Dynamic transcriptomic m6A decoration: writers, erasers, readers and functions in RNA metabolism - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Dynamic transcriptomic m6A decoration: writers, erasers, readers and functions in RNA metabolism
Ying Yang et al. Cell Res. 2018 Jun.
Abstract
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is a chemical modification present in multiple RNA species, being most abundant in mRNAs. Studies on enzymes or factors that catalyze, recognize, and remove m6A have revealed its comprehensive roles in almost every aspect of mRNA metabolism, as well as in a variety of physiological processes. This review describes the current understanding of the m6A modification, particularly the functions of its writers, erasers, readers in RNA metabolism, with an emphasis on its role in regulating the isoform dosage of mRNAs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
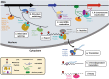
Fig. 1
Diverse molecular functions of m6A. In eukaryotic cells, RNA m6A level is dynamically regulated by “writers” and “erasers”, and recognized by “readers” in direct or indirect ways. The diversity of cellular processes involving m6A is mainly contributed by various “readers”. The nuclear m6A modulates a mRNA alternative splicing,,–,–,,– b secondary structure switching,,, c mRNA export,, d pri-miRNA processing,, e mRNA stability and f _XIST_-dependent X chromosome inactivation, while the cytoplasmic m6A (g and h) enhances mRNA translation efficiency,,,, and i accelerates mRNA decay.,,,
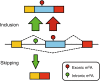
Fig. 2
Schematic summary of the roles of m6A in regulating mRNA splicing. Exonic and most intronic m6A sites promotes exon inclusion while a small proportion of intronic m6A sites can also lead to exon skipping through a refined buffering system composed of its writers, readers, erasers as well as other splicing-related factors
References
- Liu N, Pan T. N6-methyladenosine-encoded epitranscriptomics. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2016;23:98–102. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases