appreci8: a pipeline for precise variant calling integrating 8 tools - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2018 Dec 15;34(24):4205-4212.
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty518.
Mohsen Karimi 2, Aniek O de Graaf 3, Christian Rohde 4, Stefanie Göllner 4, Julian Varghese 1, Jan Ernsting 1, Gunilla Walldin 5, Bert A van der Reijden 3, Carsten Müller-Tidow 4, Luca Malcovati 6, Eva Hellström-Lindberg 5, Joop H Jansen 3, Martin Dugas 1
Affiliations
- PMID: 29945233
- PMCID: PMC6289140
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty518
appreci8: a pipeline for precise variant calling integrating 8 tools
Sarah Sandmann et al. Bioinformatics. 2018.
Abstract
Motivation: The application of next-generation sequencing in research and particularly in clinical routine requires valid variant calling results. However, evaluation of several commonly used tools has pointed out that not a single tool meets this requirement. False positive as well as false negative calls necessitate additional experiments and extensive manual work. Intelligent combination and output filtration of different tools could significantly improve the current situation.
Results: We developed appreci8, an automatic variant calling pipeline for calling single nucleotide variants and short indels by combining and filtering the output of eight open-source variant calling tools, based on a novel artifact- and polymorphism score. Appreci8 was trained on two data sets from patients with myelodysplastic syndrome, covering 165 Illumina samples. Subsequently, appreci8's performance was tested on five independent data sets, covering 513 samples. Variation in sequencing platform, target region and disease entity was considered. All calls were validated by re-sequencing on the same platform, a different platform or expert-based review. Sensitivity of appreci8 ranged between 0.93 and 1.00, while positive predictive value ranged between 0.65 and 1.00. In all cases, appreci8 showed superior performance compared to any evaluated alternative approach.
Availability and implementation: Appreci8 is freely available at https://hub.docker.com/r/wwuimi/appreci8/. Sequencing data (BAM files) of the 678 patients analyzed with appreci8 have been deposited into the NCBI Sequence Read Archive (BioProjectID: 388411; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioproject/PRJNA388411).
Supplementary information: Supplementary data are available at Bioinformatics online.
Figures
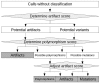
Fig. 1.
Overview of the analysis performed by appreci8
Fig. 2.
General principle of filtration with appreci8. Calls are classified as ‘Mutations’, ‘Polymorphism’ or ‘Artifact’ on the basis of an artifact- and a polymorphism score
Fig. 3.
Relation between positive predictive value and sensitivity in case of GATK, Platypus, VarScan, LoFreq, FreeBayes, SNVer, SAMtools, VarDict, the combined output of all tools (eight tools), single-appreci8 and appreci8 in training sets 1 and 2
Fig. 4.
Relation between positive predictive value and sensitivity in case of GATK, Platypus, VarScan, LoFreq, FreeBayes, SNVer, SAMtools, VarDict, the combined output of all tools (eight tools), single-appreci8 and appreci8 in test sets 1–5
Similar articles
- Evaluating Variant Calling Tools for Non-Matched Next-Generation Sequencing Data.
Sandmann S, de Graaf AO, Karimi M, van der Reijden BA, Hellström-Lindberg E, Jansen JH, Dugas M. Sandmann S, et al. Sci Rep. 2017 Feb 24;7:43169. doi: 10.1038/srep43169. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28233799 Free PMC article. - AMLVaran: a software approach to implement variant analysis of targeted NGS sequencing data in an oncological care setting.
Wünsch C, Banck H, Müller-Tidow C, Dugas M. Wünsch C, et al. BMC Med Genomics. 2020 Feb 4;13(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s12920-020-0668-3. BMC Med Genomics. 2020. PMID: 32019565 Free PMC article. - tarSVM: Improving the accuracy of variant calls derived from microfluidic PCR-based targeted next generation sequencing using a support vector machine.
Gillies CE, Otto EA, Vega-Warner V, Robertson CC, Sanna-Cherchi S, Gharavi A, Crawford B, Bhimma R, Winkler C; Nephrotic Syndrome Study Network (NEPTUNE); C-PROBE InvestigatorGroup of the Michigan Kidney Translational Core Center; Kang HM, Sampson MG. Gillies CE, et al. BMC Bioinformatics. 2016 Jun 10;17(1):233. doi: 10.1186/s12859-016-1108-4. BMC Bioinformatics. 2016. PMID: 27287006 Free PMC article. - VIPER: a web application for rapid expert review of variant calls.
Wöste M, Dugas M. Wöste M, et al. Bioinformatics. 2018 Jun 1;34(11):1928-1929. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty022. Bioinformatics. 2018. PMID: 29346510 Free PMC article. - Calling Variants in the Clinic: Informed Variant Calling Decisions Based on Biological, Clinical, and Laboratory Variables.
Bohannan ZS, Mitrofanova A. Bohannan ZS, et al. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2019 Apr 8;17:561-569. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2019.04.002. eCollection 2019. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2019. PMID: 31049166 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Dynamic microfluidic single-cell screening identifies pheno-tuning compounds to potentiate tuberculosis therapy.
Mistretta M, Cimino M, Campagne P, Volant S, Kornobis E, Hebert O, Rochais C, Dallemagne P, Lecoutey C, Tisnerat C, Lepailleur A, Ayotte Y, LaPlante SR, Gangneux N, Záhorszká M, Korduláková J, Vichier-Guerre S, Bonhomme F, Pokorny L, Albert M, Tinevez JY, Manina G. Mistretta M, et al. Nat Commun. 2024 May 16;15(1):4175. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-48269-2. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38755132 Free PMC article. - Structural, topological, and functional characterization of transmembrane proteins TMEM213, 207, 116, 72 and 30B provides a potential link to ccRCC etiology.
Wesoly J, Pstrąg N, Derylo K, Michalec-Wawiórka B, Derebecka N, Nowicka H, Kajdasz A, Kluzek K, Srebniak M, Tchórzewski M, Kwias Z, Bluyssen H. Wesoly J, et al. Am J Cancer Res. 2023 May 15;13(5):1863-1883. eCollection 2023. Am J Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37293153 Free PMC article. - Resources and tools for rare disease variant interpretation.
Licata L, Via A, Turina P, Babbi G, Benevenuta S, Carta C, Casadio R, Cicconardi A, Facchiano A, Fariselli P, Giordano D, Isidori F, Marabotti A, Martelli PL, Pascarella S, Pinelli M, Pippucci T, Russo R, Savojardo C, Scafuri B, Valeriani L, Capriotti E. Licata L, et al. Front Mol Biosci. 2023 May 10;10:1169109. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1169109. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 37234922 Free PMC article. Review. - Simple combination of multiple somatic variant callers to increase accuracy.
Trevarton AJ, Chang JT, Symmans WF. Trevarton AJ, et al. Sci Rep. 2023 May 25;13(1):8463. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-34925-y. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37231022 Free PMC article. - Performance comparisons between clustering models for reconstructing NGS results from technical replicates.
Zhai Y, Bardel C, Vallée M, Iwaz J, Roy P. Zhai Y, et al. Front Genet. 2023 Mar 16;14:1148147. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1148147. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 37007945 Free PMC article.
References
- Ashley E.A. (2016) Towards precision medicine. Nat. Rev. Genet., 17, 507–522. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous