Management of Hyperglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes, 2018. A Consensus Report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) - PubMed (original) (raw)
Practice Guideline
. 2018 Dec;41(12):2669-2701.
doi: 10.2337/dci18-0033. Epub 2018 Oct 4.
Affiliations
- PMID: 30291106
- PMCID: PMC6245208
- DOI: 10.2337/dci18-0033
Practice Guideline
Management of Hyperglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes, 2018. A Consensus Report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD)
Melanie J Davies et al. Diabetes Care. 2018 Dec.
Abstract
The American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes convened a panel to update the prior position statements, published in 2012 and 2015, on the management of type 2 diabetes in adults. A systematic evaluation of the literature since 2014 informed new recommendations. These include additional focus on lifestyle management and diabetes self-management education and support. For those with obesity, efforts targeting weight loss, including lifestyle, medication, and surgical interventions, are recommended. With regards to medication management, for patients with clinical cardiovascular disease, a sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor or a glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist with proven cardiovascular benefit is recommended. For patients with chronic kidney disease or clinical heart failure and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, an SGLT2 inhibitor with proven benefit is recommended. GLP-1 receptor agonists are generally recommended as the first injectable medication.
© 2018 American Diabetes Association and European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
Figures
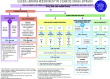
Figure 1
Decision cycle for patient-centered glycemic management in type 2 diabetes.
Figure 2
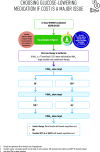
Glucose-lowering medication in type 2 diabetes: overall approach. CV, cardiovascular; DPP-4i, dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitor; GLP-1 RA, glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist; SGLT2i, SGLT2 inhibitor; SU, sulfonylurea.
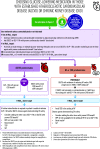
Figure 3
Choosing glucose-lowering medication in those with established ASCVD, HF, and CKD. CV, cardiovascular; DPP-4i, dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitor; GLP-1 RA, glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist; SGLT2i, SGLT2 inhibitor; SU, sulfonylurea.
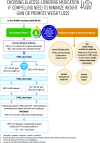
Figure 4
Choosing glucose-lowering medication if compelling need to minimize weight gain or promote weight loss. GLP-1 RA, glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist; T2DM, type 2 diabetes; SGLT2i, SGLT2 inhibitor; SU, sulfonylurea.
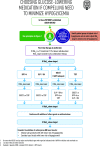
Figure 5
Choosing glucose-lowering medication if compelling need to minimize hypoglycemia. DPP-4i, dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitor; GLP-1 RA, glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist; SGLT2i, SGLT2 inhibitor.
Figure 6
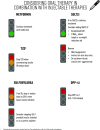
Choosing glucose-lowering medication if cost is a major issue. DPP-4i, dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitor; SGLT2i, SGLT2 inhibitor; SU, sulfonylurea.
Figure 7
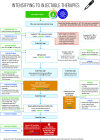
Intensifying to injectable therapies. FRC, fixed-ratio combination; GLP-1 RA, glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist; FBG, fasting blood glucose; FPG, fasting plasma glucose; max, maximum; PPG, postprandial glucose.
Figure 8
Considering oral therapy in combination with injectable therapies. DKA, diabetic ketoacidosis; DPP-4i, dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitor; GLP-1 RA, glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist; SGLT2i, SGLT2 inhibitor; SU, sulfonylurea.
Comment in
- Comment on the consensus report on the management of hyperglycaemia in Type 2 diabetes by the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
Skinner T, Byrne M, Dickinson JK, Fisher L, Funnell M, Guzman S, Hendrieckx C, Hermanns N, Kanc K, Lloyd C, Mocan A, Nouwen A, Pouwer F, Saleh-Stattin N, Snoek F, Speight J, Sturt J, Vallis M, Wagner J, Willaing I, Young-Hyman D, Zoffmann V. Skinner T, et al. Diabet Med. 2019 Jul;36(7):911-912. doi: 10.1111/dme.13934. Epub 2019 Apr 3. Diabet Med. 2019. PMID: 30785642 No abstract available.
Similar articles
- Management of hyperglycaemia in type 2 diabetes, 2018. A consensus report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD).
Davies MJ, D'Alessio DA, Fradkin J, Kernan WN, Mathieu C, Mingrone G, Rossing P, Tsapas A, Wexler DJ, Buse JB. Davies MJ, et al. Diabetologia. 2018 Dec;61(12):2461-2498. doi: 10.1007/s00125-018-4729-5. Diabetologia. 2018. PMID: 30288571 - 2019 Update to: Management of Hyperglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes, 2018. A Consensus Report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD).
Buse JB, Wexler DJ, Tsapas A, Rossing P, Mingrone G, Mathieu C, D'Alessio DA, Davies MJ. Buse JB, et al. Diabetes Care. 2020 Feb;43(2):487-493. doi: 10.2337/dci19-0066. Epub 2019 Dec 19. Diabetes Care. 2020. PMID: 31857443 Free PMC article. - Management of hyperglycaemia in type 2 diabetes, 2022. A consensus report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD).
Davies MJ, Aroda VR, Collins BS, Gabbay RA, Green J, Maruthur NM, Rosas SE, Del Prato S, Mathieu C, Mingrone G, Rossing P, Tankova T, Tsapas A, Buse JB. Davies MJ, et al. Diabetologia. 2022 Dec;65(12):1925-1966. doi: 10.1007/s00125-022-05787-2. Epub 2022 Sep 24. Diabetologia. 2022. PMID: 36151309 Free PMC article. Review. - Management of Hyperglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes, 2022. A Consensus Report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD).
Davies MJ, Aroda VR, Collins BS, Gabbay RA, Green J, Maruthur NM, Rosas SE, Del Prato S, Mathieu C, Mingrone G, Rossing P, Tankova T, Tsapas A, Buse JB. Davies MJ, et al. Diabetes Care. 2022 Nov 1;45(11):2753-2786. doi: 10.2337/dci22-0034. Diabetes Care. 2022. PMID: 36148880 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Empagliflozin reduces cardiorenal events, healthcare resource use and mortality in Sweden compared to dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors: Real world evidence from the Nordic EMPRISE study.
Nyström T, Toresson Grip E, Gunnarsson J, Casajust P, Karlsdotter K, Skogsberg J, Ustyugova A; EMPRISE Study Group. Nyström T, et al. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2023 Jan;25(1):261-271. doi: 10.1111/dom.14870. Epub 2022 Oct 10. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2023. PMID: 36097728 Free PMC article. - Quality-of-Life Comparison of Dapagliflozin Versus Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4 Inhibitors in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Randomized Controlled Trial (J-BOND Study).
Ishii H, Nakajima H, Kamei N, Niiya T, Hiyoshi T, Hiramori Y, Ohtsu S, Noto T, Shimono D. Ishii H, et al. Diabetes Ther. 2020 Dec;11(12):2959-2977. doi: 10.1007/s13300-020-00941-8. Epub 2020 Oct 15. Diabetes Ther. 2020. PMID: 33057967 Free PMC article. - Real-World Use of Insulin Glargine U100 and U300 in Insulin-Naïve Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: DosInGlar Study.
Duque N, Artime E, Romera I, Lebrec J, Díaz S, Rubio M, Sicras-Mainar A, Carretero-Anibarro E, Mundet X, Gorgojo-Martínez JJ, Reviriego J. Duque N, et al. Adv Ther. 2021 Jul;38(7):3857-3871. doi: 10.1007/s12325-021-01773-z. Epub 2021 May 29. Adv Ther. 2021. PMID: 34052987 Free PMC article. - Reversing Type 2 Diabetes: The Time for Lifestyle Medicine Has Come!
Lemieux I. Lemieux I. Nutrients. 2020 Jul 3;12(7):1974. doi: 10.3390/nu12071974. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32635141 Free PMC article. - Update to Evidence-Based Secondary Prevention Strategies After Acute Coronary Syndrome.
Fitchett DH, Leiter LA, Lin P, Pickering J, Welsh R, Stone J, Gregoire J, McFarlane P, Langer A, Gupta A, Goodman SG. Fitchett DH, et al. CJC Open. 2020 Apr 10;2(5):402-415. doi: 10.1016/j.cjco.2020.04.002. eCollection 2020 Sep. CJC Open. 2020. PMID: 32995726 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Rodriguez-Gutierrez R, Gionfriddo MR, Ospina NS, et al. . Shared decision making in endocrinology: present and future directions. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2016;4:706–716 - PubMed
- American Diabetes Association 6. Glycemic targets: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2018. Diabetes Care 2018;41(Suppl. 1):S55–S64 - PubMed
- American Diabetes Association 8. Pharmacologic approaches to glycemic treatment: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2018. Diabetes Care 2018;41(Suppl. 1):S73–S85 - PubMed
- Inzucchi SE, Bergenstal RM, Buse JB, et al. .; Position Statement of the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) . Management of hyperglycaemia in type 2 diabetes a patient-centered approach. Position statement of the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetologia 2012;55:1577–1596 - PubMed
- Inzucchi SE, Bergenstal RM, Buse JB, et al. . Management of hyperglycaemia in type 2 diabetes, 2015: a patient-centred approach. Update to a position statement of the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. Diabetologia 2015;58:429–442 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials