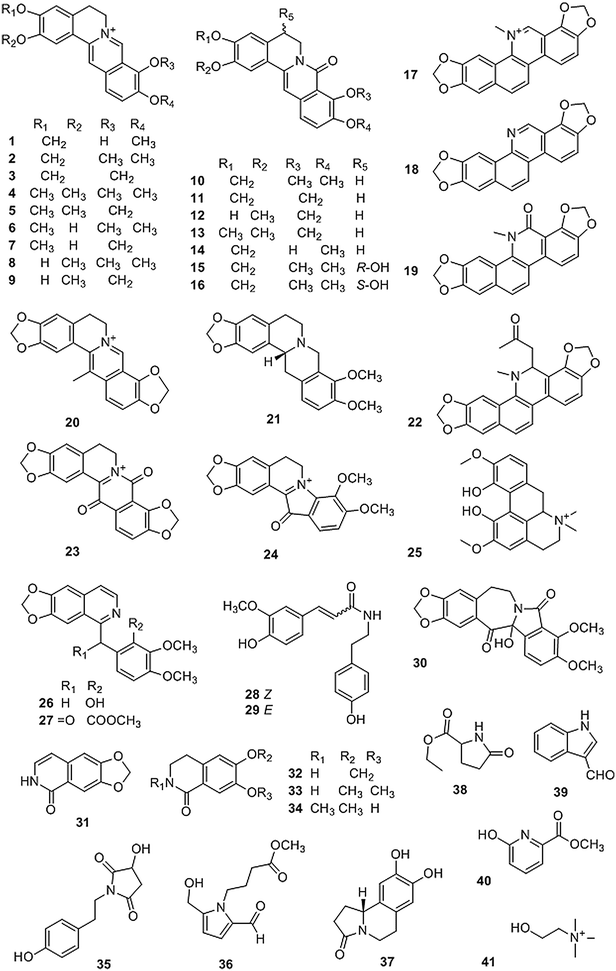
Fig. 1
Structures of alkaloids isolated from Coptis genus
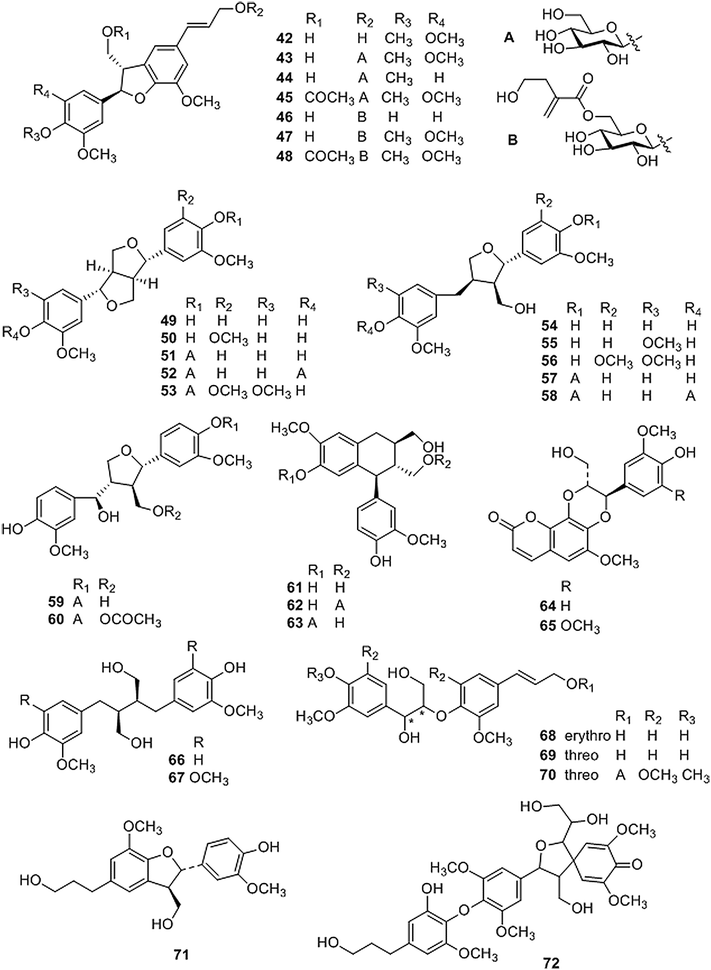
Fig. 2
Structures of lignans isolated from Coptis genus
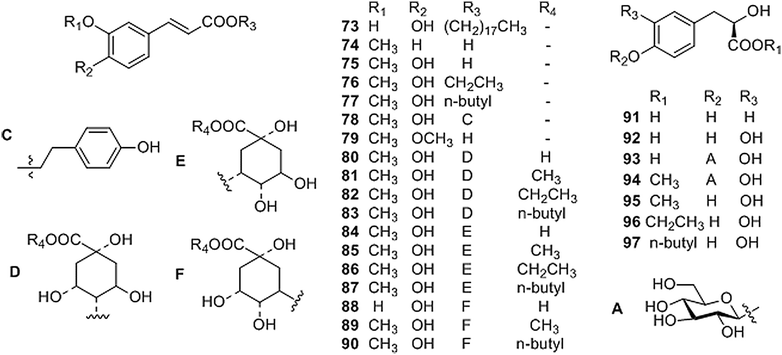
Fig. 3
Structures of phenylpropanoids isolated from Coptis genus
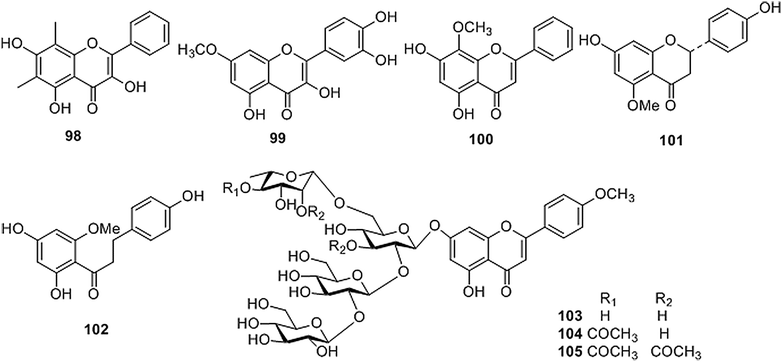
Fig. 4
Structures of flavonoids isolated from Coptis genus
Fig. 5
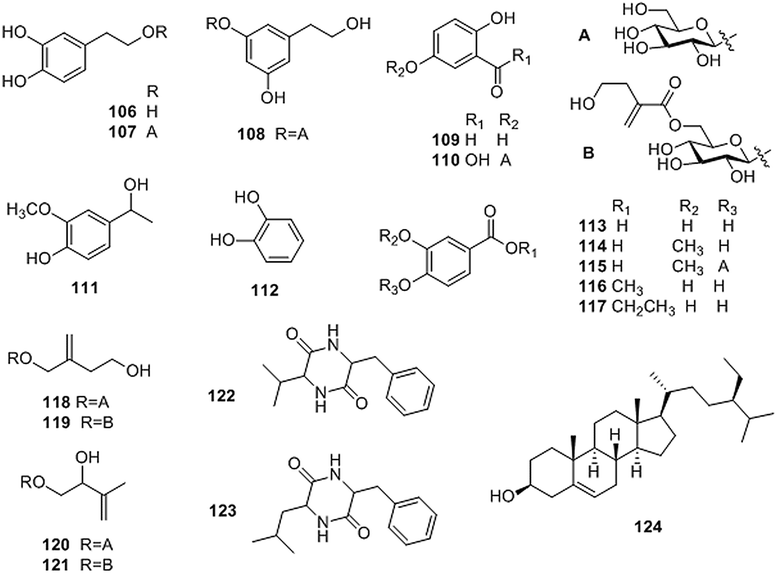
Structures of other compounds isolated from Coptis genus
Similar articles
- Coptidis Rhizoma: a comprehensive review of its traditional uses, botany, phytochemistry, pharmacology and toxicology.
Wang J, Wang L, Lou GH, Zeng HR, Hu J, Huang QW, Peng W, Yang XB. Wang J, et al. Pharm Biol. 2019 Dec;57(1):193-225. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2019.1577466. Pharm Biol. 2019. PMID: 30963783 Free PMC article. Review. - Integration of HPLC-based fingerprint and quantitative analyses for differentiating botanical species and geographical growing origins of Rhizoma coptidis.
Lv X, Li Y, Tang C, Zhang Y, Zhang J, Fan G. Lv X, et al. Pharm Biol. 2016 Dec;54(12):3264-3271. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2016.1223699. Epub 2016 Aug 27. Pharm Biol. 2016. PMID: 27569515 - Quality evaluation and species differentiation of Rhizoma coptidis by using proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy.
Fan G, Zhang MY, Zhou XD, Lai XR, Yue QH, Tang C, Luo WZ, Zhang Y. Fan G, et al. Anal Chim Acta. 2012 Oct 17;747:76-83. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2012.08.038. Epub 2012 Aug 30. Anal Chim Acta. 2012. PMID: 22986138 - Ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry for the determination of 10 alkaloids in beagle plasma after the oral administration of the three Coptidis rhizoma extracts.
Ren Y, Wang Z, Wu C, Dong H, Gan C, Fan L, Wang W, Yang C. Ren Y, et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2019 Jul 15;239:111896. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.111896. Epub 2019 Apr 24. J Ethnopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31028858 - Rhizoma Coptidis: A Potential Cardiovascular Protective Agent.
Tan HL, Chan KG, Pusparajah P, Duangjai A, Saokaew S, Mehmood Khan T, Lee LH, Goh BH. Tan HL, et al. Front Pharmacol. 2016 Oct 7;7:362. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2016.00362. eCollection 2016. Front Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27774066 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- The impact of traditional Chinese medicine and dietary compounds on modulating gut microbiota in hepatic fibrosis: A review.
Xue X, Zhou H, Gao J, Li X, Wang J, Bai W, Bai Y, Fan L, Chang H, Shi S. Xue X, et al. Heliyon. 2024 Sep 26;10(19):e38339. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e38339. eCollection 2024 Oct 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39391468 Free PMC article. Review. - ROS-Mediated Anti-Tumor Effect of Coptidis Rhizoma against Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Hep3B Cells and Xenografts.
Kim SY, Park C, Kim MY, Ji SY, Hwangbo H, Lee H, Hong SH, Han MH, Jeong JW, Kim GY, Son CG, Cheong J, Choi YH. Kim SY, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 30;22(9):4797. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094797. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33946527 Free PMC article. - Active Ingredients and Mechanism of Action of Rhizoma Coptidis against Type 2 Diabetes Based on Network-Pharmacology and Bioinformatics.
Sun Y, Xiong YY, Wu HZ, Xiong WC, Liu B, Xie ZT, Xiao WP, Huang BS, Yang YF. Sun Y, et al. Curr Med Sci. 2020 Apr;40(2):257-264. doi: 10.1007/s11596-020-2182-4. Epub 2020 Apr 26. Curr Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 32337687 - A Natural Isoquinoline Alkaloid With Antitumor Activity: Studies of the Biological Activities of Berberine.
Liu D, Meng X, Wu D, Qiu Z, Luo H. Liu D, et al. Front Pharmacol. 2019 Feb 14;10:9. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00009. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30837865 Free PMC article. Review. - Self-assembled aggregations in Coptidis Rhizoma decoction dynamically regulate intestinal tissue permeability through Peyer's patch-associated immunity.
Zhang QQ, Yang Y, Ren RR, Chen QQ, Wu JJ, Zheng YY, Hou XH, Zhang YF, Xue MS, Yin DK. Zhang QQ, et al. Chin Herb Med. 2021 Jun 30;13(3):370-380. doi: 10.1016/j.chmed.2021.06.004. eCollection 2021 Jul. Chin Herb Med. 2021. PMID: 36118921 Free PMC article.
References
- Qian XC, Zhang L, Tao Y, Huang P, Li JS, Chai C, Li W, Di LQ, Cai BC. Simultaneous determination of ten alkaloids of crude and wine-processed rhizoma Coptidis aqueous extracts in rat plasma by UHPLC–ESI–MS/MS and its application to a comparative pharmacokinetic study. J. Pharm Biomed. 2015;105:64–73. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2014.11.049. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources