An Analysis of the Expression and Association with Immune Cell Infiltration of the cGAS/STING Pathway in Pan-Cancer - PubMed (original) (raw)
doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2018.11.003. Epub 2018 Nov 20.
Yuanyuan Zhu 1, Tongsen Zheng 2, Guangyu Wang 2, Minghui Zhang 3, Jiade Li 4, Hongbo Ji 3, Shijun Li 5, Shucai Yang 6, Dandan Xu 7, Zhiwei Li 2, Tianzhen Wang 1, Yan He 1, Lei Zhang 1, Weiwei Yang 1, Ran Zhao 1, Dapeng Hao 8, Xiaobo Li 9
Affiliations
- PMID: 30583098
- PMCID: PMC6305687
- DOI: 10.1016/j.omtn.2018.11.003
An Analysis of the Expression and Association with Immune Cell Infiltration of the cGAS/STING Pathway in Pan-Cancer
Xiang An et al. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2019.
Abstract
Recent evidence shows that cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS)/stimulator of interferon (IFN) genes (STING) signaling is essential for antitumor immunity by inducing the production of type I IFN and thus activating both innate and adaptive immunity based on gene knockout mouse models. However, the extensive detection of the expression of cGAS/STING signaling in human cancer and mining the roles of this signaling pathway in human cancer immunity have not been performed until now. In this study, we revealed that four key molecules (cGAS, STING, TANK binding kinase 1 [TBK1], and IFN regulatory factor 3 [IRF3]) in the cGAS/STING signaling are highly expressed in cancer tissues, and the expression levels of these genes are negatively correlated with their methylation levels in most of the detected cancer types. We also showed that highly upregulated cGAS/STING signaling is negatively correlated with the infiltration of immune cells in some tumor types, and consistent with these findings, we showed that a high level of cGAS/STING signaling predicts a poor prognosis in patients with certain cancers. This study suggests that it is necessary to deeply and fully evaluate the function of cGAS/STING signaling in cancer immunity and cancer progression before the application of the STING agonist-based anticancer immune therapy in the clinic.
Keywords: cGAS/STING; immune infiltration; interferon; methylation; prognosis.
Copyright © 2018 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Graphical abstract
Figure 1
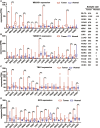
The Expression of the cGAS/STING Pathway in Different Types of Cancer TCGA RNA-seq data were first TPM normalized, and the differential expression was assessed by an unpaired t test to generate a p value. (A) The expression of MB21D1 in pan-cancer. (B) The expression of TMEM173 in pan-cancer. (C) The expression of TBK1 in pan-cancer. (D) The expression of IRF3 in pan-cancer. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001.
Figure 2
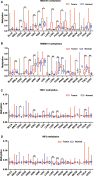
Promoter Methylation Level of the cGAS/STING Pathway in Different Types of Cancer The p value was assessed by an unpaired t test. (A) Methylation level of MB21D1 gene promoter. (B) Methylation level of TMEM173 gene promoter. (C) Methylation level of TBK1 gene promoter. (D) Methylation level of IRF3 gene promoter. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001.
Figure 3
Somatic Mutation Rate of the MB21D1, TMEM173, TBK1, and IRF3 Genes in Various Tumors
Figure 4
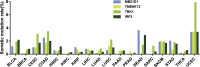
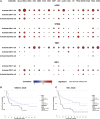
The Correlation between the Expression of cGAS/STING Signaling and the Infiltration of Immune Cells (A) The correlation between the expression of MB21D1, TMEM173, TBK1, IRF3, and the infiltration of activated CD4, CD8 T cell, and DC. Node color is determined by correlation, and node size indicates the significance of correlation. (B) The high expression of TMEM173 predicts a favorable prognosis of metastatic melanoma patients treated with monoclonal antibody against CTLA-4. (C) The high expression of TBK1 indicates a favorable prognosis of metastatic melanoma patients treated with monoclonal antibody against CTLA-4.
Figure 5
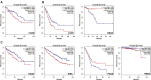
cGAS/STING Pathway Expression as a Prognostic Factor in Various Tumors (A) MB21D1. (B) TBK1. (C) IRF3.
Similar articles
- The cGAS-STING signaling in cardiovascular and metabolic diseases: Future novel target option for pharmacotherapy.
Oduro PK, Zheng X, Wei J, Yang Y, Wang Y, Zhang H, Liu E, Gao X, Du M, Wang Q. Oduro PK, et al. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022 Jan;12(1):50-75. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.05.011. Epub 2021 May 20. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022. PMID: 35127372 Free PMC article. Review. - Radiation Therapy Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Immune Cloaking via PD-L1 Upregulation Induced by cGAS-STING Activation.
Du SS, Chen GW, Yang P, Chen YX, Hu Y, Zhao QQ, Zhang Y, Liu R, Zheng DX, Zhou J, Fan J, Zeng ZC. Du SS, et al. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2022 Apr 1;112(5):1243-1255. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2021.12.162. Epub 2022 Jan 2. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2022. PMID: 34986380 - Association of Abnormal Elevations in IFIT3 With Overactive Cyclic GMP-AMP Synthase/Stimulator of Interferon Genes Signaling in Human Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Monocytes.
Wang J, Dai M, Cui Y, Hou G, Deng J, Gao X, Liao Z, Liu Y, Meng Y, Wu L, Yao C, Wang Y, Qian J, Guo Q, Ding H, Qu B, Shen N. Wang J, et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018 Dec;70(12):2036-2045. doi: 10.1002/art.40576. Epub 2018 Oct 14. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018. PMID: 29806091 - Identification and validation of the prognostic value of cyclic GMP-AMP synthase-stimulator of interferon (cGAS-STING) related genes in gastric cancer.
Yang KS, Xu CQ, Lv J. Yang KS, et al. Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(1):1238-1250. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1911557. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 33843442 Free PMC article. - The role of cGAS-STING signalling in liver diseases.
Chen R, Du J, Zhu H, Ling Q. Chen R, et al. JHEP Rep. 2021 Jun 24;3(5):100324. doi: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2021.100324. eCollection 2021 Oct. JHEP Rep. 2021. PMID: 34381984 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Multi-Omics Data Analysis of Gene Expressions and Alterations, Cancer-Associated Fibroblast and Immune Infiltrations, Reveals the Onco-Immune Prognostic Relevance of STAT3/CDK2/4/6 in Human Malignancies.
Lawal B, Lin LC, Lee JC, Chen JH, Bekaii-Saab TS, Wu ATH, Ho CL. Lawal B, et al. Cancers (Basel). 2021 Feb 25;13(5):954. doi: 10.3390/cancers13050954. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33668805 Free PMC article. - Comprehensive elaboration of the cGAS-STING signaling axis in cancer development and immunotherapy.
Zheng J, Mo J, Zhu T, Zhuo W, Yi Y, Hu S, Yin J, Zhang W, Zhou H, Liu Z. Zheng J, et al. Mol Cancer. 2020 Aug 27;19(1):133. doi: 10.1186/s12943-020-01250-1. Mol Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32854711 Free PMC article. Review. - Loss of the DNA repair protein, polynucleotide kinase/phosphatase, activates the type 1 interferon response independent of ionizing radiation.
Kate WD, Fanta M, Weinfeld M. Kate WD, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Sep 9;52(16):9630-9653. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae654. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 39087523 Free PMC article. - Multi-Omics Immune Interaction Networks in Lung Cancer Tumorigenesis, Proliferation, and Survival.
Ye Q, Hickey J, Summers K, Falatovich B, Gencheva M, Eubank TD, Ivanov AV, Guo NL. Ye Q, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 29;23(23):14978. doi: 10.3390/ijms232314978. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36499305 Free PMC article. - A Bibliometric Analysis of the Innate Immune DNA Sensing cGAS-STING Pathway from 2013 to 2021.
Shi X, Wang S, Wu Y, Li Q, Zhang T, Min K, Feng D, Liu M, Wei J, Zhu L, Mo W, Xiao Z, Yang H, Chen Y, Lv X. Shi X, et al. Front Immunol. 2022 Jun 3;13:916383. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.916383. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35720348 Free PMC article.
References
- Prehn R.T. Tumor specific immunity to nonviral tumors. Proc. Can. Cancer Conf. 1963;5:387–395. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous