Optimal cut-off for neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio: Fact or Fantasy? A prospective cohort study in metastatic cancer patients - PubMed (original) (raw)
Optimal cut-off for neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio: Fact or Fantasy? A prospective cohort study in metastatic cancer patients
Yann-Alexandre Vano et al. PLoS One. 2018.
Abstract
This study assessed the prognostic value of pre-treatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) in patients with metastatic solid tumors. Clinical and biological data for patients with metastatic solid tumors treated in an oncology outpatient department and prospectively followed by a call center (PROCHE program) between January 2008 and December 2011 were analyzed. All patients with an NLR value within 28 days before the first cycle of first-line of chemotherapy were included (cohort 1). To assess influence of chemotherapy line on NLR prognostic value, data from patients treated with later chemotherapy lines were also analyzed (cohort 2). Adjusted multivariate Cox regressions with or without non-linear and time-dependent effects were performed. Optimal NLR cut-off was investigated by time-dependent sensitivity analysis using several indices. There were 317 and 134 patients in cohorts 1 and 2, respectively. Elevated NLR was associated with worse survival (hazard ratio [HR] for death, 1.35 [95% confidence interval 1.19-1.54]; p<0.0001). The optimal NLR cut-off in cohort 1 was dependent on index used and time of assessment: HR values were non-significant at a cut-off of 3.0 (1.34 [0.99-1.32], but significant when the cut-off was 4.0 (1.53 [1.11-2.10]). NLR was linearly related to mortality risk; in subgroup analysis, no significant interaction was found with co-variables or tumor localization overall (cohorts 1+2). Pre-treatment NLR is a useful prognostic tool in patients with metastatic solid tumors, irrespective of primary tumor site, chemotherapy line, age, gender and performance status. However, using an NLR cut-off value for clinical decision-making requires extreme caution.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
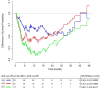
Fig 1. Survival probability for patients with a neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) at the cut-off value or higher versus below the cut-off value for each unit variation of NLR cut-off (Cox univariate model).
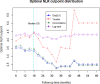
Fig 2. Sensitivity analysis of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) cut-off using 4 different indices.
Using the log-rank test-base method, the NLR cut-off value displaying the greatest stability over time was determined to be between 4.0 and 4.5.
Fig 3
Subgroup analysis illustrating the impact of the choice of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) cut-off value; examples with NLR ≥3.0 (A) and NLR ≥4.0 (B). The model was adjusted for age, sex, disease site and European Co-operative Oncology Group performance status, and the interaction test remained statistically non-significant across the different subgroups, irrespective of the cut-off value, in favour of a persisting negative effect of a high NLR value on prognosis. *Likelihood-ratio txt for interaction of term with NLR cut-off = 3.
Similar articles
- High neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio persistent during first-line chemotherapy predicts poor clinical outcome in patients with advanced urothelial cancer.
Rossi L, Santoni M, Crabb SJ, Scarpi E, Burattini L, Chau C, Bianchi E, Savini A, Burgio SL, Conti A, Conteduca V, Cascinu S, De Giorgi U. Rossi L, et al. Ann Surg Oncol. 2015 Apr;22(4):1377-84. doi: 10.1245/s10434-014-4097-4. Epub 2014 Sep 19. Ann Surg Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25234022 - Prognostic value of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with first-line and subsequent second-line targeted therapy: A proposal of the modified-IMDC risk model.
Tanaka N, Mizuno R, Yasumizu Y, Ito K, Shirotake S, Masunaga A, Ito Y, Miyazaki Y, Hagiwara M, Kanao K, Mikami S, Nakagawa K, Momma T, Masuda T, Asano T, Oyama M, Oya M. Tanaka N, et al. Urol Oncol. 2017 Feb;35(2):39.e19-39.e28. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2016.10.001. Epub 2016 Nov 4. Urol Oncol. 2017. PMID: 27825515 - Change in Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte Ratio in Response to Targeted Therapy for Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma as a Prognosticator and Biomarker of Efficacy.
Templeton AJ, Knox JJ, Lin X, Simantov R, Xie W, Lawrence N, Broom R, Fay AP, Rini B, Donskov F, Bjarnason GA, Smoragiewicz M, Kollmannsberger C, Kanesvaran R, Alimohamed N, Hermanns T, Wells JC, Amir E, Choueiri TK, Heng DY. Templeton AJ, et al. Eur Urol. 2016 Aug;70(2):358-64. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2016.02.033. Epub 2016 Feb 28. Eur Urol. 2016. PMID: 26924770 Clinical Trial. - High pretreatment neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio predicts recurrence and poor prognosis for combined small cell lung cancer.
Shao N, Cai Q. Shao N, et al. Clin Transl Oncol. 2015 Oct;17(10):772-8. doi: 10.1007/s12094-015-1289-8. Epub 2015 Aug 5. Clin Transl Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26243392 - The systemic inflammation-based neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio: experience in patients with cancer.
Guthrie GJ, Charles KA, Roxburgh CS, Horgan PG, McMillan DC, Clarke SJ. Guthrie GJ, et al. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2013 Oct;88(1):218-30. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2013.03.010. Epub 2013 Apr 17. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2013. PMID: 23602134 Review.
Cited by
- Prognostic Impact of the Advanced Lung Cancer Inflammation Index (ALI) in Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treated with First Line Chemotherapy.
Chantharakhit C, Sujaritvanichpong N. Chantharakhit C, et al. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2021 Apr 1;22(4):1149-1156. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2021.22.4.1149. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2021. PMID: 33906307 Free PMC article. - Use of machine learning models for identification of predictors of survival and tumour recurrence in liver transplant recipients with hepatocellular carcinoma.
Bezjak M, Kocman B, Jadrijević S, Filipec Kanižaj T, Antonijević M, Dalbelo Bašić B, Mikulić D. Bezjak M, et al. Ann Transl Med. 2023 Aug 30;11(10):345. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-6469. Epub 2023 Jun 29. Ann Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 37675331 Free PMC article. - The authors respond: Anticipating Covid prognosis from white blood cell count.
Moradi EV, Rezaee R, Morovatdar N, Ghorani V. Moradi EV, et al. Am J Emerg Med. 2021 Sep;47:297-298. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2021.04.078. Epub 2021 May 1. Am J Emerg Med. 2021. PMID: 33966924 Free PMC article. No abstract available. - Variation in neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR) as predictor of outcomes in metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC) and non-small cell lung cancer (mNSCLC) patients treated with nivolumab.
Simonaggio A, Elaidi R, Fournier L, Fabre E, Ferrari V, Borchiellini D, Thouvenin J, Barthelemy P, Thibault C, Tartour E, Oudard S, Vano YA. Simonaggio A, et al. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2020 Dec;69(12):2513-2522. doi: 10.1007/s00262-020-02637-1. Epub 2020 Jun 19. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2020. PMID: 32561968 Free PMC article. - Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR) Reflects Myocardial Inhomogeneities in Hemodialyzed Patients.
Bołtuć K, Bociek A, Dziugieł R, Bociek M, Zapolski T, Dąbrowski W, Jaroszyński A. Bołtuć K, et al. Mediators Inflamm. 2020 Sep 3;2020:6027405. doi: 10.1155/2020/6027405. eCollection 2020. Mediators Inflamm. 2020. PMID: 32963494 Free PMC article.
References
- Balkwill F. Cancer and the chemokine network. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4(7):540–50. doi: 10.1038/nrc1388 . - DOI - PubMed
- Cho H, Kim JH. Multiplication of neutrophil and monocyte counts (MNM) as an easily obtainable tumour marker for cervical cancer. Biomarkers. 2009;14(3):161–70. doi: 10.1080/13547500902777616 . - DOI - PubMed
- Miskolci V, Rollins J, Vu HY, Ghosh CC, Davidson D, Vancurova I. NFkappaB is persistently activated in continuously stimulated human neutrophils. Mol Med. 2007;13(3–4):134–42. doi: 10.2119/2006-00072.Miskolci ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC1892764. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Sadik CD, Kim ND, Luster AD. Neutrophils cascading their way to inflammation. Trends Immunol. 2011;32(10):452–60. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2011.06.008 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3470857. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Schmidt H, Bastholt L, Geertsen P, Christensen IJ, Larsen S, Gehl J, et al. Elevated neutrophil and monocyte counts in peripheral blood are associated with poor survival in patients with metastatic melanoma: a prognostic model. Br J Cancer. 2005;93(3):273–8. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6602702 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC2361564. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
The authors received no specific funding for this work.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous