Is it Useful to Repeat Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Sacroiliac Joints After Three Months or One Year in the Diagnosis of Patients With Chronic Back Pain and Suspected Axial Spondyloarthritis? - PubMed (original) (raw)
Multicenter Study
. 2019 Mar;71(3):382-391.
doi: 10.1002/art.40718. Epub 2019 Feb 6.
Affiliations
- PMID: 30203929
- PMCID: PMC6593866
- DOI: 10.1002/art.40718
Multicenter Study
Is it Useful to Repeat Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Sacroiliac Joints After Three Months or One Year in the Diagnosis of Patients With Chronic Back Pain and Suspected Axial Spondyloarthritis?
P A C Bakker et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019 Mar.
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the value of repeated magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the sacroiliac (SI) joints in diagnosing chronic back pain patients in whom axial spondyloarthritis (SpA) is suspected and to examine determinants of positive MRI findings in SI joints.
Methods: Patients with chronic back pain (duration 3 months-2 years, age ≥16 years, age at onset <45 years) with ≥1 SpA feature who were included in the Spondyloarthritis Caught Early cohort underwent visits at baseline, at 3 months, and at 1 year. Visits included an evaluation of all SpA features and repeated MRI of SI joints. MRI-detected axial SpA positivity (according to the definition from the Assessment of SpondyloArthritis international Society) was evaluated by 2 or 3 well-trained readers who were blinded with regard to clinical information. The likelihood of a positive MRI finding at follow-up visits (taking into consideration contributing factors) was calculated by generalized estimating equation analysis.
Results: Of the 188 patients, 38.3% were male, the mean ± SD age was 31.0 ± 8.2 years, and the mean ± SD symptom duration was 13.2 ± 7.1 months. Thirty-one patients (16.5%) had positive MRI findings in the SI joints at baseline. After 3 months and after 1 year, the MRI results had changed from positive to negative in 3 of 27 patients (11.1%) and 11 of 29 patients (37.9%), respectively, which was attributable in part to the initiation of anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy. Status changes from negative to positive were seen in 5 of 116 patients (4.3%) after 3 months and in 10 of 138 patients (7.2%) after 1 year. HLA-B27 positivity and male sex were independent determinants of the likelihood of a positive MRI scan at any time point (42% in HLA-B27+ men and 6% in HLA-B27- women). If the baseline results were negative, the likelihood of a positive scan at follow-up was very low (≤7%).
Conclusion: MRI-detected status changes in the SI joints were seen in a minority of the patients, and both male sex and HLA-B27 positivity were important predictors of MRI positivity. Our findings indicate that conducting MRI scans after 3 months or after 1 year in patients with suspected early axial SpA is not diagnostically useful.
© 2018 The Authors. Arthritis & Rheumatology published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of American College of Rheumatology.
Figures
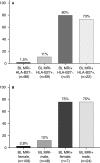
Figure 1
Likelihood of a positive magnetic resonance imaging result at any time point (baseline, 3 months, and 1 year) in chronic back pain patients investigated for axial spondyloarthritis.
HLA
–B27 status and sex were used as variables.
Figure 2
Likelihood of a positive magnetic resonance imaging result at 3‐month or 1‐year follow‐up in chronic back pain patients investigated for axial spondyloarthritis. A, Baseline
MRI
result and
HLA
–B27 status were used as variables. B, Baseline
MRI
result and sex were used as variables.
Comment in
- Negative Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings Are Not Dependable for Excluding Axial Spondyloarthritis: Comment on the Article by Bakker et al.
Major GA. Major GA. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020 Jun;72(6):1041-1042. doi: 10.1002/art.41225. Epub 2020 Apr 16. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020. PMID: 32067387 No abstract available.
Similar articles
- Are Additional Tests Needed to Rule Out Axial Spondyloarthritis in Patients Ages 16-45 Years With Short-Duration Chronic Back Pain and Maximally One Spondyloarthritis Feature?
Bakker PA, Ez-Zaitouni Z, van Lunteren M, van den Berg R, De Hooge M, Fagerli KM, Landewé R, van Oosterhout M, Ramonda R, Reijnierse M, van der Heijde D, van Gaalen FA. Bakker PA, et al. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2016 Nov;68(11):1726-1730. doi: 10.1002/acr.22883. Epub 2016 Oct 6. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2016. PMID: 26990879 - Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Sacroiliac Joints Indicating Sacroiliitis According to the Assessment of SpondyloArthritis international Society Definition in Healthy Individuals, Runners, and Women With Postpartum Back Pain.
de Winter J, de Hooge M, van de Sande M, de Jong H, van Hoeven L, de Koning A, Berg IJ, Ramonda R, Baeten D, van der Heijde D, Weel A, Landewé R. de Winter J, et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018 Jul;70(7):1042-1048. doi: 10.1002/art.40475. Epub 2018 May 23. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018. PMID: 29513924 Free PMC article. - Presence of multiple spondyloarthritis (SpA) features is important but not sufficient for a diagnosis of axial spondyloarthritis: data from the SPondyloArthritis Caught Early (SPACE) cohort.
Ez-Zaitouni Z, Bakker PAC, van Lunteren M, Berg IJ, Landewé R, van Oosterhout M, Lorenzin M, van der Heijde D, van Gaalen FA. Ez-Zaitouni Z, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017 Jun;76(6):1086-1092. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-210119. Epub 2017 Jan 6. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017. PMID: 28062405 - Assessment of spinal pain.
Braun J, Baraliakos X, Regel A, Kiltz U. Braun J, et al. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2014 Dec;28(6):875-87. doi: 10.1016/j.berh.2015.04.031. Epub 2015 May 28. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2014. PMID: 26096091 Review. - The diagnostic utility of MRI in spondyloarthritis.
Pedersen SJ, Weber U, Ostergaard M. Pedersen SJ, et al. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2012 Dec;26(6):751-66. doi: 10.1016/j.berh.2012.10.005. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2012. PMID: 23273790 Review.
Cited by
- 5-year follow-up of spinal and sacroiliac MRI abnormalities in early axial spondyloarthritis: data from the DESIR cohort.
Madari Q, Sepriano A, Ramiro S, Molto A, Claudepierre P, Wendling D, Dougados M, van der Heijde D, van Gaalen FA. Madari Q, et al. RMD Open. 2020 Feb;6(1):e001093. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2019-001093. RMD Open. 2020. PMID: 32396521 Free PMC article. - Australian Consensus Statements for the Assessment and Management of Non-radiographic Axial Spondyloarthritis.
Truong SL, McEwan T, Bird P, Lim I, Saad NF, Schachna L, Taylor AL, Robinson PC. Truong SL, et al. Rheumatol Ther. 2022 Feb;9(1):1-24. doi: 10.1007/s40744-021-00416-7. Epub 2021 Dec 28. Rheumatol Ther. 2022. PMID: 34962620 Free PMC article. - Axial spondyloarthritis: concept, construct, classification and implications for therapy.
Robinson PC, van der Linden S, Khan MA, Taylor WJ. Robinson PC, et al. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2021 Feb;17(2):109-118. doi: 10.1038/s41584-020-00552-4. Epub 2020 Dec 23. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2021. PMID: 33361770 Review. - Non-Radiographic Axial Spondyloarthritis (nr-axSpA): Advances in Classification, Imaging and Therapy.
Robinson PC, Sengupta R, Siebert S. Robinson PC, et al. Rheumatol Ther. 2019 Jun;6(2):165-177. doi: 10.1007/s40744-019-0146-6. Epub 2019 Feb 20. Rheumatol Ther. 2019. PMID: 30788779 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Van den Berg R, de Hooge M, Rudwaleit M, Sieper J, van Gaalen F , Reijnierse M, et al. ASAS modification of the Berlin algorithm for diagnosing axial spondyloarthritis: results from the SPondyloArthritis Caught Early (SPACE)‐cohort and from the Assessment of SpondyloArthritis international Society (ASAS)‐cohort. Ann Rheum Dis 2013;72:1646–53. - PubMed
- Feldtkeller E, Bruckel J, Khan MA. Scientific contributions of ankylosing spondylitis patient advocacy groups. Curr Opin Rheumatol 2000;12:239–47. - PubMed
- Rudwaleit M, Khan MA, Sieper J. The challenge of diagnosis and classification in early ankylosing spondylitis: do we need new criteria? Arthritis Rheum 2005;52:1000–8. - PubMed
- Kroon FP, van der Burg LR, Ramiro S, Landewe RB, Buchbinder R, Falzon L, et al. Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs for axial spondyloarthritis: a Cochrane review. J Rheumatol 2016;43:607–17. - PubMed
- Van der Heijde D, Ramiro S, Landewe R, Baraliakos X, van den Bosch F, Sepriano A, et al. 2016 update of the ASAS‐EULAR management recommendations for axial spondyloarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 2017;76:978–91. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials