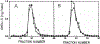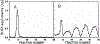Steroid metabolic disturbances in Prader-Willi syndrome - PubMed (original) (raw)
Steroid metabolic disturbances in Prader-Willi syndrome
F I Chasalow et al. Am J Med Genet. 1987 Dec.
Abstract
We have studied steroid sulfate conjugates in serum samples from 17 children with Prader-Willi syndrome (PWS) by extraction, enzymatic hydrolysis and chromatography of the hydrolysed, free steroids. The chromatograms in patients with PWS can be divided into 2 classes. Ten (4 with the deletion on chromosome 15 and 6 without) of 17 had a normal pattern with dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) as the only steroid detected. However, 7 out of 17 (3 with the deletion and 4 without) had a very different pattern. The chromatogram derived from these hydrolysates had 5 major peaks. One of these was DHEA; a second peak was tentatively identified as 16 alpha-hydroxy-DHEA on the basis of column retention time and immunoreactivity. The remaining 3, more polar, compounds have not yet been identified. The presence of unusual steroid sulfoconjugates in serum may correlate with other features of PWS and may be the basis for dividing PWS into two separate disease states: a) PWS-1 associated with DHEA-S as the only sulfo-conjugate and b) PWS-2 associated with unusual sulfo-conjugates. One interesting possibility is that these sulfo-conjugates may have a hormonal function, even though no function has yet been recognized for DHEA-S. Then, PWS may be the common clinical manifestation of a variety of different defects in the sulfo-conjugate metabolic pathway.
Figures
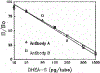
Figure 1.
Displacement curves for antibodies A and B with authentic DHEA-S.
Figure 2.
Sephasorb HP column chromatography of steroid sulfo-conjugates from children with PWS. Panel A - Chromatogram derived Case 14. Panel B - Chromatogram derived case 3.
Figure 3.
Sephadex LH-20 column chromatography of steroid sulfo-conjugates from children with PWS after hydrolysis with Glusalase. Panel A - Chromatogram derived from Case 14. Panel B - Chromatogram derived from Case 3.
Similar articles
- Obsessive-compulsive symptoms in Prader-Willi and "Prader-Willi-Like" patients.
State MW, Dykens EM, Rosner B, Martin A, King BH. State MW, et al. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 1999 Mar;38(3):329-34. doi: 10.1097/00004583-199903000-00021. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 1999. PMID: 10087695 - Routine screening for microdeletions by FISH in 77 patients suspected of having Prader-Willi or Angelman syndromes using YAC clone 273A2 (D15S10).
Erdel M, Schuffenhauer S, Buchholz B, Barth-Witte U, Köchl S, Utermann B, Duba HC, Utermann G. Erdel M, et al. Hum Genet. 1996 Jun;97(6):784-93. doi: 10.1007/BF02346190. Hum Genet. 1996. PMID: 8641697 - Metabolic syndrome in adult patients with Prader-Willi syndrome.
Grugni G, Crinò A, Bedogni G, Cappa M, Sartorio A, Corrias A, Di Candia S, Gargantini L, Iughetti L, Pagano C, Ragusa L, Salvatoni A, Spera S, Vettor R, Chiumello G, Brambilla P. Grugni G, et al. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2013 Nov;23(11):1134-40. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2012.11.006. Epub 2012 Dec 7. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2013. PMID: 23220075 - Interstitial 6q deletion with a Prader-Willi-like phenotype: a new case and review of the literature.
Gilhuis HJ, van Ravenswaaij CM, Hamel BJ, Gabreëls FJ. Gilhuis HJ, et al. Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 2000;4(1):39-43. doi: 10.1053/ejpn.1999.0259. Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 2000. PMID: 10701104 Review. - Prader-Willi syndrome with an unusually large 15q deletion due to an unbalanced translocation t(4;15).
Varela MC, Lopes GM, Koiffmann CP. Varela MC, et al. Ann Genet. 2004 Jul-Sep;47(3):267-73. doi: 10.1016/j.anngen.2004.01.003. Ann Genet. 2004. PMID: 15337472 Review.
Cited by
- Characterization of Obesity in the Prader-Labhart-Willi Syndrome: Fatness Patterning.
Meaney FJ, Butler MG. Meaney FJ, et al. Med Anthropol Q. 1989 Sep;3(3):294-305. doi: 10.1525/maq.1989.3.3.02a00080. Epub 2009 Oct 28. Med Anthropol Q. 1989. PMID: 27695159 Free PMC article. - Whole genome microarray analysis of gene expression in Prader-Willi syndrome.
Bittel DC, Kibiryeva N, Sell SM, Strong TV, Butler MG. Bittel DC, et al. Am J Med Genet A. 2007 Mar 1;143A(5):430-42. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.31606. Am J Med Genet A. 2007. PMID: 17236194 Free PMC article. - Prader-Willi syndrome: current understanding of cause and diagnosis.
Butler MG. Butler MG. Am J Med Genet. 1990 Mar;35(3):319-32. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320350306. Am J Med Genet. 1990. PMID: 2309779 Free PMC article.
References
- Buster JE, Abraham GE (1972): Radioimmunoassay of plasma dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate. Analyt Lett 5:543–551.
- Chasalow FI (1979): Mechanism and control of testicular steroidogenesis. J Biol Chem 254:3000–3005. - PubMed
- Chasalow FI, Blethen SL (1985): Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) measurements in cord blood. Steroids 45:187–193. - PubMed
- Chasalow FI, Blethen SL, Taysi K (1985): Possible abnormalities of steroid secretion in children with Smith-Lemli-Opitz Syndrome and their parents. Steroids 46: 827–843. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical