The cGAS-cGAMP-STING pathway connects DNA damage to inflammation, senescence, and cancer - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
. 2018 May 7;215(5):1287-1299.
doi: 10.1084/jem.20180139. Epub 2018 Apr 5.
Affiliations
- PMID: 29622565
- PMCID: PMC5940270
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20180139
Review
The cGAS-cGAMP-STING pathway connects DNA damage to inflammation, senescence, and cancer
Tuo Li et al. J Exp Med. 2018.
Abstract
Detection of microbial DNA is an evolutionarily conserved mechanism that alerts the host immune system to mount a defense response to microbial infections. However, this detection mechanism also poses a challenge to the host as to how to distinguish foreign DNA from abundant self-DNA. Cyclic guanosine monophosphate (GMP)-adenosine monophosphate (AMP) synthase (cGAS) is a DNA sensor that triggers innate immune responses through production of the second messenger cyclic GMP-AMP (cGAMP), which binds and activates the adaptor protein STING. However, cGAS can be activated by double-stranded DNA irrespective of the sequence, including self-DNA. Although how cGAS is normally kept inactive in cells is still not well understood, recent research has provided strong evidence that genomic DNA damage leads to cGAS activation to stimulate inflammatory responses. This review summarizes recent findings on how genomic instability and DNA damage trigger cGAS activation and how cGAS serves as a link from DNA damage to inflammation, cellular senescence, and cancer.
© 2018 Li and Chen.
Figures
Figure 1.
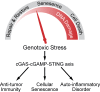
Inflammatory response is another biological outcome of genomic instability. Genotoxic stress leads to DNA damage repair, cellular senescence, and cell death in a manner that depends on the severity of the DNA damage**.** The cGAS–cGAMP–STING pathway is activated by DNA damage to mediate antitumor immunity, senescence, and inflammatory responses.
Figure 2.
The cGAS–cGAMP–STING pathway detects cytoplasmic DNA after DNA damage and activate type I IFNs and other cytokines. Like DDR, the immune response is induced by various forms of genotoxic stress, ranging from ionizing radiation, DNA-damaging drugs, oxidative stress, oncogenic signaling, telomere shortening, and chromosome missegregation to viral infections and activation of endogenous retroelements. Nuclear DNA damage can generate cytoplasmic DNA in two possible ways. First, certain genomic damage causes chromosome to missegregate in subsequent cell division; the chromosome failing to partition into the new nuclei will form micronuclei. When the nuclear evelope (NE) of micronuclei ruptures, the DNA content is exposed to cGAS surveillance. Second, nuclear DNA damage can also generate ssDNA in the cytoplasm in a less understood process (dashed line and question mark). Such cytoplasmic DNA is degraded by Trex1, the loss of which leads to cGAS activation. Active cGAS dimerizes to synthesize cGAMP from GTP and ATP. cGAMP acts as a second messenger to activate STING on the ER surface. STING then activates transcription factors IRF3 and NF-κB via kinases TBK1 and IKK, respectively. IRF3 and NF-κB translocate into the nucleus to elicit the expression of IFNs and other cytokines. Damage to mitochondria or mitochondrial DNA can also lead to accumulation of mitochondrial DNA in the cytosol, resulting in cGAS activation and sterile inflammation (not depicted).
Similar articles
- Structures and Mechanisms in the cGAS-STING Innate Immunity Pathway.
Zhang X, Bai XC, Chen ZJ. Zhang X, et al. Immunity. 2020 Jul 14;53(1):43-53. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2020.05.013. Immunity. 2020. PMID: 32668227 Review. - cGAMP-activated cGAS-STING signaling: its bacterial origins and evolutionary adaptation by metazoans.
Patel DJ, Yu Y, Xie W. Patel DJ, et al. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2023 Mar;30(3):245-260. doi: 10.1038/s41594-023-00933-9. Epub 2023 Mar 9. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 36894694 Review. - Cyclic Guanosine Monophosphate-Adenosine Monophosphate Synthase (cGAS), a Multifaceted Platform of Intracellular DNA Sensing.
Verrier ER, Langevin C. Verrier ER, et al. Front Immunol. 2021 Feb 23;12:637399. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.637399. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33708225 Free PMC article. Review. - The cGAS-STING pathway: The role of self-DNA sensing in inflammatory lung disease.
Ma R, Ortiz Serrano TP, Davis J, Prigge AD, Ridge KM. Ma R, et al. FASEB J. 2020 Oct;34(10):13156-13170. doi: 10.1096/fj.202001607R. Epub 2020 Aug 28. FASEB J. 2020. PMID: 32860267 Free PMC article. Review. - Second messenger 2'3'-cyclic GMP-AMP (2'3'-cGAMP): the cell autonomous and non-autonomous roles in cancer progression.
Ma XY, Chen MM, Meng LH. Ma XY, et al. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2024 May;45(5):890-899. doi: 10.1038/s41401-023-01210-7. Epub 2024 Jan 4. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2024. PMID: 38177693 Review.
Cited by
- A dataset of transcriptomic effects of camptothecin treatment on early zebrafish embryos.
Prykhozhij SV, Ban K, Brown ZL, Kobar K, Wajnberg G, Fuller C, Chacko S, Lacroix J, Crapoulet N, Midgen C, Shlien A, Malkin D, Berman JN. Prykhozhij SV, et al. Data Brief. 2024 Oct 16;57:111041. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2024.111041. eCollection 2024 Dec. Data Brief. 2024. PMID: 39554546 Free PMC article. - The role of the cGAS-STING pathway in chronic pulmonary inflammatory diseases.
Tian M, Li F, Pei H, Liu X, Nie H. Tian M, et al. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Oct 30;11:1436091. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1436091. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39540037 Free PMC article. Review. - The senomorphic impact of astaxanthin on irradiated rat spleen: STING, TLR4 and mTOR contributed pathway.
Aziz MM, El-Sheikh MM, Mohamed MA, Abdelrahman SS, Mekkawy MH. Aziz MM, et al. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2024 Jan-Dec;38:3946320241297342. doi: 10.1177/03946320241297342. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39475763 Free PMC article. - Dual-tDCS Ameliorates Cerebral Injury and Promotes Motor Function Recovery via cGAS-STING Signaling Pathway in a Rat Model of Ischemic Stroke.
Huang J, Bao C, Yang C, Qu Y. Huang J, et al. Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Oct 26. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04574-x. Online ahead of print. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 39455539 - RSK2-mediated cGAS phosphorylation induces cGAS chromatin-incorporation-mediated cell transformation and cancer cell colony growth.
Chen W, Lee GE, Jeung D, Byun J, Wu J, Li X, Lee JY, Kang HC, Lee HS, Kim KD, Nam SB, Lee CJ, Kwon YJ, Cho YY. Chen W, et al. Cell Death Discov. 2024 Oct 18;10(1):442. doi: 10.1038/s41420-024-02208-8. Cell Death Discov. 2024. PMID: 39424777 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials