The impact of co-morbidity on the quality of life of people with dementia: findings from the IDEAL study - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2019 May 1;48(3):361-367.
doi: 10.1093/ageing/afy155.
Yu-Tzu Wu 1 2, Fiona E Matthews 3, Anthony Martyr 1, Catherine Quinn 1, Isla Rippon 4, Jennifer Rusted 5, Jeanette M Thom 6, Michael D Kopelman 7, John V Hindle 1, Roy W Jones 8, Linda Clare 1 9
Affiliations
- PMID: 30403771
- PMCID: PMC6503940
- DOI: 10.1093/ageing/afy155
The impact of co-morbidity on the quality of life of people with dementia: findings from the IDEAL study
Sharon M Nelis et al. Age Ageing. 2019.
Abstract
Background: The aim was to investigate the co-morbidity profile of people with dementia and examine the associations between severity of co-morbidity, health-related quality of life (HRQoL) and quality of life (QoL).
Methods: The improving the experience of Dementia and Enhancing Active Life (IDEAL) cohort consisted of 1,547 people diagnosed with dementia who provided information on the number and type of co-morbid conditions. Participants also provided ratings of their health-related and dementia-specific QoL.
Results: The majority of the sample were living with more than one chronic condition. Hypertension was commonly reported and frequently combined with connective tissue disease, diabetes and depression. The number of co-morbid conditions was associated with low QoL scores, and those with severe co-morbidity (≥5 conditions) showed the greatest impact on their well-being.
Conclusions: Co-morbidity is an important risk factor for poor QoL and health status in people with dementia. Greater recognition of the nature and impact of co-morbidity is needed to inform support and interventions for people with dementia and a multidisciplinary approach to care provision is recommended.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s; depression; multimorbidities; older people.
© The Author(s) 2018 Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Geriatrics Society.
Figures
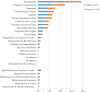
Figure 1
Prevalence of co-morbid conditions associated with dementia
Comment in
- Co-morbidities in dementia: time to focus more on assessing and managing co-morbidities.
Subramaniam H. Subramaniam H. Age Ageing. 2019 May 1;48(3):314-315. doi: 10.1093/ageing/afz007. Age Ageing. 2019. PMID: 31063580 No abstract available. - Comorbidity is a risk factor for poor quality of life in people with dementia.
Zhang N. Zhang N. Evid Based Nurs. 2020 Oct;23(4):105. doi: 10.1136/ebnurs-2019-103161. Epub 2019 Nov 15. Evid Based Nurs. 2020. PMID: 31732611 No abstract available.
Similar articles
- Do changes in specific cognitive functions predict changes in health-related quality of life in people with Alzheimer's disease?
Bosboom PR, Almeida OP. Bosboom PR, et al. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2014 Jul;29(7):694-703. doi: 10.1002/gps.4050. Epub 2013 Nov 25. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2014. PMID: 24273030 - Dementia subtype and living well: results from the Improving the experience of Dementia and Enhancing Active Life (IDEAL) study.
Wu YT, Clare L, Hindle JV, Nelis SM, Martyr A, Matthews FE; Improving the experience of Dementia and Enhancing Active Life study. Wu YT, et al. BMC Med. 2018 Sep 11;16(1):140. doi: 10.1186/s12916-018-1135-2. BMC Med. 2018. PMID: 30200957 Free PMC article. - Developing a dementia-specific health state classification system for a new preference-based instrument AD-5D.
Nguyen KH, Mulhern B, Kularatna S, Byrnes J, Moyle W, Comans T. Nguyen KH, et al. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2017 Jan 25;15(1):21. doi: 10.1186/s12955-017-0585-0. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2017. PMID: 28122626 Free PMC article. - Quality of life in people living with dementia in nursing homes.
Moyle W, O'Dwyer S. Moyle W, et al. Curr Opin Psychiatry. 2012 Nov;25(6):480-4. doi: 10.1097/YCO.0b013e32835a1ccf. Curr Opin Psychiatry. 2012. PMID: 23037963 Review. - The concept of quality of life in dementia in the different stages of the disease.
Ettema TP, Dröes RM, de Lange J, Ooms ME, Mellenbergh GJ, Ribbe MW. Ettema TP, et al. Int Psychogeriatr. 2005 Sep;17(3):353-70. doi: 10.1017/s1041610205002073. Int Psychogeriatr. 2005. PMID: 16252370 Review.
Cited by
- The impact of chronic kidney disease on health-related quality of life (HRQoL): key insights from a hospital-based cross-sectional study.
Sahu G, Arora P, Tiwari P, D'Cruz S, Tahlan A. Sahu G, et al. J Bras Nefrol. 2025 Jul-Sep;47(3):e20240229. doi: 10.1590/2175-8239-JBN-2024-0229en. J Bras Nefrol. 2025. PMID: 40531614 Free PMC article. - Effects of Chronic Comorbidities on the Health-Related Quality of Life among Older Patients after Falls in Vietnamese Hospitals.
Vu HM, Nguyen LH, Tran TH, Pham KTH, Phan HT, Nguyen HN, Tran BX, Latkin CA, Ho CSH, Ho RCM. Vu HM, et al. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019 Sep 27;16(19):3623. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16193623. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019. PMID: 31569612 Free PMC article. - Structural capabilities in primary care practices where nurse practitioners care for persons living with dementia.
Hovsepian VE, Liu J, Schlak AE, Sadak T, Martsolf G, Bilazarian A, McHugh MD, Poghosyan L. Hovsepian VE, et al. Int J Older People Nurs. 2023 Sep;18(5):e12556. doi: 10.1111/opn.12556. Epub 2023 Jul 11. Int J Older People Nurs. 2023. PMID: 37431711 Free PMC article. - Predicting Hospice Transitions in Dementia Caregiving Dyads: An Exploratory Machine Learning Approach.
Sullivan SS, Bo W, Li CS, Xu W, Chang YP. Sullivan SS, et al. Innov Aging. 2022 Aug 11;6(6):igac051. doi: 10.1093/geroni/igac051. eCollection 2022. Innov Aging. 2022. PMID: 36452051 Free PMC article.
References
- Melzer D, Delgado J, Winder R, Masoli J, Richards S, Ble A. The Age UK Almanac of Disease Profiles in Later Life. UK: Ageing Research Group, University of Exeter, 2015.
- Barnett K, Mercer SW, Norbury M, Watt G, Wyke S, Guthrie B. Epidemiology of multimorbidity and implications for health care, research, and medical education: a cross-sectional study. Lancet 2012; 380: 37–43. - PubMed
- Meyers BS. Depression and dementia: comorbidities, identification, and treatment. J Geriatr Psychiatry Neurol 1998; 11: 201–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical