RAGE and TLRs as Key Targets for Antiatherosclerotic Therapy - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
. 2018 Aug 26:2018:7675286.
doi: 10.1155/2018/7675286. eCollection 2018.
Affiliations
- PMID: 30225265
- PMCID: PMC6129363
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/7675286
Review
RAGE and TLRs as Key Targets for Antiatherosclerotic Therapy
Wioletta Olejarz et al. Biomed Res Int. 2018.
Abstract
Receptor for advanced glycation end-products (RAGE) and toll-like receptors (TLRs) are the key factors indicating a danger to the organism. They recognize the microbial origin pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) or damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs). The primary response induced by PAMPs or DAMPs is inflammation. Excessive stimulation of the innate immune system occurs in arterial wall with the participation of effector cells. Persistent adaptive responses can also cause tissue damage and disease. However, inflammation mediated by the molecules innate responses is an important way in which the adaptive immune system protects us from infection. The specific detection of PAMPs and DAMPs by host receptors drives a cascade of signaling that converges at nuclear factor-_κ_B (NF-_κ_B) and interferon regulatory factors (IRFs) and induces the secretion of proinflammatory cytokines, type I interferon (IFN), and chemokines, which promote direct killing of the pathogen. Therefore, signaling of these receptors' pathways also appear to present new avenue for the modulation of inflammatory responses and to serve as potential novel therapeutic targets for antiatherosclerotic therapy.
Figures
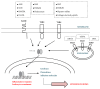
Figure 1
Stimulation of RAGE and TLRs leads to the activation of the transcription nuclear factor NF-_κ_B. Transfer of NF-_κ_B to the nucleus induces inflammatory response and leukocyte recruitment. AGE: advanced glycation end-products, HMGB1: high-mobility group box 1 protein, Ox LDL: oxidized low-density lipoprotein, HSP: Heat shock proteins, and NF-_κ_B: nuclear factor _κ_B.
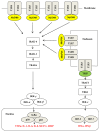
Figure 2
Toll-like receptor signaling pathways. IRFs: interferon regulatory factors, NF-_κ_B: nuclear factor κ_B, IRAK: IL-1 receptor-associated kinases; MAL: MyD88-adaptor-like; MyD88: Myeloid differentiation protein 88; TLR: toll-like receptor; TRAF: tumour necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6; TRAM: TRIF-related adaptor molecule; TRIF: TIR domain-containing adaptor inducing interferon-β. I_κ_B_α : inhibitory protein kappa-B and IKK: inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B kinase.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical