Baclofen for alcohol use disorder - PubMed (original) (raw)
Meta-Analysis
Baclofen for alcohol use disorder
Silvia Minozzi et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018.
Update in
- Baclofen for alcohol use disorder.
Agabio R, Saulle R, Rösner S, Minozzi S. Agabio R, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Jan 13;1(1):CD012557. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012557.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 36637087 Free PMC article. Review.
Abstract
Background: Alcohol use disorder (AUD) and alcohol-related impairments belong to the most widespread psychiatric disorders leading to specific psychophysical, affective and cognitive symptoms and consequences for psychosocial well-being and health. Alcohol consumption is increasingly becoming a problem in many developing regions and AUD prevalence is estimated at 4.1% worldwide, with highest prevalence in European countries (7.5%), and the North America (6.0%). Therapeutic approaches, including pharmacotherapy, play an important role in treating patients with AUD.
Objectives: To assess the efficacy and safety of baclofen for treating people with AUD, who are currently drinking, with the aim of achieving and maintaining abstinence or reducing alcohol consumption.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Drugs and Alcohol Specialised Register, CENTRAL, MEDLINE, Embase, two further databases and two clinical trials registries, conference proceedings, and the reference lists of retrieved articles. The date of the most recent search was 30 January 2018.
Selection criteria: Randomised controlled trials (RCTs) of at least four weeks' treatment duration and 12 weeks' overall study duration comparing baclofen for relapse prevention of AUD with placebo, no treatment or other treatments.
Data collection and analysis: We used standard methodological procedures expected by Cochrane.
Main results: We included 12 RCTs (1128 participants). All studies but three recruited fewer than 100 participants. Participants had a diagnosis of alcohol dependence according the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) IV or the International Classification of Diseases (ICD)-10 criteria who were currently drinking. The mean age of participants was 48 years, and there were more men (69%), than women. All studies compared baclofen to placebo, except for one study that evaluated baclofen versus acamprosate. The included studies considered baclofen at different doses (range 10 mg a day to 150 mg a day). In all but one of the studies, participants in both the baclofen and placebo groups received psychosocial treatment or counselling of various intensity.We judged most of the studies at low risk of selection, performance, detection (subjective outcome), attrition and reporting bias.We did not find any difference between baclofen and placebo for the primary outcomes: relapse-return to any drinking (RR 0.88, 95% CI 0.74 to 1.04; 5 studies, 781 participants, moderate certainty evidence); frequency of use by percentage of days abstinent (MD 0.39, 95% CI -11.51 to 12.29; 6 studies, 465 participants, low certainty evidence) and frequency of use by percentage of heavy drinking days at the end of treatment (MD 0.25, 95% CI -1.25 to 1.76; 3 studies, 186 participants, moderate certainty evidence); number of participants with at least one adverse event (RR 1.04, 95% CI 0.99 to 1.10; 4 studies, 430 participants, high certainty evidence); the dropout rate at the end of treatment (RR 0.98, 95% CI 0.77 to 1.26, 8 studies, 977 participants, high certainty evidence) and dropout due to adverse events (RR 1.11, 95% CI 0.59 to 2.07; 7 studies, 913 participants, high certainty evidence).We found evidence that baclofen increases amount of use (drink per drinking days), (MD 1.55, 95% CI 1.32 to 1.77; 2 studies, 72 participants, low certainty evidence).Among secondary outcomes, there was no difference on craving (MD 1.38, 95% CI -1.28 to 4.03, 5 studies, 469 participants), and anxiety (SMD 0.07, 95% CI -0.14 to 0.28; 5 trials, 509 participants). We found that baclofen increased depression (SMD 0.27, 95% CI 0.05 to 0.48; 3 studies, 387 participants).Concerning the specific adverse events we found that baclofen increased: vertigo (RR 2.16, 95% CI 1.24 to 3.74; 7 studies, 858 participants), somnolence/sedation (RR 1.48, 95%CI 1.11 to 1.96; 8 studies, 946 participants), paraesthesia (RR 4.28, 95% CI 2.11 to 8.67; 4 studies, 593 participants), and muscle spasms/rigidity (RR 1.94, 95%CI 1.08 to 3.48; 3 studies, 551 participants). For all the other adverse events we did not find significant differences between baclofen and placebo.For the comparison baclofen versus acamprosate, we were only able to extract data for one outcome, craving. For this outcome, we found that baclofen increased craving compared with acamprosate (MD 14.62, 95% CI 12.72 to 16.52; 1 study, 49 participants).
Authors' conclusions: None of the primary or secondary outcomes of the review showed evidence of a difference between baclofen and placebo. The high heterogeneity among primary studies results limits the interpretation of the summary estimate, the identification of moderators and mediators of baclofen's effects on alcohol use remains a challenge for further research. Even though some results from RCTs are promising, current evidence remains uncertain regarding the use of baclofen as a first-line treatment for people with AUDs.
Conflict of interest statement
Silvia Minozzi: no conflict of interest known
Rosella Saulle: no conflict of interest known
Susanne Rösner: no conflict of interest known
Figures
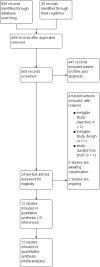
1
Study flow diagram
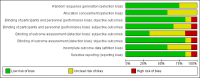
2
Risk of bias graph: review authors' judgements about each risk of bias item presented as percentages across all included studies
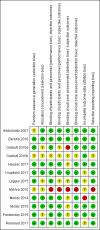
3
Risk of bias summary: review authors' judgements about each risk of bias item for each included study
Similar articles
- Baclofen for alcohol use disorder.
Agabio R, Saulle R, Rösner S, Minozzi S. Agabio R, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Jan 13;1(1):CD012557. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012557.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 36637087 Free PMC article. Review. - Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas.
Crider K, Williams J, Qi YP, Gutman J, Yeung L, Mai C, Finkelstain J, Mehta S, Pons-Duran C, Menéndez C, Moraleda C, Rogers L, Daniels K, Green P. Crider K, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article. - Psychosocial and pharmacologic interventions to reduce harmful alcohol use in low- and middle-income countries.
Greene MC, Kane J, Alto M, Giusto A, Lovero K, Stockton M, McClendon J, Nicholson T, Wainberg ML, Johnson RM, Tol WA. Greene MC, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 May 9;5(5):CD013350. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013350.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37158538 Free PMC article. Review. - Antidepressants for the treatment of people with co-occurring depression and alcohol dependence.
Agabio R, Trogu E, Pani PP. Agabio R, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Apr 24;4(4):CD008581. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008581.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29688573 Free PMC article. Review. - Alcoholics Anonymous and other 12-step programs for alcohol use disorder.
Kelly JF, Humphreys K, Ferri M. Kelly JF, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Mar 11;3(3):CD012880. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012880.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32159228 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Pharmacotherapies and personalized medicine for alcohol use disorder: a review.
Lohoff FW. Lohoff FW. Pharmacogenomics. 2020 Oct;21(15):1117-1138. doi: 10.2217/pgs-2020-0079. Epub 2020 Aug 18. Pharmacogenomics. 2020. PMID: 32807012 Free PMC article. Review. - Alkohol.
Vyssoki B. Vyssoki B. Neuropsychiatr. 2020 Dec;34(4):155-156. doi: 10.1007/s40211-020-00376-4. Neuropsychiatr. 2020. PMID: 33231832 German. No abstract available. - Advances in the science and treatment of alcohol use disorder.
Witkiewitz K, Litten RZ, Leggio L. Witkiewitz K, et al. Sci Adv. 2019 Sep 25;5(9):eaax4043. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aax4043. eCollection 2019 Sep. Sci Adv. 2019. PMID: 31579824 Free PMC article. Review. - Medications for the Treatment of Alcohol Dependence-Current State of Knowledge and Future Perspectives from a Public Health Perspective.
Stokłosa I, Więckiewicz G, Stokłosa M, Piegza M, Pudlo R, Gorczyca P. Stokłosa I, et al. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Jan 19;20(3):1870. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20031870. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36767234 Free PMC article. Review. - Baclofen in the treatment of alcohol use disorder: tailored doses matter.
de Beaurepaire R, Jaury P. de Beaurepaire R, et al. Alcohol Alcohol. 2024 Jan 17;59(2):agad090. doi: 10.1093/alcalc/agad090. Alcohol Alcohol. 2024. PMID: 38266071 Free PMC article. Review.
References
References to studies included in this review
Addolorato 2007 {published data only}
- Addolorato G, Leggio L, Ferrulli A, Cardone S, Vonghia L, Mirijello A, et al. Effectiveness and safety of baclofen for maintenance of alcohol abstinence in alcohol‐dependent patients with liver cirrhosis: randomised, double‐blind controlled study. Lancet 2007;370(9603):1915‐22. [DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61814-5] - DOI - PubMed
Beraha 2016 {published data only}
- Beraha EM, Salemink E, Goudriaan AE, Bakker A, Jong D, Smits N, et al. Efficacy and safety of high‐dose baclofen for the treatment of alcohol dependence: a multicentre, randomised, double‐blind controlled trial. European Neuropsychopharmacology 2017;26(12):1950‐9. - PubMed
Garbutt 2010a {published data only}
- Garbutt JC, Kampov‐Polevoy AB, Gallop R, Kalka‐Juhl L, Flannery BA. Efficacy and safety of baclofen for alcohol dependence: a randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research 2010;34(11):1849‐57. [DOI: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2010.01273.x] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Garbutt 2010b {published data only}
Hauser 2017 {published data only}
Krupitskii 2017 {published data only}
- Krupitskii EM, Rybakova KV, Kiselev AS, Alekseeva YV, Berntsev VA, Chekhlatyi EI, et al. Efficacy and safety of the use of baclofen in the treatment of alcohol dependent (a double‐blind, randomized, placebo‐controlled pilot study). Neuroscience and Behavioral Physiology 2017;47(2):153‐62. [DOI: 10.1007/s11055-016-0379-6] - DOI
- Krupitsky EM, Rybakova KV, Kiselev AS, Alexeeva YV, Berntsev VA, Chekhlaty EI, et al. Double blind placebo controlled randomized pilot clinical trial of baclofen (Baclosan®) for alcohol dependence. Zhurnal Nevrologii i Psikhiatrii Imeni S.S. Korsakova 2015;115(6):53‐62. [DOI: 10.17116/jnevro20151156153-62] - DOI - PubMed
Leggio 2015 {published data only}
- Bollinger J, Edwards SM, Zywiak WK, Tidey JW, Swift RW, Kenna GA, et al. A double‐blind, placebo‐controlled randomized pilot study of the effects of baclofen on alcohol‐tobacco co‐use and alcohol cue‐reactivity in alcoholic smokers. Clinical and Translational Science 2014;7(3):265.
Mishra 2010 {published data only}
- Mishra SN, Rath NM, Mishra A, Swain SP, Shukla RK. A study of comparative efficacy of baclofen vs acamprosate in reducing alcohol craving and abuse. Indian Journal of Psychiatry 2010;52:S69.
Morley 2014 {published data only}
Muller 2015 {published data only}
Ponizovsky 2015 {published data only}
- Ponizovsky AM, Rosca P, Aronovich E, Weizman A, Grinshpoon A. Baclofen as add‐on to standard psychosocial treatment for alcohol dependence: a randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial with 1 year follow‐up. Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment 2015;52:24‐30. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jsat.2014.11.007] - DOI - PubMed
Reynaud 2017 {published data only}
- Reynaud M, Aubin HJ, Trinquet F, Zakine B, Dano C, Dematteis M, et al. A randomized, placebo‐controlled study of high‐dose baclofen in alcohol‐dependent patients—the ALPADIR Study. Alcohol and Alcoholism 2017;52(4):439‐46. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Addolorato 2002 {published data only}
- Addolorato G, Caputo F, Capristo E, Domenicali M, Bernardi M, Janiri M, et al. Baclofen efficacy in reducing alcohol craving and intake: a preliminary double‐blind randomised controlled study. Alcohol & Alcoholism 2002;37:504‐8. - PubMed
Flannery 2004 {published data only}
- Flannery BA, Garbutt JC, Cody MW, Renn W, Grace K, Osborne M, et al. Baclofen for alcohol dependence: a preliminary open‐label study. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research 2004;28(10):1517‐23. - PubMed
Leggio 2011 {published data only}
- Leggio L, Kenna G, Zywiak W, Edwards S, Fricchione S, Taveres T. Baclofen as a novel pharmacotherapy for alcohol dependence: preliminary findings from a human laboratory double‐blind placebo‐controlled randomized study [abstract]. Neuropsychopharmacology 2011;36:Poster #187.
Leggio 2013 {published data only}
References to studies awaiting assessment
Addolorato 2011 {published data only}
- Addolorato G, Leggio L, Ferrulli A, Cardone S, Bedogni G, Caputo F, et al. Dose‐response effect of baclofen in reducing daily alcohol intake in alcohol dependence: secondary analysis of a randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. Alcohol and Alcoholism (Oxford, Oxfordshire) 2011;46(3):312‐7. [DOI: 10.1093/alcalc/agr017] - DOI - PubMed
CTRI/2016/01/006525 {published data only}
- CTRI/2016/01/006525. Role of baclofen and topiramate in alcoholism. ctri.nic.in/Clinicaltrials/pmaindet2.php?trialid=13646 2016.
Farokhnia 2014 {published data only}
- Farokhnia M, Edwards SM, Bollinger J, Amodio J, Zywiak WH, Tidey JW. Baclofen as a pharmacotherapy for the treatment of concurrent alcohol and nicotine dependence: a double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, randomized trial. Neuropsychopharmacology 2014;39:S340. [DOI: 10.1038/npp.2014.281] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Farokhnia M, Edwards SM, Bollinger J, Amodio J, Zywiak WH, Tidey JW, et al. Corrigendum: T76. Baclofen as a pharmacotherapy for the treatment of concurrent alcohol and nicotine dependence: a double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, randomized trial (Neuropsychopharmacology (2014) 39 (S291‐S472) DOI: 10.1038/npp.2014.281). Neuropsychopharmacology 2015;40(6):1560. - PMC - PubMed
Jaury 2014 {published data only}
- Jaury PH. Baclofen for the treatment of alcohol drinkers (Bacloville). Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research 2014;38:215a.
Morley 2013 {published data only}
Sharma 2012 {published data only}
- Sharma V, Sharma R, Chaturvedi M, Bharadwaj B. A dose‐response effect of baclofen in reducing daily alcohol intake in alcohol‐dependent subjects. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2012;27:263. [DOI: 10.1111/jgh.12006] - DOI
References to ongoing studies
CTRI/2011/11/002154 {published data only}
- CTRI/2011/11/002154. Efficacy and safety of baclofen GRS for treatment of alcohol dependence, a 12 week study. ctri.nic.in/Clinicaltrials/pmaindet2.php?trialid=3752 (first received 21 November 2011).
NCT01980706 {published data only}
- NCT01980706. Efficacy and safety of high dose baclofen for alcohol dependence. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01980706 (first received November 11, 2013).
Additional references
Agabio 2007
- Agabio R, Marras P, Addolorato G, Carpiniello B, Gessa GL. Baclofen suppresses alcohol intake and craving for alcohol in a schizophrenic alcohol‐dependent patient: a case report. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 2007;27(3):319‐20. - PubMed
Agabio 2013
- Agabio R, Preti A, Gessa GL. Efficacy and tolerability of baclofen in substance use disorders: a systematic review. European Addiction Research 2013;19(6):325‐45. - PubMed
Agabio 2014
Alonso 2004
- Alonso J, Angermeyer MC, Bernert S, Bruffaerts R, Brugha TS, Bryson H, et al. Prevalence of mental disorders in Europe: results from the European Study of the Epidemiology of Mental Disorders (ESEMeD) project. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica. Supplementum 2004;420:21‐7. - PubMed
Amato 2010
Amato 2011
Ameisen 2005
- Ameisen O. Complete and prolonged suppression of symptoms and consequences of alcohol‐dependence using high‐dose baclofen: a self‐case report of a physician. Alcohol and Alcoholism (Oxford, Oxfordshire) 2005;40(2):147‐50. - PubMed
APA 1980
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 3rd Edition. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association, 1980.
APA 1987
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 3rd Edition. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association, 1987.
APA 2000
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 4th Edition. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association, 2000.
APA 2013
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th Edition. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association, 2013.
Boels 2017
- Boels D, Victorri‐Vigneau C, Grall‐Bronnec M, Touré A, Garnier A, Turcant A, et al. Baclofen and alcohol‐dependent patients: a real risk of severe self‐poisoning. Basic & Clinical Pharmacology & Toxicology 2017;121(4):353‐9. - PubMed
Brennan 2013
Bucknam 2006
- Bucknam W. Suppression of symptoms of alcohol dependence and craving using high‐dose baclofen. Alcohol and Alcoholism 2006;2(42):158‐60. - PubMed
Chick 2012
- Chick J, Nutt DJ. Substitution therapy for alcoholism: time for a reappraisal?. Journal of Psychopharmacology 2012;26(2):205‐12. - PubMed
Colombo 2003
- Colombo G, Vacca G, Serra S, Brunetti G, Carai MA, Gessa GL. Baclofen suppresses motivation to consume alcohol in rats. Psychopharmacology 2003;167(3):221‐4. - PubMed
Covidence [Computer program]
- Veritas Health Innovation. Covidence. Melbourne, Australia: Veritas Health Innovation, accessed 30 January 2018.
Cryan 2005
- Cryan JF, Kaupmann K. Don't worry 'B' happy!: a role for GABA(B) receptors in anxiety and depression. Trends in Pharmacological Sciences 2005;26:36‐43. - PubMed
Dario 2004
- Dario A, Tomei G. A benefit‐risk assessment of baclofen in severe spinal spasticity. Drug Safety 2004;27(11):799‐818. - PubMed
Deeks 2017
- Deeks JJ, Higgins JP, Altman DG (editors) on behalf of the Cochrane Statistical Methods Group. Chapter 9: Analysing data and undertaking meta‐analyses. In: Higgins JPT, Churchill R, Chandler J, Cumpston MS (editors), Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 5.2.0 (updated June 2017), Cochrane, 2017. Available from www.training.cochrane.org/handbook.
Feinn 2005
- Feinn R, Kranzler HR. Does effect size in naltrexone trials for alcohol dependence differ for single‐site vs. multi‐center studies?. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research 2005;29(6):983‐8. - PubMed
Garbutt 2010
Gillman 2007
GRADE 2004
GRADEpro GDT 2015 [Computer program]
- McMaster University (developed by Evidence Prime). GRADEpro GDT. Version accessed 30 January 2018. Hamilton (ON): McMaster University (developed by Evidence Prime), 2015.
Grant 2015
Grant 2017
- Grant BF, Chou SP, Saha TD, Pickering RP, Kerridge BT, Ruan WJ, et al. Prevalence of 12‐month alcohol use, high‐risk drinking, and DSM‐IV alcohol use disorder in the United States, 2001‐2002 to 2012‐2013: results from the National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions. JAMA Psychiatry 2017;74(9):911‐23. - PMC - PubMed
Guyatt 2008
Guyatt 2011
- Guyatt G, Oxman AD, Akl EA, Kunz R, Vist G, Brozek J, et al. GRADE guidelines 1. Introduction‐GRADE evidence profiles and summary of findings tables. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2011;64:383‐94. - PubMed
Hasin 2006
- Hasin D, Hatzenbuehler ML, Keyes K, Ogburn E. Substance use disorders: Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, fourth edition (DSM‐IV) and International Classification of Diseases, tenth edition (ICD‐10). Addiction 2006;101(Suppl 1):59‐75. - PubMed
Hasin 2013
Higgins 2003
Higgins 2011
- Higgins JP, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.handbook.cochrane.org.
Higgins 2017
- Higgins JP, Altman DG, Sterne JA (editors). Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in included studies. In: Higgins JPT, Churchill R, Chandler J, Cumpston MS (editors), Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 5.2.0 (updated June 2017), Cochrane, 2017. Available from www.training.cochrane.org/handbook.
Holla 2015
- Holla B, Gowda GS, Prabhu L, Baby S, Viswanath B, Chand P, et al. High doses of baclofen as suicide attempt in patients with alcohol use disorders ‐ a serious concern. Asian Journal of Psychiatry 2015;17:99‐100. - PubMed
Hróbjartsson 2014
Jorgensen 2011
- Jorgensen CH, Pedersen B, Tonnesen H. The efficacy of disulfiram for the treatment of alcohol use disorder. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research 2011;35:1749‐58. - PubMed
Kagereki 2016
Krupitsky 1993
- Krupitsky EM, Burakov AM, Ivanov VB, Krandashova GF, Lapin IP, Grinenko AJ, et al. Baclofen administration for the treatment of affective disorders in alcoholic patients. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 1993;33(2):157‐63. - PubMed
Lefebvre 2011
- Lefebvre C, Manheimer E, Glanville J. Chapter 6: Searching for studies. In: Higgins JP, Green S, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org.
Leggio 2010
- Leggio L, Garbutt JC, Addolorato G. Effectiveness and safety of baclofen in the treatment of alcohol dependent patients. CNS & Neurological Disorders Drug Targets 2010;9:33‐44. - PubMed
Leone 2010
Lesouef 2014
- Lesouef N, Bellet F, Mounier G, Beyens MN. Efficacy of baclofen on abstinence and craving in alcohol‐dependent patients: a meta‐analysis of randomized controlled trials. Therapie 2014;69(5):427‐35. - PubMed
Liu 2015
Maccioni 2005
- Maccioni P, Serra S, Vacca G, Orrù A, Pes D, Agabio R, et al. Baclofen‐induced reduction of alcohol reinforcement in alcohol‐preferring rats. Alcohol 2005;36(3):161‐8. - PubMed
Maccioni 2009
- Maccioni P, Colombo G. Role of the GABA(B) receptor in alcohol‐seeking and drinking behavior. Alcohol 2009;43(7):555‐8. - PubMed
Maccioni 2012
- Maccioni P, Zaru A, Loi B, Lobina C, Carai MA, Gessa GL, et al. Comparison of the effect of the GABAΒ receptor agonist, baclofen, and the positive allosteric modulator of the GABAB receptor, GS39783, on alcohol self‐administration in 3 different lines of alcohol‐preferring rats. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research 2012;36(10):1748‐66. - PMC - PubMed
Martin‐Fardon 2013
Minozzi 2010
Moher 2009
Moncrieff 2004
Moos 2006
Mutschler 2016
- Mutschler J, Grosshans M, Soyka M, Rösner S. Current findings and mechanisms of action of disulfiram in the treatment of alcohol dependence. Pharmacopsychiatry 2016;49(4):137‐41. - PubMed
Nickerson 1998
- Nickerson RS. Confirmation bias: a ubiquitous phenomenon in many guises. Review of General Psychology 1998;2(2):175‐220.
Pani 2014
Pastor 2012
- Pastor A, Jones D, Currie J. High‐dose baclofen for treatment‐resistant alcohol dependence. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 2012;32:266‐8. - PubMed
Pedersen 2013
- Pedersen B, Askgaard G, Oppedal K. Disulfiram for alcohol use disorder. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2013, Issue 4. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD010487] - DOI
Pellisier 2017
- Pelissier F, Haro L, Cardona F, Picot C, Puskarczyk E, Sapori JM, et al. Self‐poisoning with baclofen in alcohol‐dependent patients: national reports to French Poison Control Centers, 2008‐2013. Clinical Toxicology 2017;55(4):275‐84. - PubMed
Pitman 2014
- Pitman KA, Puil E, Borgland SL. GABA(B) modulation of dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens core. European Journal of Neuroscience 2014;40(10):3472‐80. - PubMed
Rehm 2009
- Rehm J, Mathers C, Popova S, Thavorncharoensap M, Teerawattananon Y, Patra J. Global burden of disease and injury and economic cost attributable to alcohol use and alcohol‐use disorders. Lancet 2009;373(9682):2223‐33. - PubMed
Rehm 2013
- Rehm J, Marmet S, Anderson P, Gual A, Kraus L, Nutt DJ, et al. Defining substance use disorders: do we really need more than heavy use?. Alcohol and Alcoholism 2013;48(6):633‐40. - PubMed
Roerecke 2013
- Roerecke M, Rehm J. Alcohol use disorders and mortality: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Addiction 2013;108(9):1562‐78. - PubMed
Rolland 2013
- Rolland B, Bordet R, Deheul S, Cottencin O. Baclofen for alcohol‐dependence: anticraving or partial substitution?. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 2013;33(2):280‐1. - PubMed
Rose 2018
- Rose AK, Jones A. Baclofen: its effectiveness in reducing harmful drinking, craving, and negative mood. A meta‐analysis. Addiction 2018;113(8):1396‐406. - PubMed
Rösner 2010a
Rösner 2010b
Sarai 2013
Schwarz Pharma 2003
- Schwarz Pharma. Kemstro® (oral baclofen tablets) package insert. Schwarz Pharma, Monheim, Germany 2003.
Schünemann 2006
- Schünemann HJ, Jaeschke R, Cook D, Bria W, El‐Solh A, Ernst A. An official ATS statement: grading the quality of evidence and strength of recommendations in ATS guidelines and recommendations. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2006;174(5):605‐14. - PubMed
Steardo 1984
- Steardo L, Leo A, Marano E. Efficacy of baclofen in trigeminal neuralgia and some other painful conditions. A clinical trial. European Neurology 1984;23(1):51‐5. - PubMed
Sterne 2017
- Sterne JAC, Egger M, Moher D, Boutron I (editors). Chapter 10: Addressing reporting biases. In: Higgins JPT, Churchill R, Chandler J, Cumpston MS (editors), Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 5.2.0 (updated June 2017), Cochrane, 2017. Available fromwww.training.cochrane.org/handbook.
Thompson 2017
- Thompson A, Owens L, Richardson P, Pirmohamed M. Systematic review: baclofen dosing protocols for alcohol use disorders used in observational studies. European Neuropsychopharmacology 2017;27(11):1077‐89. - PubMed
Vaz de Lima 2010
- Vaz de Lima FB, Andriolo RB, Silveira DX. Dopaminergic antagonists for alcohol dependence. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2010, Issue 4. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD003352.pub4] - DOI
Volkow 2011
Walker 2007
White 2015
- White A, Castle IJ, Chen CM, Shirley M, Roach D, Hingson R. Converging patterns of alcohol use and related outcomes among females and males in the United States, 2002 to 2012. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research 2015;39(9):1712‐26. - PubMed
WHO 1992
- World Health Organization. International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, 10th Revision (ICD‐10). Geneva (Switzerland): World Health Organization, 1992.
WHO 2002a
- World Health Organization. The world health report 2002 – Reducing risks to health, promoting healthy life. Geneva: WHO2002.. The World Health Report 2002 – reducing risks, promoting healthy life. Geneva: WHO, 2002.
WHO 2002b
- World Health Organization. Alcohol in developing societies: a public health approach. Geneva: WHO, 2002.
WHO 2010
- World Health Organization. International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems. 4th Edition. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2010.
WHO 2014
- World Health Organization. Global status report on alcohol and health. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2014.
Wilsey 2016
Wise 2009
Young 2014
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical