miR-30 Family: A Promising Regulator in Development and Disease - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
. 2018 May 29:2018:9623412.
doi: 10.1155/2018/9623412. eCollection 2018.
Affiliations
- PMID: 30003109
- PMCID: PMC5996469
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/9623412
Review
miR-30 Family: A Promising Regulator in Development and Disease
Ling Mao et al. Biomed Res Int. 2018.
Abstract
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small noncoding RNAs that negatively regulate posttranscriptional expression of target genes. Accumulating evidences have demonstrated that the miR-30 family, as a member of microRNAs, played a crucial regulating role in the development of tissues and organs and the pathogenesis of clinical diseases, which indicated that it may be a promising regulator in development and disease. This review aims to clarify the current progress on the regulating role of miR-30 family in tissues and organs development and related disease and highlight their research prospective in the future.
Figures
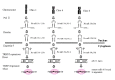
Figure 1
The biogenesis of miR-30 family.
Similar articles
- A MicroRNA Screen Identifies the Wnt Signaling Pathway as a Regulator of the Interferon Response during Flavivirus Infection.
Smith JL, Jeng S, McWeeney SK, Hirsch AJ. Smith JL, et al. J Virol. 2017 Mar 29;91(8):e02388-16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02388-16. Print 2017 Apr 15. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28148804 Free PMC article. - MicroRNAs: Novel Players in Aortic Aneurysm.
Fu XM, Zhou YZ, Cheng Z, Liao XB, Zhou XM. Fu XM, et al. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:831641. doi: 10.1155/2015/831641. Epub 2015 Jun 28. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 26221607 Free PMC article. Review. - miR-155 and miR-146b negatively regulates IL6 in Helicobacter pylori (cagA+) infected gastroduodenal ulcer.
Cheng SF, Li L, Wang LM. Cheng SF, et al. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2015 Feb;19(4):607-13. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2015. PMID: 25753878 - miR-133b, a particular member of myomiRs, coming into playing its unique pathological role in human cancer.
Li D, Xia L, Chen M, Lin C, Wu H, Zhang Y, Pan S, Li X. Li D, et al. Oncotarget. 2017 Jul 25;8(30):50193-50208. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16745. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28422730 Free PMC article. Review. - Noncoding RNAs, cytokines, and inflammation-related diseases.
Marques-Rocha JL, Samblas M, Milagro FI, Bressan J, Martínez JA, Marti A. Marques-Rocha JL, et al. FASEB J. 2015 Sep;29(9):3595-611. doi: 10.1096/fj.14-260323. Epub 2015 Jun 11. FASEB J. 2015. PMID: 26065857 Review.
Cited by
- miR-30 inhibits proliferation of trophoblasts in preeclampsia rats partially related to MAPK/ERK pathway.
Wang Y, Jie L, Gong H, Li Y, Xie A, Li Y, Guo H. Wang Y, et al. Exp Ther Med. 2020 Aug;20(2):1379-1384. doi: 10.3892/etm.2020.8866. Epub 2020 Jun 10. Exp Ther Med. 2020. PMID: 32742372 Free PMC article. - New insights into the cardio-renal benefits of SGLT2 inhibitors and the coordinated role of miR-30 family.
El Khayari A, Hakam SM, Malka G, Rochette L, El Fatimy R. El Khayari A, et al. Genes Dis. 2023 Nov 23;11(6):101174. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2023.101174. eCollection 2024 Nov. Genes Dis. 2023. PMID: 39224109 Free PMC article. Review. - The Expression Profile of MicroRNAs in Small and Large Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms.
Černá V, Ostašov P, Pitule P, Moláček J, Třeška V, Pešta M. Černá V, et al. Cardiol Res Pract. 2019 Nov 29;2019:8645840. doi: 10.1155/2019/8645840. eCollection 2019. Cardiol Res Pract. 2019. PMID: 31885906 Free PMC article. - Cardiovascular Alterations and Structural Changes in the Setting of Chronic Kidney Disease: a Review of Cardiorenal Syndrome Type 4.
Minciunescu A, Genovese L, deFilippi C. Minciunescu A, et al. SN Compr Clin Med. 2023;5(1):15. doi: 10.1007/s42399-022-01347-2. Epub 2022 Dec 3. SN Compr Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 36530959 Free PMC article. Review. - Downregulation of Neurofilament Light Chain Expression in Human Neuronal-Glial Cell Co-Cultures by a Microbiome-Derived Lipopolysaccharide-Induced miRNA-30b-5p.
Pogue AI, Jaber VR, Sharfman NM, Zhao Y, Lukiw WJ. Pogue AI, et al. Front Neurol. 2022 Jun 24;13:900048. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.900048. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35812116 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources