Protective roles of ginseng against bacterial infection - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Protective roles of ginseng against bacterial infection
Ye-Ram Kim et al. Microb Cell. 2018.
Abstract
Ginseng (Panax ginseng Meyer) is a well-known traditional herbal medicine that plays a protective role against microbial attack. Several studies have revealed its anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory, and immune-modulatory effects. Ginseng contains several components that vary according to the year of cultivation and the processing method used, such as heating, drying, and steaming, which induce different degrees of pharmacological activities. This review discusses the antibacterial effects of ginseng against pathogenic bacterial infections. We describe how ginseng regulates pathogenic factors that are harmful to the host and discuss the therapeutic potential of ginseng as a natural antibacterial drug to combat bacterial infectious disease, which is a global public health challenge. The components of ginseng could be novel alternatives to solve the growing problem of antibiotic resistance and toxicity.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
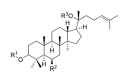
Figure 1. FIGURE 1: General structure of the saponin.
Saponins are glucosides with foaming characteristics. Saponins consist of a polycyclic aglycones attached to one or more sugar side chains. The aglycone part, which is also called sapogenin, is either a steroid (C27) or a triterpene (C30). The foaming ability of saponins is caused by the combination of a hydrophobic (fat-soluble) sapogenin and a hydrophilic (water-soluble) sugar part (R1, R2, R3: -sugar or -H group).
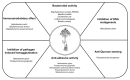
Figure 2. FIGURE 2: The main types of antibacterial activities of Panax ginseng.
P. ginseng shows various antibacterial activities against infectious agents. P. ginseng convers antimicrobial therapy via various mechanisms, including bactericidal activity, immunomodulatory effects, inhibition of pathogen-induced hemagglutination, anti-adhesive activity, and anti-quorum sensing activity.
Similar articles
- Ginseng, the natural effectual antiviral: Protective effects of Korean Red Ginseng against viral infection.
Im K, Kim J, Min H. Im K, et al. J Ginseng Res. 2016 Oct;40(4):309-314. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2015.09.002. Epub 2015 Sep 16. J Ginseng Res. 2016. PMID: 27746682 Free PMC article. Review. - Antimicrobial activities of Asian ginseng, American ginseng, and notoginseng.
Wang L, Huang Y, Yin G, Wang J, Wang P, Chen ZY, Wang T, Ren G. Wang L, et al. Phytother Res. 2020 Jun;34(6):1226-1236. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6605. Epub 2019 Dec 29. Phytother Res. 2020. PMID: 31885119 Review. - Anti-acne properties of hydrophobic fraction of red ginseng (Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer) and its active components.
Hou JH, Shin H, Jang KH, Park CK, Koo B, Shin H, Yuk SH, Lee KY. Hou JH, et al. Phytother Res. 2019 Mar;33(3):584-590. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6243. Epub 2018 Dec 3. Phytother Res. 2019. PMID: 30506753 Clinical Trial. - Change of Ginsenoside Profiles in Processed Ginseng by Drying, Steaming, and Puffing.
Shin JH, Park YJ, Kim W, Kim DO, Kim BY, Lee H, Baik MY. Shin JH, et al. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019 Feb 28;29(2):222-229. doi: 10.4014/jmb.1809.09056. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 30609886 - Current Status and Problem-Solving Strategies for Ginseng Industry.
Li XY, Sun LW, Zhao DQ. Li XY, et al. Chin J Integr Med. 2019 Dec;25(12):883-886. doi: 10.1007/s11655-019-3046-2. Epub 2019 Oct 15. Chin J Integr Med. 2019. PMID: 31630359 Review.
Cited by
- The Role of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Chinese Pharmacopoeia in the Evaluation and Treatment of COVID-19.
Gasmi A, Noor S, Dadar M, Semenova Y, Menzel A, Gasmi Benahmed A, Bjørklund G. Gasmi A, et al. Curr Pharm Des. 2024;30(14):1060-1074. doi: 10.2174/0113816128217263240220060252. Curr Pharm Des. 2024. PMID: 38523518 Review. - Antiviral activities of ginseng and its potential and putative benefits against monkeypox virus: A mini review.
Chandra Das R, Ratan ZA, Rahman MM, Runa NJ, Mondal S, Konstantinov K, Hosseinzadeh H, Cho JY. Chandra Das R, et al. J Ginseng Res. 2023 Apr 1;47(6):687-93. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2023.03.002. Online ahead of print. J Ginseng Res. 2023. PMID: 37362081 Free PMC article. Review. - Effect of hydro-alcoholic extract of Panax ginseng and Ampicillin treatment in an animal model of _Listeria monocytogenes_-induced endocarditis.
Athari SZ, Karamouz Z, Nourazar MA, Doustar Y, Anzabi Y. Athari SZ, et al. Avicenna J Phytomed. 2023 Mar-Apr;13(2):109-117. doi: 10.22038/AJP.2022.21227. Avicenna J Phytomed. 2023. PMID: 37333474 Free PMC article. - Protective effects of Korean Red Ginseng against toxicity of endocrine-disrupting chemicals.
Jung EM, Lee SH, Lee GS. Jung EM, et al. J Ginseng Res. 2023 Mar;47(2):193-198. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2022.11.007. Epub 2022 Dec 5. J Ginseng Res. 2023. PMID: 36926605 Free PMC article. Review. - Probiotic Characteristics and Safety Assessment of Lacticaseibacillus casei KGC1201 Isolated from Panax ginseng.
Lee YS, Yu HY, Kwon M, Lee SH, Park JI, Seo J, Kim SK. Lee YS, et al. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023 Apr 28;33(4):519-526. doi: 10.4014/jmb.2211.11029. Epub 2023 Jan 31. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36788470 Free PMC article.
References
- Lee OR, Sathiyaraj G, Kim YJ, In JG, Kwon WS, Kim JH, Yang DC. Defense Genes Induced by Pathogens and Abiotic Stresses in Panax Ginseng C. A. Meyer. J Ginseng Res. 2011;35(1):1–11. doi: 10.5142/jgr.2011.35.1.001. - DOI
- Helmes S. Cancer Prevention and Therapeutics: Panax Ginseng. Altern Med Rev. 2004;9(3):259–275. - PubMed
- Radad K, Gille G, Liu L, Rausch WD. Use of Ginseng in Medicine With Emphasis on Neurodegenerative Disorders. J Pharmacol Sci. 2006;100(3):175–186. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIP) (No. 2016R1D1A1A02937312). This work was supported by the research fund of Hanyang University (HY-2015-N).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources