Food impaction: etiology over 35 years and association with eosinophilic esophagitis - PubMed (original) (raw)
Food impaction: etiology over 35 years and association with eosinophilic esophagitis
C J Lenz et al. Dis Esophagus. 2019.
Erratum in
- Food impaction: etiology over 35 years and association with eosinophilic esophagitis.
Lenz CJ, Leggett C, Katzka DA, Larson JJ, Enders FT, Alexander JA. Lenz CJ, et al. Dis Esophagus. 2019 Apr 1;32(4):doz010. doi: 10.1093/dote/doz010. Dis Esophagus. 2019. PMID: 30847465 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
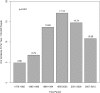
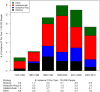
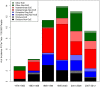
With the emergence of eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) as a common cause of food impaction (FI) and a presumed increase in incidence of EoE in the population, the effect on the incidence of FI has not been well described. The aim of this study is to describe the incidence of FI and endoscopic findings in these patients and the association with EoE. A population-based retrospective chart review of the Rochester Epidemiology Project database was performed to identify all patients within Olmsted County that presented with FI from 1976 to 2012. A review of all endoscopic findings, biopsy results, and demographic data was performed. 497 patients were identified with FI from 1976 to 2012. The overall incidence of FI has changed from 1976 to 2012 (Fig. 1) (P < 0.001). The peak incidence of 17.12 per 100,000 people occurred in the time period 1995 to 2000. Both the incidence of comorbid gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and proton pump inhibitor (PPI) use increased over the time period of the study (P < 0.001 for both). Of these patients, 188 (46.7%) had no abnormalities on their endoscopy. The most common endoscopic finding was stricture in 71 (17.6%) patients followed closely by Schatzki's ring in 68 (16.9%) patients. 139 patients had biopsies performed within 2 years of FI and 50 (36.0%) of those were diagnosed with EoE. We present for the first time the changing incidence of FI over the last 35 years in a population-based setting. We also demonstrate the rise of EoE as an important clinical consideration in patients with FI.
Keywords: dysphagia; eosinophilic esophagitis; esophagus; food impaction.
© The Author(s) 2018. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of International Society for Diseases of the Esophagus.
Figures
Figure 1.
Incidence of food impaction from 1976 to 2012.
Figure 2.
Endoscopic findings in food impaction as determined at the time of initial endoscopy.
Figure 3.
Initial endoscopic findings and eventual diagnosis of eosinophilic esophagitis within each endoscopic finding group.
Similar articles
- Temporal trends in the relative prevalence of dysphagia etiologies from 1999-2009.
Kidambi T, Toto E, Ho N, Taft T, Hirano I. Kidambi T, et al. World J Gastroenterol. 2012 Aug 28;18(32):4335-41. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i32.4335. World J Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 22969196 Free PMC article. - Similarities and differences among eosinophilic esophagitis, proton-pump inhibitor-responsive esophageal eosinophilia, and reflux esophagitis: comparisons of clinical, endoscopic, and histopathological findings in Japanese patients.
Jiao D, Ishimura N, Maruyama R, Ishikawa N, Nagase M, Oshima N, Aimi M, Okimoto E, Mikami H, Izumi D, Okada M, Ishihara S, Kinoshita Y. Jiao D, et al. J Gastroenterol. 2017 Feb;52(2):203-210. doi: 10.1007/s00535-016-1213-1. Epub 2016 Apr 23. J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 27108416 - Esophageal eosinophilic infiltration responds to proton pump inhibition in most adults.
Molina-Infante J, Ferrando-Lamana L, Ripoll C, Hernandez-Alonso M, Mateos JM, Fernandez-Bermejo M, Dueñas C, Fernandez-Gonzalez N, Quintana EM, Gonzalez-Nuñez MA. Molina-Infante J, et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011 Feb;9(2):110-7. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2010.09.019. Epub 2010 Oct 1. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011. PMID: 20920599 - Esophageal Food Impaction and Eosinophilic Esophagitis: A Retrospective Study, Systematic Review, and Meta-Analysis.
Hiremath GS, Hameed F, Pacheco A, Olive A, Davis CM, Shulman RJ. Hiremath GS, et al. Dig Dis Sci. 2015 Nov;60(11):3181-93. doi: 10.1007/s10620-015-3723-8. Epub 2015 Jun 12. Dig Dis Sci. 2015. PMID: 26065368 Free PMC article. Review. - Diagnosis and treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis in clinical practice.
Abe Y, Sasaki Y, Yagi M, Yaoita T, Nishise S, Ueno Y. Abe Y, et al. Clin J Gastroenterol. 2017 Apr;10(2):87-102. doi: 10.1007/s12328-017-0725-4. Epub 2017 Feb 28. Clin J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 28247277 Review.
Cited by
- A retrospective cohort study on oesophageal food bolus obstruction in the North Denmark region in 2021-two thirds were never diagnosed with a cause.
Terkelsen JH, Hollænder M, Bredal K, Nielsen SM, Thomsen KVK, Baggerman A, Ofverlind E, Koc AM, Pakes H, Mahdi MB, Larsen SØ, Gonzalez VP, Riis J, Frandsen LT, Melgaard D, Krarup AL. Terkelsen JH, et al. BMC Gastroenterol. 2024 Jan 2;24(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s12876-023-03077-8. BMC Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38166672 Free PMC article. - Association between time from esophageal food impaction to endoscopy and adverse events.
Redd WD, McCallen JD, Xue Z, Kiran A, Barlowe TS, Reed CC, Eluri S, Dellon ES. Redd WD, et al. Gastrointest Endosc. 2024 Apr;99(4):525-536.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2023.11.005. Epub 2023 Nov 10. Gastrointest Endosc. 2024. PMID: 37951280 - Endoscopic Diagnosis of Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Basics and Recent Advances.
Abe Y, Sasaki Y, Yagi M, Mizumoto N, Onozato Y, Umehara M, Ueno Y. Abe Y, et al. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Dec 16;12(12):3202. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12123202. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36553209 Free PMC article. Review. - The Risk of Esophageal Food Impaction in Eosinophilic Esophagitis Patients: The Role of Clinical and Socioeconomic Factors.
Alhmoud T, Ghazaleh S, Ghanim M, Redfern RE. Alhmoud T, et al. Clin Exp Gastroenterol. 2022 Sep 15;15:153-161. doi: 10.2147/CEG.S364994. eCollection 2022. Clin Exp Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 36132486 Free PMC article. - British Society of Gastroenterology (BSG) and British Society of Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition (BSPGHAN) joint consensus guidelines on the diagnosis and management of eosinophilic oesophagitis in children and adults.
Dhar A, Haboubi HN, Attwood SE, Auth MKH, Dunn JM, Sweis R, Morris D, Epstein J, Novelli MR, Hunter H, Cordell A, Hall S, Hayat JO, Kapur K, Moore AR, Read C, Sami SS, Turner PJ, Trudgill NJ. Dhar A, et al. Gut. 2022 Aug;71(8):1459-1487. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2022-327326. Epub 2022 May 23. Gut. 2022. PMID: 35606089 Free PMC article.
References
- Landres R T, Kuster G G, Strum W B. Eosinophilic esophagitis in a patient with vigorous achalasia. Gastroenterology 1978; 74: 1298–301. - PubMed
- Arora A S, Yamazaki K. Eosinophilic esophagitis: asthma of the esophagus? Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2004; 2: 523–30. - PubMed
- Liacouras C A, Furuta G T, Hirano I et al. .. Eosinophilic esophagitis: updated consensus recommendations for children and adults. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2011; 128: 3–20.e6; quiz 1–2. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical