Calcium signalling and related ion channels in neutrophil recruitment and function - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
. 2018 Nov;48 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):e12964.
doi: 10.1111/eci.12964. Epub 2018 Jun 22.
Affiliations
- PMID: 29873837
- PMCID: PMC6221920
- DOI: 10.1111/eci.12964
Review
Calcium signalling and related ion channels in neutrophil recruitment and function
Roland Immler et al. Eur J Clin Invest. 2018 Nov.
Abstract
The recruitment of neutrophils to sites of inflammation, their battle against invading microorganisms through phagocytosis and the release of antimicrobial agents is a highly coordinated and tightly regulated process that involves the interplay of many different receptors, ion channels and signalling pathways. Changes in intracellular calcium levels, caused by cytosolic Ca2+ store depletion and the influx of extracellular Ca2+ via ion channels, play a critical role in synchronizing neutrophil activation and function. In this review, we provide an overview of how Ca2+ signalling is initiated in neutrophils and how changes in intracellular Ca2+ levels modulate neutrophil function.
Keywords: CRAC channels; Orai1; P2X receptors; SOCE; STIM1; TRP channels; calcium channels; calcium signalling; leucocyte recruitment cascade; neutrophil; potassium channels.
© 2018 Stichting European Society for Clinical Investigation Journal Foundation.
Figures
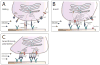
Figure 1. Calcium signaling cascade in neutrophils
(A) Store operated calcium entry (SOCE) can be initiated either via activation of Fcγ-receptors (FcγRs), β2-integrins, the engagement of P-selectin glycoprotein ligand 1 (PSGL-1) and L-selectin with E-selectin expressed on inflamed endothelium, or via G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs). Activation of GPCRs leads to dissociation of the G-protein subunits α and βγ and subsequent activation of phospholipase (PLC) β. FcγRs, β2-integrins and PSGL-1/L-selectin signaling in turn, activate PLCγ involving spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk). Both, activated PLCβ and PLCγ convert phosphatidylinositol 4,5 bisphosphate (PIP2) into diacylglycerol (DAG) and inositol-1,4,5 triphosphate (IP3). IP3 binds to and opens the IP3 receptor (IP3R) in the membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) which results in Ca2+ flux out of the ER into the cytoplasm via IP3R. Upon store depletion, the Ca2+ sensor stromal interaction molecule 1 (STIM1) translocates to PM-ER-junctions and activates Orai1, the predominant Ca2+ release activated Ca2+ (CRAC) channel in neutrophils. This allows the entry of extracellular Ca2+ into the neutrophil, exerting a variety of functions, including (B) phagocytosis, ROS production, secretion and degranulation of vesicles, activation of β2-integrins and cytoskeletal rearrangement leading to polarization and migration.
Figure 2. Calcium signaling functions to synchronize events in neutrophil recruitment
Neutrophil rolling via PSGL-1, L-selectin, and E-selectin causes downstream activation of IP3R and subsequent release of ER stored Ca2+, which in turn shifts LFA-1 from a low to an intermediate and high affinity state. This shift leads to deceleration of the rolling neutrophil via LFA-1-ICAM-1 interaction. The activation of GPCRs by chemokines further increases intracellular Ca2+ levels via IP3R. Additionally, GPCR signaling via DAG activates additional LFA-1 which increases the number of LFA-1/ICAM-1 bonds, resulting in total arrest of the neutrophil (inside-out signaling). High affinity LFA-1 binding to ICAM-1 further enhances rise in intracellular Ca2+ concentrations (outside-in signaling), amplified by shear forces. Upon force transduction, Kindlin-3 binds to β2-integrin tails, recruits Orai1 and thus forms a complex which ensures increase in Ca2+ levels directly at focal adhesion spots, a process again highly dependent on shear forces to orient cell polarization and migration. This is followed by clustering of LFA-1 and the recruitment of Talin1 which links the focal adhesion spots to the cytoskeleton, enabling intraluminal crawling of the neutrophil.
Similar articles
- Local Ca²+ entry via Orai1 regulates plasma membrane recruitment of TRPC1 and controls cytosolic Ca²+ signals required for specific cell functions.
Cheng KT, Liu X, Ong HL, Swaim W, Ambudkar IS. Cheng KT, et al. PLoS Biol. 2011 Mar;9(3):e1001025. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001025. Epub 2011 Mar 8. PLoS Biol. 2011. PMID: 21408196 Free PMC article. - Store-operated CRAC channels regulate gene expression and proliferation in neural progenitor cells.
Somasundaram A, Shum AK, McBride HJ, Kessler JA, Feske S, Miller RJ, Prakriya M. Somasundaram A, et al. J Neurosci. 2014 Jul 2;34(27):9107-23. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0263-14.2014. J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24990931 Free PMC article. - Orai1 controls C5a-induced neutrophil recruitment in inflammation.
Sogkas G, Vögtle T, Rau E, Gewecke B, Stegner D, Schmidt RE, Nieswandt B, Gessner JE. Sogkas G, et al. Eur J Immunol. 2015 Jul;45(7):2143-53. doi: 10.1002/eji.201445337. Epub 2015 May 15. Eur J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25912155 - Ion channels in pain transmission.
Xie W. Xie W. Int Anesthesiol Clin. 2007 Spring;45(2):107-20. doi: 10.1097/AIA.0b013e31803419e7. Int Anesthesiol Clin. 2007. PMID: 17426512 Review. No abstract available. - STIM-TRP Pathways and Microdomain Organization: Contribution of TRPC1 in Store-Operated Ca2+ Entry: Impact on Ca2+ Signaling and Cell Function.
Ong HL, Ambudkar IS. Ong HL, et al. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;993:159-188. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-57732-6_9. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 28900914 Review.
Cited by
- The emerging role of neutrophil extracellular traps in ulcerative colitis.
Long D, Mao C, Xu Y, Zhu Y. Long D, et al. Front Immunol. 2024 Aug 7;15:1425251. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1425251. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39170617 Free PMC article. Review. - Role of neutrophil extracellular traps in inflammatory evolution in severe acute pancreatitis.
Kang H, Yang Y, Zhu L, Zhao X, Li J, Tang W, Wan M. Kang H, et al. Chin Med J (Engl). 2022 Dec 5;135(23):2773-2784. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000002359. Chin Med J (Engl). 2022. PMID: 36729096 Free PMC article. Review. - Neutrophil Immunomodulatory Activity of Natural Organosulfur Compounds.
Schepetkin IA, Kirpotina LN, Khlebnikov AI, Balasubramanian N, Quinn MT. Schepetkin IA, et al. Molecules. 2019 May 10;24(9):1809. doi: 10.3390/molecules24091809. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31083328 Free PMC article. - STIM1/2 maintain signaling competence at ER-PM contact sites during neutrophil spreading.
Rabesahala de Meritens C, Carreras-Sureda A, Rosa N, Pick R, Scheiermann C, Demaurex N. Rabesahala de Meritens C, et al. J Cell Biol. 2025 May 5;224(5):e202406053. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202406053. Epub 2025 Mar 21. J Cell Biol. 2025. PMID: 40116769 Free PMC article. - The voltage-gated potassium channel KV1.3 regulates neutrophil recruitment during inflammation.
Immler R, Nadolni W, Bertsch A, Morikis V, Rohwedder I, Masgrau-Alsina S, Schroll T, Yevtushenko A, Soehnlein O, Moser M, Gudermann T, Barnea ER, Rehberg M, Simon SI, Zierler S, Pruenster M, Sperandio M. Immler R, et al. Cardiovasc Res. 2022 Mar 25;118(5):1289-1302. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvab133. Cardiovasc Res. 2022. PMID: 33881519 Free PMC article.
References
- Kolaczkowska E, Kubes P. Neutrophil recruitment and function in health and inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2013;13:159–175. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- AI047924/National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases
- R01 AI047294/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI047924/United States National Institute of Health
- R01 AI129302/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI129302/United States National Institute of Health
- AI129302/National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases
- SFB914, Project B1 and Z3/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous