Fragment size and level of cell-free DNA provide prognostic information in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer - PubMed (original) (raw)
Fragment size and level of cell-free DNA provide prognostic information in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer
Morten Lapin et al. J Transl Med. 2018.
Abstract
Background: It was recently demonstrated that the size of cell-free DNA (cfDNA) fragments that originates from tumor cells are shorter than cfDNA fragments that originates from non-malignant cells. We investigated whether cfDNA fragment size and cfDNA levels might have prognostic value in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer.
Methods: Blood samples were obtained from patients with advanced pancreatic cancer, before (n = 61) initiation of chemotherapy and after the first cycle of chemotherapy (n = 39). Samples were separated with density centrifugation and plasma DNA was isolated. Mode cfDNA fragment size and cfDNA levels were then determined using a 2100 Bioanalyzer. A cohort of partially age-matched healthy volunteers (n = 28) constituted the control group.
Results: Both a pre-treatment cfDNA fragment size of ≤ 167 bp (mode) and high pre-treatment cfDNA levels were associated with shorter progression-free survival (PFS) (p = 0.002 and p < 0.001, respectively) and overall survival (OS) (p = 0.001 and p = 0.001, respectively). Furthermore, multivariable Cox regression analyses demonstrated that pre-treatment cfDNA levels could independently predict prognosis for both PFS (HR = 3.049, p = 0.005) and OS (HR = 2.236, p = 0.028).
Conclusion: This study demonstrates that cfDNA fragment size and cfDNA levels can be used to predict disease outcome in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer. The described approach, using a rapid, economic and simple test to reveal prognostic information, has potential for future treatment stratification and monitoring.
Keywords: Cell-free DNA; Pancreatic cancer; cfDNA; cfDNA fragment size.
Figures
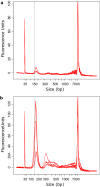
Fig. 1
Distribution of cfDNA fragment size and cfDNA level in plasma. a cfDNA from healthy controls (n = 10) displayed larger fragment size (X-axis) and lower cfDNA level (Y-axis) compared to b cfDNA from patients with pancreatic cancer (n = 10). The dotted line placed at 150 bp indicates a shift towards shorter fragment size in patient samples
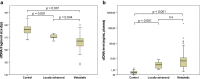
Fig. 2
Distributions of cfDNA fragment size and cfDNA levels in patient and control samples. Boxplot shows differences in a cfDNA fragment size and b cfDNA levels between samples from healthy controls (n = 28), patients with localized disease (n = 6), and patients with metastatic disease (n = 55). Abbreviation: n.s, not significant
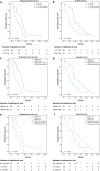
Fig. 3
Kaplan-Meier analyses of pre-treatment samples. a, c, e Progression-free survival and b, d, f overall survival are shown for a, b patients with short (≤ 167 bp) vs those with long (> 167 bp) cfDNA fragment size; c, d patients with high vs those with low cfDNA levels, and e, f patients positive for two markers, vs those with one or no markers
Similar articles
- Enrichment of short mutant cell-free DNA fragments enhanced detection of pancreatic cancer.
Liu X, Liu L, Ji Y, Li C, Wei T, Yang X, Zhang Y, Cai X, Gao Y, Xu W, Rao S, Jin D, Lou W, Qiu Z, Wang X. Liu X, et al. EBioMedicine. 2019 Mar;41:345-356. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.02.010. Epub 2019 Mar 9. EBioMedicine. 2019. PMID: 30857943 Free PMC article. - Circulating Cell-Free DNA and Circulating Tumor Cells as Prognostic and Predictive Biomarkers in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients Treated with First-Line Chemotherapy.
Coco S, Alama A, Vanni I, Fontana V, Genova C, Dal Bello MG, Truini A, Rijavec E, Biello F, Sini C, Burrafato G, Maggioni C, Barletta G, Grossi F. Coco S, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2017 May 11;18(5):1035. doi: 10.3390/ijms18051035. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28492516 Free PMC article. - Association of EGFR L858R Mutation in Circulating Free DNA With Survival in the EURTAC Trial.
Karachaliou N, Mayo-de las Casas C, Queralt C, de Aguirre I, Melloni B, Cardenal F, Garcia-Gomez R, Massuti B, Sánchez JM, Porta R, Ponce-Aix S, Moran T, Carcereny E, Felip E, Bover I, Insa A, Reguart N, Isla D, Vergnenegre A, de Marinis F, Gervais R, Corre R, Paz-Ares L, Morales-Espinosa D, Viteri S, Drozdowskyj A, Jordana-Ariza N, Ramirez-Serrano JL, Molina-Vila MA, Rosell R; Spanish Lung Cancer Group. Karachaliou N, et al. JAMA Oncol. 2015 May;1(2):149-57. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2014.257. JAMA Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26181014 Clinical Trial. - Prognostic value of circulating cell-free DNA in patients with pancreatic cancer: A systemic review and meta-analysis.
Chen L, Zhang Y, Cheng Y, Zhang D, Zhu S, Ma X. Chen L, et al. Gene. 2018 Dec 30;679:328-334. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2018.09.029. Epub 2018 Sep 15. Gene. 2018. PMID: 30227250 Review. - Cell-Free DNA in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.
Spindler KG, Boysen AK, Pallisgård N, Johansen JS, Tabernero J, Sørensen MM, Jensen BV, Hansen TF, Sefrioui D, Andersen RF, Brandslund I, Jakobsen A. Spindler KG, et al. Oncologist. 2017 Sep;22(9):1049-1055. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2016-0178. Epub 2017 Aug 4. Oncologist. 2017. PMID: 28778958 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Integrative analysis of multi-omics data for liquid biopsy.
Chen G, Zhang J, Fu Q, Taly V, Tan F. Chen G, et al. Br J Cancer. 2023 Feb;128(4):505-518. doi: 10.1038/s41416-022-02048-2. Epub 2022 Nov 10. Br J Cancer. 2023. PMID: 36357703 Free PMC article. Review. - A ligation-based single-stranded library preparation method to analyze cell-free DNA and synthetic oligos.
Troll CJ, Kapp J, Rao V, Harkins KM, Cole C, Naughton C, Morgan JM, Shapiro B, Green RE. Troll CJ, et al. BMC Genomics. 2019 Dec 27;20(1):1023. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-6355-0. BMC Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31881841 Free PMC article. - Age-related changes in antigen-specific natural antibodies are influenced by sex.
Webster SE, Tsuji NL, Clemente MJ, Holodick NE. Webster SE, et al. Front Immunol. 2023 Jan 12;13:1047297. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1047297. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36713434 Free PMC article. - Dynamic monitoring of circulating tumor DNA reveals outcomes and genomic alterations in patients with relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphoma undergoing CAR T-cell therapy.
Zou H, Liu W, Wang X, Wang Y, Wang C, Qiu C, Liu H, Shan D, Xie T, Huang W, Sui W, Yi S, An G, Xu Y, Ma T, Wang J, Qiu L, Zou D. Zou H, et al. J Immunother Cancer. 2024 Mar 4;12(3):e008450. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2023-008450. J Immunother Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38443094 Free PMC article.
References
- Shaw JA, Guttery DS, Hills A, Fernandez-Garcia D, Page K, Rosales BM, et al. Mutation analysis of cell-free DNA and single circulating tumor cells in metastatic breast cancer patients with high circulating tumor cell counts. Clin Cancer Res. 2017;23(1):88–96. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-0825. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical