The Benefits of Exercise on Structural and Functional Plasticity in the Rodent Hippocampus of Different Disease Models - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
The Benefits of Exercise on Structural and Functional Plasticity in the Rodent Hippocampus of Different Disease Models
Anna R Patten et al. Brain Plast. 2015.
Abstract
In this review, the benefits of physical exercise on structural and functional plasticity in the hippocampus are discussed. The evidence is clear that voluntary exercise in rats and mice can lead to increases in hippocampal neurogenesis and enhanced synaptic plasticity which ultimately result in improved performance in hippocampal-dependent tasks. Furthermore, in models of neurological disorders, including fetal alcohol spectrum disorders, traumatic brain injury, stroke, and neurodegenerative disorders including Alzheimer's, Parkinson's and Huntington's disease exercise can also elicit beneficial effects on hippocampal function. Ultimately this review highlights the multiple benefits of exercise on hippocampal function in both the healthy and the diseased brain.
Keywords: Cornu Ammonis; Exercise; behaviour; dentate gyrus; hippocampus; neurogenesis; synaptic plasticity.
Figures
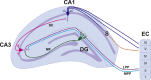
Fig.1
A simplified hippocampal circuitry illustrating trisynaptic and monosynaptic circuits. The basic circuitry of the hippocampus is commonly termed the trisynaptic circuit. Layer II of the entorhinal cortex provides input to the granule cells of the dentate gyrus via the medial (light blue) and lateral (purple) perforant paths. The dentate granule cells project to pyramidal cells of the CA3 via the mossy fibre pathway (green). CA3 pyramidal neurons project to the CA1 via schaffer collaterals (pink). The CA1 pyramidal cells project to both the subiculum and to layers V and VI of the entorhinal cortex. Abbreviations: Cornu Ammonis (CA); Dentate Gyrus (DG); Entorhinal Cortex (EC); Lateral Perforant Path (LPP); Medial Perforant Path (LPP); Mossy Fibres (MF); Schaffer Collaterals (SC); Subiculum (S).
Similar articles
- Enhancement of Hippocampal Plasticity by Physical Exercise as a Polypill for Stress and Depression: A Review.
Li A, Yau SY, Machado S, Wang P, Yuan TF, So KF. Li A, et al. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2019;18(4):294-306. doi: 10.2174/1871527318666190308102804. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2019. PMID: 30848219 Review. - Structural Plasticity of the Hippocampus in Neurodegenerative Diseases.
Weerasinghe-Mudiyanselage PDE, Ang MJ, Kang S, Kim JS, Moon C. Weerasinghe-Mudiyanselage PDE, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 20;23(6):3349. doi: 10.3390/ijms23063349. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35328770 Free PMC article. Review. - Physical exercise reserved amyloid-beta induced brain dysfunctions by regulating hippocampal neurogenesis and inflammatory response via MAPK signaling.
Sun LN, Qi JS, Gao R. Sun LN, et al. Brain Res. 2018 Oct 15;1697:1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2018.04.040. Epub 2018 May 2. Brain Res. 2018. PMID: 29729254 - Effects of physical exercise and stress on hippocampal CA1 and dentate gyrus synaptic transmission and long-term potentiation in adolescent and adult Wistar rats.
Dahlin E, Andersson M, Thorén A, Hanse E, Seth H. Dahlin E, et al. Neuroscience. 2019 Jun 1;408:22-30. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2019.03.046. Epub 2019 Mar 26. Neuroscience. 2019. PMID: 30926550 - Voluntary exercise induces adult hippocampal neurogenesis and BDNF expression in a rodent model of fetal alcohol spectrum disorders.
Boehme F, Gil-Mohapel J, Cox A, Patten A, Giles E, Brocardo PS, Christie BR. Boehme F, et al. Eur J Neurosci. 2011 May;33(10):1799-811. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2011.07676.x. Epub 2011 May 3. Eur J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21535455
Cited by
- The impact of adult neurogenesis on affective functions: of mice and men.
Alonso M, Petit AC, Lledo PM. Alonso M, et al. Mol Psychiatry. 2024 Aug;29(8):2527-2542. doi: 10.1038/s41380-024-02504-w. Epub 2024 Mar 18. Mol Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38499657 Free PMC article. Review. - Temporal endurance of exercise-induced benefits on hippocampus-dependent memory and synaptic plasticity in female mice.
Dong TN, Kramár EA, Beardwood JH, Al-Shammari A, Wood MA, Keiser AA. Dong TN, et al. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2022 Oct;194:107658. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2022.107658. Epub 2022 Jul 8. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2022. PMID: 35811066 Free PMC article. - Basal Forebrain Impairment: Understanding the Mnemonic Function of the Septal Region Translates in Therapeutic Advances.
Tsanov M. Tsanov M. Front Neural Circuits. 2022 May 31;16:916499. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2022.916499. eCollection 2022. Front Neural Circuits. 2022. PMID: 35712645 Free PMC article. Review. - Adult Neurogenesis under Control of the Circadian System.
Ali AAH, von Gall C. Ali AAH, et al. Cells. 2022 Feb 22;11(5):764. doi: 10.3390/cells11050764. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35269386 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Anderson P, Morris R, Amaral D, Bliss T, O’Keefe J. The Hippocampus Book [Internet]. Oxford University Press. 2007. 872 p. Available from: http://books.google.com/books/about/The_hippocampus_book.html?id=zg6oyF1...
- Kitamura T, Mishina M, Sugiyama H. Dietary restriction increases hippocampal neurogenesis by molecular mechanisms independent of NMDA receptors. Neurosci Lett [Internet]. 2005/12/17 ed. 2006;393(2-3):94-6. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&dop... - PubMed
- Helfer JL, Goodlett CR, Greenough WT, Klintsova AY. The effects of exercise on adolescent hippocampal neurogenesis in a rat model of binge alcohol exposure during the brain growth spurt. Brain Res [Internet]. 2009/08/04 ed. 2009;1294:1-11. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&dop... - PMC - PubMed
- Marlatt MW, Potter MC, Lucassen PJ, van Praag H. Running throughout middle-age improves memory function, hippocampal neurogenesis, and BDNF levels in female C57BL/6J mice. Dev Neurobiol [Inter- net]. 2012 Jun [cited 2015 Mar 19];72(6):943-52. Available from: http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?artid=3485396&tool=p... - PMC - PubMed
- Van Praag H, Shubert T, Zhao C, Gage FH. Exercise enhances learning and hippocampal neurogenesis in aged mice. J Neurosci [Internet]. 2005 Sep 21 [cited 2014 Jul 14];25(38):8680-5. Available from: http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?artid=1360197&tool=p... - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources