xiSPEC: web-based visualization, analysis and sharing of proteomics data - PubMed (original) (raw)
xiSPEC: web-based visualization, analysis and sharing of proteomics data
Lars Kolbowski et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018.
Abstract
We present xiSPEC, a standard compliant, next-generation web-based spectrum viewer for visualizing, analyzing and sharing mass spectrometry data. Peptide-spectrum matches from standard proteomics and cross-linking experiments are supported. xiSPEC is to date the only browser-based tool supporting the standardized file formats mzML and mzIdentML defined by the proteomics standards initiative. Users can either upload data directly or select files from the PRIDE data repository as input. xiSPEC allows users to save and share their datasets publicly or password protected for providing access to collaborators or readers and reviewers of manuscripts. The identification table features advanced interaction controls and spectra are presented in three interconnected views: (i) annotated mass spectrum, (ii) peptide sequence fragmentation key and (iii) quality control error plots of matched fragments. Highlighting or selecting data points in any view is represented in all other views. Views are interactive scalable vector graphic elements, which can be exported, e.g. for use in publication. xiSPEC allows for re-annotation of spectra for easy hypothesis testing by modifying input data. xiSPEC is freely accessible at http://spectrumviewer.org and the source code is openly available on https://github.com/Rappsilber-Laboratory/xiSPEC.
Figures
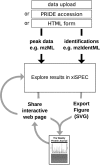
Figure 1.
Overview of xiSPEC workflow. The input for xiSPEC are peak list data and peptide identifications. The user can either upload files directly to the xiSPEC server or select them from the PRIDE repository by providing the PXD accession number. For single spectra analysis data can be provided via HTML form input. Users can save datasets (publicly or password protected) and share them using a unique URL. Results can be exported as SVG for use in publications and presentations.
Figure 2.
SVG output of xiSPEC’s views for a cross-linked peptide example. (A) Peptide sequence with fragmentation key. Amino acid residues in one-letter code. Lines show matched peptide fragments. Grayed-out residues are not included in currently selected fragment. (B) Annotated mass spectrum. Matched peaks are colored and labeled (though labels of neutral-loss fragments are hidden in this example). (C) and (D) show spectra QC plots. Each point represents a matched peak of the mass spectrum. (C) Fragment match error over peak intensity. (D) Match error over m/z. Coloring (red and blue) is used to differentiate between the two peptides. Neutral-loss fragments are displayed in a lighter color. Yellow highlight is the currently selected fragment (interconnected between all views).
Figure 3.
xiSPEC feature examples. (A) Settings view. Peptide input data can be modified in the displayed tab. Appearance customization can be done through the ‘appearance’ tab. (B) Changing PSM modification positions. (C) Use of measuring tool in zoomed-in excerpt of spectrum. Measure distance between peaks with automatic calculation and amino-acid residue matching for multiple charge states. (D) Changing cross-linker position.
Similar articles
- PRIDE Inspector Toolsuite: Moving Toward a Universal Visualization Tool for Proteomics Data Standard Formats and Quality Assessment of ProteomeXchange Datasets.
Perez-Riverol Y, Xu QW, Wang R, Uszkoreit J, Griss J, Sanchez A, Reisinger F, Csordas A, Ternent T, Del-Toro N, Dianes JA, Eisenacher M, Hermjakob H, Vizcaíno JA. Perez-Riverol Y, et al. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2016 Jan;15(1):305-17. doi: 10.1074/mcp.O115.050229. Epub 2015 Nov 6. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2016. PMID: 26545397 Free PMC article. - Interactive Peptide Spectral Annotator: A Versatile Web-based Tool for Proteomic Applications.
Brademan DR, Riley NM, Kwiecien NW, Coon JJ. Brademan DR, et al. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2019 Aug 9;18(8 suppl 1):S193-S201. doi: 10.1074/mcp.TIR118.001209. Epub 2019 May 14. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2019. PMID: 31088857 Free PMC article. - ms-data-core-api: an open-source, metadata-oriented library for computational proteomics.
Perez-Riverol Y, Uszkoreit J, Sanchez A, Ternent T, Del Toro N, Hermjakob H, Vizcaíno JA, Wang R. Perez-Riverol Y, et al. Bioinformatics. 2015 Sep 1;31(17):2903-5. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btv250. Epub 2015 Apr 24. Bioinformatics. 2015. PMID: 25910694 Free PMC article. - Proteomics data exchange and storage: the need for common standards and public repositories.
Jiménez RC, Vizcaíno JA. Jiménez RC, et al. Methods Mol Biol. 2013;1007:317-33. doi: 10.1007/978-1-62703-392-3_14. Methods Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23666733 Review. - Proteomic repository data submission, dissemination, and reuse: key messages.
Perez-Riverol Y. Perez-Riverol Y. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2022 Jul-Dec;19(7-12):297-310. doi: 10.1080/14789450.2022.2160324. Epub 2022 Dec 26. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2022. PMID: 36529941 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- TopMSV: A Web-Based Tool for Top-Down Mass Spectrometry Data Visualization.
Choi IK, Jiang T, Kankara SR, Wu S, Liu X. Choi IK, et al. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2021 Jun 2;32(6):1312-1318. doi: 10.1021/jasms.0c00460. Epub 2021 Mar 29. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2021. PMID: 33780241 Free PMC article. - Noncovalently Associated Peptides Observed during Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry and Their Effect on Cross-Link Analyses.
Giese SH, Belsom A, Sinn L, Fischer L, Rappsilber J. Giese SH, et al. Anal Chem. 2019 Feb 19;91(4):2678-2685. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.8b04037. Epub 2019 Feb 1. Anal Chem. 2019. PMID: 30649854 Free PMC article. - DIPAN: Detecting personalized intronic polyadenylation derived neoantigens from RNA sequencing data.
Liu X, Jin W, Bao D, He T, Wang W, Li Z, Yang X, Tong Y, Shu M, Wang Y, Yuan J, Yang Y. Liu X, et al. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2024 May 9;23:2057-2066. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2024.05.008. eCollection 2024 Dec. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2024. PMID: 38783901 Free PMC article. - The CroCo cross-link converter: a user-centred tool to convert results from cross-linking mass spectrometry experiments.
Bender J, Schmidt C. Bender J, et al. Bioinformatics. 2020 Feb 15;36(4):1296-1297. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btz732. Bioinformatics. 2020. PMID: 31562766 Free PMC article. - Borealin-nucleosome interaction secures chromosome association of the chromosomal passenger complex.
Abad MA, Ruppert JG, Buzuk L, Wear M, Zou J, Webb KM, Kelly DA, Voigt P, Rappsilber J, Earnshaw WC, Jeyaprakash AA. Abad MA, et al. J Cell Biol. 2019 Dec 2;218(12):3912-3925. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201905040. Epub 2019 Sep 30. J Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 31570499 Free PMC article.
References
- Rappsilber J., Mann M.. What does it mean to identify a protein in proteomics. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2002; 27:74–78. - PubMed
- Nesvizhskii A.I., Aebersold R.. Interpretation of shotgun proteomic data: the protein inference problem. Mol. Cell. Proteomics. 2005; 4:1419–1440. - PubMed
- Walzthoeni T., Leitner A., Stengel F., Aebersold R.. Mass spectrometry supported determination of protein complex structure. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2013; 23:252–260. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources