Enhancing the fatty acid profile of milk through forage-based rations, with nutrition modeling of diet outcomes - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2018 Feb 28;6(3):681-700.
doi: 10.1002/fsn3.610. eCollection 2018 May.
Affiliations
- PMID: 29876120
- PMCID: PMC5980250
- DOI: 10.1002/fsn3.610
Enhancing the fatty acid profile of milk through forage-based rations, with nutrition modeling of diet outcomes
Charles M Benbrook et al. Food Sci Nutr. 2018.
Abstract
Consumer demand for milk and meat from grass-fed cattle is growing, driven mostly by perceived health benefits and concerns about animal welfare. In a U. S.-wide study of 1,163 milk samples collected over 3 years, we quantified the fatty acid profile in milk from cows fed a nearly 100% forage-based diet (grassmilk) and compared it to profiles from a similar nationwide study of milk from cows under conventional and organic management. We also explored how much the observed differences might help reverse the large changes in fatty acid intakes that have occurred in the United States over the last century. Key features of the fatty acid profile of milk fat include its omega-6/omega-3 ratio (lower is desirable), and amounts of total omega-3, conjugated linoleic acid, and long-chain omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. For each, we find that grassmilk is markedly different than both organic and conventional milk. The omega-6/omega-3 ratios were, respectively, 0.95, 2.28, and 5.77 in grassmilk, organic, and conventional milk; total omega-3 levels were 0.049, 0.032, and 0.020 g/100 g milk; total conjugated linoleic acid levels were 0.043, 0.023, and 0.019 g/100 g milk; and eicosapentaenoic acid levels were 0.0036, 0.0033, and 0.0025 g/100 g milk. Because of often high per-capita dairy consumption relative to most other sources of omega-3 fatty acids and conjugated linoleic acid, these differences in grassmilk can help restore a historical balance of fatty acids and potentially reduce the risk of cardiovascular and other metabolic diseases. Although oily fish have superior concentrations of long-chain omega-3 fatty acids, most fish have low levels of α-linolenic acid (the major omega-3), and an omega-6/omega-3 ratio near 7. Moreover, fish is not consumed regularly, or at all, by ~70% of the U. S.
Keywords: GrassmilkTM; dairy farming; dairy fatty acids; grass milk; omega‐6/omega‐3 ratio; organic milk.
Figures
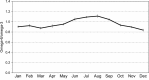
Figure 1
Monthly variation in mean ω‐6/ω‐3 ratio over all geographical regions, 2014–2016 (429 samples). The vertical bars show _SE_s from the least squares analysis
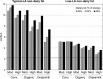
Figure 2
Decreases in dietary
LA
/
ALA
ratios for an adult woman consuming two levels of conventional, organic, and grassmilk dairy products and two types of nondairy fat. The diets contain moderate “Mod.”(3 servings/day) or “High” (4.5 servings/day) amounts of dairy products made from conventional (“Conv.”), “Organic,” or “Grassmilk,” in the contexts of total fat contributing 20%, 33%, or 45% of energy, and nondairy fat containing typical amounts of
LA
(left side) or low amounts of
LA
(right side)
Similar articles
- Organic production enhances milk nutritional quality by shifting fatty acid composition: a United States-wide, 18-month study.
Benbrook CM, Butler G, Latif MA, Leifert C, Davis DR. Benbrook CM, et al. PLoS One. 2013 Dec 9;8(12):e82429. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0082429. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24349282 Free PMC article. - Milk production and milk fatty acid profile as a response to feeding dairy cows with flax products during the persistence period.
El-Ganainy SMM, Shams AS, Kandial MHH, Badr AMM. El-Ganainy SMM, et al. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl). 2023 Sep;107(5):1187-1197. doi: 10.1111/jpn.13816. Epub 2023 Apr 4. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl). 2023. PMID: 37016439 - Fish oil and extruded soybeans fed in combination increase conjugated linoleic acids in milk of dairy cows more than when fed separately.
Whitlock LA, Schingoethe DJ, Hippen AR, Kalscheur KF, Baer RJ, Ramaswamy N, Kasperson KM. Whitlock LA, et al. J Dairy Sci. 2002 Jan;85(1):234-43. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(02)74072-1. J Dairy Sci. 2002. PMID: 11860116 - Oilseed Supplementation Improves Milk Composition and Fatty Acid Profile of Cow Milk: A Meta-Analysis and Meta-Regression.
Plata-Pérez G, Angeles-Hernandez JC, Morales-Almaráz E, Del Razo-Rodríguez OE, López-González F, Peláez-Acero A, Campos-Montiel RG, Vargas-Bello-Pérez E, Vieyra-Alberto R. Plata-Pérez G, et al. Animals (Basel). 2022 Jun 26;12(13):1642. doi: 10.3390/ani12131642. Animals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35804541 Free PMC article. Review. - Review: Effect of essential fatty acids and conjugated linoleic acid on the adaptive physiology of dairy cows during the transition period.
Veshkini A, Ceciliani F, Bonnet M, Hammon HM. Veshkini A, et al. Animal. 2023 Jun;17 Suppl 2:100757. doi: 10.1016/j.animal.2023.100757. Epub 2023 Mar 7. Animal. 2023. PMID: 36966026 Review.
Cited by
- Effects of Agricultural Intensification on Mediterranean Diets: A Narrative Review.
Hasanaliyeva G, Sufar EK, Wang J, Rempelos L, Volakakis N, Iversen PO, Leifert C. Hasanaliyeva G, et al. Foods. 2023 Oct 14;12(20):3779. doi: 10.3390/foods12203779. Foods. 2023. PMID: 37893672 Free PMC article. Review. - Production, Composition and Nutritional Properties of Organic Milk: A Critical Review.
Linehan K, Patangia DV, Ross RP, Stanton C. Linehan K, et al. Foods. 2024 Feb 11;13(4):550. doi: 10.3390/foods13040550. Foods. 2024. PMID: 38397527 Free PMC article. Review. - Patterns of Biodynamic Milk Fatty Acid Composition Explained by A Climate-Geographical Approach.
Baars T, Wohlers J, Rohrer C, Lorkowski S, Jahreis G. Baars T, et al. Animals (Basel). 2019 Mar 22;9(3):111. doi: 10.3390/ani9030111. Animals (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30909506 Free PMC article. - Nutritional Benefits from Fatty Acids in Organic and Grass-Fed Beef.
Davis H, Magistrali A, Butler G, Stergiadis S. Davis H, et al. Foods. 2022 Feb 23;11(5):646. doi: 10.3390/foods11050646. Foods. 2022. PMID: 35267281 Free PMC article. Review. - Is Grassfed Meat and Dairy Better for Human and Environmental Health?
Provenza FD, Kronberg SL, Gregorini P. Provenza FD, et al. Front Nutr. 2019 Mar 19;6:26. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2019.00026. eCollection 2019. Front Nutr. 2019. PMID: 30941351 Free PMC article.
References
- AGA . (2016). Grassfed Dairy Standards. American Grassfed Association (AGA). Retrieved from http://www.americangrassfed.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/AGA-Grassfed-...
- Ailhaud, G. , Massiera, F. , Alessandri, J.‐M. , & Guesnet, P. (2007). Fatty acid composition as an early determinant of childhood obesity. Genes and Nutrition, 2, 39–40. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-789X.2004.00121.x - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- AOAC International . (2012). Official methods of analysis of AOAC International, 19th ed. Retrieved from http://www.aoac.org/aoac_prod_imis/AOAC/Publications/Official_Methods_of...
- APHIS . (2014). Dairy 2014: Dairy Cattle Management Practices in the United States, 2014. NAHMS #692.0216. USDA‐Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service (APHIS)‐Veterinary Services (VS)‐Center for Epidemiology and Health (CEAH), Fort Collins, CO. Retrieved from https://www.aphis.usda.gov/animal_health/nahms/dairy/downloads/dairy14/D...
- ARS . (2010). Report of the Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee on the Dietary Guidelines for Americans, 2010. Agricultural Research Service (ARS), U.S. Department of Agriculture. Retrieved from https://www.cnpp.usda.gov/sites/default/files/dietary_guidelines_for_ame...
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources