Navigating the social world: The role of social competence, peer victimisation and friendship quality in the development of social anxiety in childhood - PubMed (original) (raw)
Navigating the social world: The role of social competence, peer victimisation and friendship quality in the development of social anxiety in childhood
Hannah Pickard et al. J Anxiety Disord. 2018 Dec.
Abstract
Social and communication (SC) difficulties predict increased social anxiety (SA) symptoms in childhood. Peer victimisation and friendship quality are commonly associated with both SC difficulties and SA. Based on this, we tested for a cascade effect of early SC difficulties, peer victimisation and friendship quality on SA in late childhood, using a population-based sample of 8028 children from the Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children (ALSPAC) cohort. Parent-reported data were collected on SC difficulties at age 7 and SA at age 7, 10 and 13. Child-reported data on peer victimisation and friendship quality were collected at age 8. Our results revealed that SC difficulties predict increased negative friendship qualities and peer victimisation. Relational victimisation predicted increased SA symptoms at 13 years old. Neither overt nor relational victimisation mediated the developmental relationship between SC difficulties and SA. Furthermore, friendship quality did not moderate the developmental relationship between SC difficulties and SA. In addition, no sex differences were observed. The evidence demonstrates that peer victimisation and friendship quality do not explain why some children with SC difficulties go on to develop SA. Future research clarifying the complex etiological pathways contributing towards the development of SA in childhood and adolescence is warranted.
Keywords: ALSPAC; Longitudinal; Social and communication difficulties; Social anxiety.
Copyright © 2018 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures
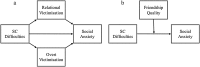
Fig. 1
Conceptual diagram illustrating our (a) mediation and (b) moderation hypotheses. Note. SC = social and communication
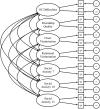
Fig. 2
Illustration of saturated model with correlated latent factors, factor items and error variance. Note. SC = social and communication. Q = question. e = error.
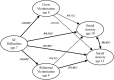
Fig. 3
Mediation pathway model showing overt and relational victimisation as mediators in the developmental relationship from social and communication difficulties to social anxiety symptoms. Note. SC = social and communication. Standardized beta coefficients and standard errors are reported. All analyses controlled for IQ, SES and social anxiety symptoms at age 7. Bold paths indicate significance*.
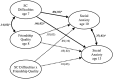
Fig. 4
Moderation pathway model testing whether friendship quality moderates the effect of social and communication difficulties on social anxiety symptoms. Note. SC = social and communication. Standardized beta coefficients and standard errors are reported. All analyses controlled for IQ, SES and social anxiety symptoms at age 7. Bold paths indicate significance*.
Similar articles
- Are Social and Communication Difficulties a Risk Factor for the Development of Social Anxiety?
Pickard H, Rijsdijk F, Happé F, Mandy W. Pickard H, et al. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2017 Apr;56(4):344-351.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.jaac.2017.01.007. Epub 2017 Feb 1. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2017. PMID: 28335879 Free PMC article. - Peer victimisation and internalising difficulties: The moderating role of friendship quality.
Woods S, Done J, Kalsi H. Woods S, et al. J Adolesc. 2009 Apr;32(2):293-308. doi: 10.1016/j.adolescence.2008.03.005. Epub 2008 Aug 8. J Adolesc. 2009. PMID: 18692234 - Problematic Peer Functioning in Girls with ADHD: A Systematic Literature Review.
Kok FM, Groen Y, Fuermaier AB, Tucha O. Kok FM, et al. PLoS One. 2016 Nov 21;11(11):e0165119. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0165119. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27870862 Free PMC article. Review. - Peer victimisation during adolescence and its impact on wellbeing in adulthood: a prospective cohort study.
Armitage JM, Wang RAH, Davis OSP, Bowes L, Haworth CMA. Armitage JM, et al. BMC Public Health. 2021 Jan 15;21(1):148. doi: 10.1186/s12889-021-10198-w. BMC Public Health. 2021. PMID: 33451312 Free PMC article. - Peer relations in childhood.
Hay DF, Payne A, Chadwick A. Hay DF, et al. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2004 Jan;45(1):84-108. doi: 10.1046/j.0021-9630.2003.00308.x. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2004. PMID: 14959804 Review.
Cited by
- Behavioral and psychiatric correlates of brain responses to social feedback.
Rappaport BI, Kujawa A, Arfer KB, Pegg S, Kelly D, Jackson JJ, Luby JL, Barch DM. Rappaport BI, et al. Psychophysiology. 2024 Jan;61(1):e14413. doi: 10.1111/psyp.14413. Epub 2023 Aug 23. Psychophysiology. 2024. PMID: 37612834 Free PMC article. - Is Future Mental Imagery Associated with Reduced Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Negative Affect and Anhedonic Symptoms in Young People?
Hutchinson T, Riddleston L, Pile V, Meehan A, Shukla M, Lau J. Hutchinson T, et al. Cognit Ther Res. 2023;47(2):168-180. doi: 10.1007/s10608-023-10352-1. Epub 2023 Feb 4. Cognit Ther Res. 2023. PMID: 36779180 Free PMC article. - Sociomoral Reasoning Skills during Childhood: A Comprehensive and Predictive Approach.
Morasse F, Bernier A, Lalonde G, Hétu S, Beauchamp MH. Morasse F, et al. Brain Sci. 2022 Sep 10;12(9):1226. doi: 10.3390/brainsci12091226. Brain Sci. 2022. PMID: 36138963 Free PMC article. - Speech, language and communication needs and mental health: the experiences of speech and language therapists and mental health professionals.
Hancock A, Northcott S, Hobson H, Clarke M. Hancock A, et al. Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2023 Jan;58(1):52-66. doi: 10.1111/1460-6984.12767. Epub 2022 Sep 18. Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2023. PMID: 36117337 Free PMC article. - Childhood Emotional Neglect and Adolescent Depression: Assessing the Protective Role of Peer Social Support in a Longitudinal Birth Cohort.
Glickman EA, Choi KW, Lussier AA, Smith BJ, Dunn EC. Glickman EA, et al. Front Psychiatry. 2021 Aug 9;12:681176. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.681176. eCollection 2021. Front Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 34434126 Free PMC article.
References
- Aguinis H., Beaty J.C., Boik R.J., Pierce C.A. Effect size and power in assessing moderating effects of categorical variables using multiple regression: A 30-year review. The Journal of Applied Psychology. 2005;90(1):94–107. - PubMed
- American Psychiatric Association . 5th ed. American Psychiatric Association; Washington, DC: 2013. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders.
- Bagwell C.L., Newcomb A.F., Bukowski W.M. Preadolescent friendship and peer rejection as predictors of adult adjustment. Child Development. 1998;69(1):140–153. - PubMed
- Beidel D.C., Turner S.M., Morris T.L. Psychopathology of childhood social phobia. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry. 1999;38(6):643–650. - PubMed
- Beidel D.C., Turner S.M., Young B.J., Ammerman R.T., Sallee F.R., Crosby L. Psychopathology of adolescent social phobia. Journal of Psychopathology and Behavioral Assessment. 2007;29(1):46–53.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources