Activation of the JAK/STAT3 and PI3K/AKT pathways are crucial for IL-6 trans-signaling-mediated pro-inflammatory response in human vascular endothelial cells - PubMed (original) (raw)
Activation of the JAK/STAT3 and PI3K/AKT pathways are crucial for IL-6 trans-signaling-mediated pro-inflammatory response in human vascular endothelial cells
Mulugeta M Zegeye et al. Cell Commun Signal. 2018.
Abstract
Background: IL-6 classic signaling is linked to anti-inflammatory functions while the trans-signaling is associated with pro-inflammatory responses. Classic signaling is induced via membrane-bound IL-6 receptor (IL-6R) whereas trans-signaling requires prior binding of IL-6 to the soluble IL-6R. In both cases, association with the signal transducing gp130 receptor is compulsory. However, differences in the downstream signaling mechanisms of IL-6 classic- versus trans-signaling remains largely elusive.
Methods: In this study, we used flow cytometry, quantitative PCR, ELISA and immuno-blotting techniques to investigate IL-6 classic and trans-signaling mechanisms in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells (HUVECs).
Results: We show that both IL-6R and gp130 are expressed on the surface of human vascular endothelial cells, and that the expression is affected by pro-inflammatory stimuli. In contrast to IL-6 classic signaling, IL-6 trans-signaling induces the release of the pro-inflammatory chemokine Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 (MCP-1) from human vascular endothelial cells. In addition, we reveal that the classic signaling induces activation of the JAK/STAT3 pathway while trans-signaling also activates the PI3K/AKT and the MEK/ERK pathways. Furthermore, we demonstrate that MCP-1 induction by IL-6 trans-signaling requires simultaneous activation of the JAK/STAT3 and PI3K/AKT pathways.
Conclusions: Collectively, our study reports molecular differences in IL-6 classic- and trans-signaling in human vascular endothelial cells; and elucidates the pathways which mediate MCP-1 induction by IL-6 trans-signaling.
Keywords: Endothelium; HUVECs; Interleukin-6 signaling; Monocyte chemoattractant Protein-1; Pro-inflammatory cytokines.
Conflict of interest statement
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Fig. 1
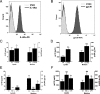
Expression and regulation of IL-6R and gp130 in human vascular endothelial cells. Flow cytometry analyses of EDTA detached endothelial cells stained for a IL-6R and b gp130. The light grey histograms show respective FMO (fluorescence minus one) controls and the dark grey histograms show IL-6R or gp130 stained cells. ELISA analyses of the levels of c IL-6R and d gp130 in cell lysates and medium after 48 h of IL-6 knockdown. ELISA analyses of the levels of e IL-6R and f gp130 in cell lysates and medium after 48 h of treatment with TNF-α (50 ng/ml) and LPS (100 ng/ml). Data is presented as mean ± SEM of at least 3–4 experiments each run-in duplicate. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 compared to control
Fig. 2
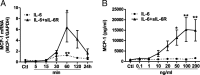
MCP-1 mRNA expression and release from human vascular endothelial cells. a qPCR analyses depicting the relative expression of MCP-1 mRNA after exposure to IL-6 (100 ng/ml) alone or in combination with sIL-6R (200 ng/ml). b ELISA data showing the MCP-1 release into medium (48 h) induced by increasing concentrations of IL-6 alone or in combination with sIL-6R. Data is presented as mean ± SEM of 3 experiments each run-in duplicate. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 compared to its respective control
Fig. 3
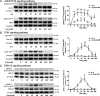
Western blot analyses showing phosphorylation of a STAT3Tyr705, b AKTSer473 and c ERK1/2Thr202/Tyr204 in human vascular endothelial cells treated with IL-6 alone (50 ng/ml) or in combination with sIL-6R (100 ng/ml). One representative blot containing the phosphorylated protein, total protein and β-tubulin (loading control) is shown for each pathway (left column). The signals from the phosphorylated proteins and total proteins are first normalized to β-tubulin, and the ratio of the phosphorylated proteins and the total proteins are calculated. The graphs show arbitrary units (a.u., control is set to 1) compiled from 3 independent experiments presented as mean ± SEM for each pathway (right column). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 compared to control
Fig. 4
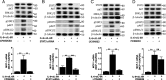
The effect of different inhibitions on IL-6 trans-signaling induced MCP-1 mRNA expression. The effect of a CP960550 (JAK inhibitor, 10 μM), b STAT3 knockdown, c LY294002 (PI3K inhibitor, 50 μM) and d PD98059 (MEK inhibitor, 10 μM) on trans-signaling (IL-6 = 100 ng/ml, sIL-6R = 200 ng/ml) induced MCP-1 expression is presented as mean ± SEM (n = 3 for each). Western blots show effect of CP960550, STAT3 knockdown, LY294002 and PD98059 on IL-6 trans-signaling (IL-6 = 50 ng/ml, sIL-6R = 100 ng/ml) induced phosphorylation of downstream pathway proteins. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 compared to control
Similar articles
- Role of the IL-6 classic- and trans-signaling pathways in corneal sterile inflammation and wound healing.
Ebihara N, Matsuda A, Nakamura S, Matsuda H, Murakami A. Ebihara N, et al. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011 Nov 1;52(12):8549-57. doi: 10.1167/iovs.11-7956. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011. PMID: 21989726 - Neuroprotection of interleukin-6 against NMDA-induced neurotoxicity is mediated by JAK/STAT3, MAPK/ERK, and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways.
Fang XX, Jiang XL, Han XH, Peng YP, Qiu YH. Fang XX, et al. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2013 Mar;33(2):241-51. doi: 10.1007/s10571-012-9891-6. Epub 2012 Nov 16. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2013. PMID: 23161148 - PD-L1 induced by IFN-γ from tumor-associated macrophages via the JAK/STAT3 and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways promoted progression of lung cancer.
Zhang X, Zeng Y, Qu Q, Zhu J, Liu Z, Ning W, Zeng H, Zhang N, Du W, Chen C, Huang JA. Zhang X, et al. Int J Clin Oncol. 2017 Dec;22(6):1026-1033. doi: 10.1007/s10147-017-1161-7. Epub 2017 Jul 26. Int J Clin Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28748356 - Interleukin-6: A Masterplayer in the Cytokine Network.
Uciechowski P, Dempke WCM. Uciechowski P, et al. Oncology. 2020;98(3):131-137. doi: 10.1159/000505099. Epub 2020 Jan 20. Oncology. 2020. PMID: 31958792 Review. - The IL-6/gp130/STAT3 signaling axis: recent advances towards specific inhibition.
Garbers C, Aparicio-Siegmund S, Rose-John S. Garbers C, et al. Curr Opin Immunol. 2015 Jun;34:75-82. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2015.02.008. Epub 2015 Mar 6. Curr Opin Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25749511 Review.
Cited by
- Identification of platelet-related subtypes and diagnostic markers in pediatric Crohn's disease based on WGCNA and machine learning.
Tang D, Huang Y, Che Y, Yang C, Pu B, Liu S, Li H. Tang D, et al. Front Immunol. 2024 Feb 14;15:1323418. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1323418. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38420127 Free PMC article. - Paraquat disrupts the blood-brain barrier by increasing IL-6 expression and oxidative stress through the activation of PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.
Liu T, Zheng F, Liu L, Zhou H, Shen T, Li Y, Zhang W. Liu T, et al. Open Med (Wars). 2024 Sep 11;19(1):20241020. doi: 10.1515/med-2024-1020. eCollection 2024. Open Med (Wars). 2024. PMID: 39291284 Free PMC article. - The probable role and therapeutic potential of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in SARS-CoV-2 induced coagulopathy.
Khezri MR, Varzandeh R, Ghasemnejad-Berenji M. Khezri MR, et al. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2022 Jan 11;27(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s11658-022-00308-w. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2022. PMID: 35016612 Free PMC article. Review. - IL-6 trans-Signaling Impairs Sprouting Angiogenesis by Inhibiting Migration, Proliferation and Tube Formation of Human Endothelial Cells.
Zegeye MM, Andersson B, Sirsjö A, Ljungberg LU. Zegeye MM, et al. Cells. 2020 Jun 5;9(6):1414. doi: 10.3390/cells9061414. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32517159 Free PMC article. - YY1 Lactylation Aggravates Autoimmune Uveitis by Enhancing Microglial Functions via Inflammatory Genes.
Huang J, Wang X, Li N, Fan W, Li X, Zhou Q, Liu J, Li W, Zhang Z, Liu X, Zeng S, Yang H, Tian M, Yang P, Hou S. Huang J, et al. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 May;11(19):e2308031. doi: 10.1002/advs.202308031. Epub 2024 Mar 17. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 38493498 Free PMC article.
References
- Suzuki M, Hashizume M, Yoshida H, Mihara M. Anti-inflammatory mechanism of tocilizumab, a humanized anti-IL-6R antibody: effect on the expression of chemokine and adhesion molecule. Rheumatol Int. 2010;30:309–15. 10.1007/s00296-009-0953-0. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 20150245 and 20120213/Knowledge Foundation/International
- K-70 31/15/Längmanska Foundation/International
- 2014-00147 and 2015-00248/Stiftelsen för Gamla Tjänarinnor/International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous