Inhibition of TREM-1 attenuates inflammation and lipid accumulation in diet-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2019 Jul;120(7):11867-11877.
doi: 10.1002/jcb.28468. Epub 2019 Feb 25.
Affiliations
- PMID: 30805986
- PMCID: PMC6593463
- DOI: 10.1002/jcb.28468
Inhibition of TREM-1 attenuates inflammation and lipid accumulation in diet-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Shenzong Rao et al. J Cell Biochem. 2019 Jul.
Abstract
In the liver tissues of obese diabetic or nondiabetic patients, triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-1 (TREM-1) is usually found to be upregulated, thus leading to upregulation of various inflammatory cytokines and lipid accumulation. On the other hand, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), characterized by excess lipid accumulation, and inflammatory injury in liver, is becoming an epidemic disease, globally. In the present study, we aimed to investigate the biological role and the underlying mechanisms of TREM-1 in NAFLD. upregulation of TREM-1 occurred in high-fat diet (HFD)-induced mice NAFLD model and oleic acid-treated HepG2 and primary mouse hepatocytes cell model at messenger RNA and protein levels. Functional studies established that overexpression of TREM-1 displayed hyperlipidemia, and increased in inflammatory indicators and lipid accumulation-related genes, which was ameliorated by knockdown of TREM-1. Our results also showed that obvious lipid accumulation and inflammatory injury occurred in the liver tissue of HFD-fed mice, while treatment with lentiviral vector short hairpin TREM showed marked improvement in tissue morphology and architecture and less lipid accumulation, thus deciphering the mechanism through which knockdown of TREM-1 ameliorated the inflammatory response and lipid accumulation of NAFLD mice through inactivation of the nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) and PI3K/AKT signal pathways, respectively. In conclusion, TREM-1/NF-κB and TREM-1/PI3K/AKT axis could be an important mechanism in ameliorating the inflammatory response and lipid accumulation, respectively, thus shedding light on the development of novel therapeutics to the treatment of NAFLD.
Keywords: TREM-1; inflammation; lipid accumulation; nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
© 2019 The Authors. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interests.
Figures
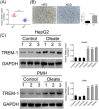
Figure 1
TREM‐1 was part of physiological response to lipotoxicity in NAFLD. A, qRT‐PCR analysis of TREM‐1 in the livers of HFD‐fed vs NCD‐fed mice. B, Immunohistochemistry analysis of TREM‐1 in the livers of HFD‐fed vs NCD‐fed mice. C, Western blot analysis of TREM‐1 in the OA‐induced HepG2/PMH vs control cells. ***P < 0.001. GAPDH, glyceraldehyde 3‐phosphate dehydrogenase; HFD, high‐fat diet; NAFLD, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; NCD, normal control diet; OA, oleic acid; PMH, primary mouse hepatocytes; qRT‐PCR, quantitative reverse‐transcription polymerase chain reaction; TREM‐1, triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells‐1
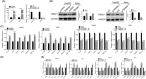
Figure 2
TREM‐1 regulated inflammatory cytokines and lipid accumulation. qRT‐PCR analysis of TREM‐1 mRNA in stable cell lines of HepG2 and PMH treated with OA that either overexpression or knockdown of TREM‐1. Western blot analysis of TREM‐1 protein in stable cell lines of HepG2 and PMH treated with OA that either overexpression or knockdown of TREM‐1. qRT‐PCR analysis of IL‐1β, IL‐6, TNF‐α, IFN‐γ, MCP‐1, and MIP‐1α mRNA in stable cell lines of HepG2 and PMH treated with OA that either overexpression or knockdown of TREM‐1. Oil Red O staining of HepG2 and PMH cells treated with OA that either overexpression or knockdown of TREM‐1. qRT‐PCR analysis of MSR1, LDLR, ABCA1, ABCG1, NPC1/2, and STARD4 mRNA in stable cell lines of HepG2 and PMH treated with OA that either overexpression or knockdown of TREM‐1. **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001. ABCA1, ATP‐binding cassette transporter‐1; ABCG1, ATP‐binding cassette sub‐family G member 1; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde 3‐phosphate dehydrogenase; HFD, high‐fat diet; IFN, interferon; IL, interleukin; LDLR, low‐density lipoprotein receptor; MCP‐1, monocyte chemoattractant protein‐1; MIP‐1α, macrophage inflammatory protein‐1α; mRNA, messenger RNA; MSR1, macrophage scavenger receptor 1; NAFLD, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; NC, negative control; NCD, normal control diet; NPC1, Niemann‐Pick disease, type C1; NPC2, NPC intracellular cholesterol transporter 2; OA, oleic acid; PMH, primary mouse hepatocytes; qRT‐PCR, quantitative reverse‐transcription polymerase chain reaction; siNC, small interfering negative control; STARD4, StAR‐related lipid transfer protein 4; TNF‐α, tumor necrosis factor‐α; TREM‐1, triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells‐1
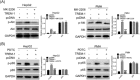
Figure 3
TREM‐1 is a positive regulator of OA‐induced PI3K/AKT and NF‐κB activation. The effect of AKT inhibitor MK‐2206 and TREM‐1 overexpression on expression of AKT and p‐AKT in both HepG2 and PMH cells was detected by Western blot analysis. The effect of NF‐κB inhibitor PDTC and TREM‐1 overexpression on expression of p65 and p‐p65 in both HepG2 and PMH cells was detected by Western blot analysis. ***P < 0.001 and ### P < 0.001. GAPDH, glyceraldehyde 3‐phosphate dehydrogenase; NF‐κB, nucleear factor‐κB; PDTC, pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate; PMH, primary mouse hepatocytes; TREM‐1, triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells‐1
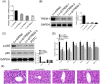
Figure 4
Knockdown of TREM‐1 alleviates inflammation in HFD‐fed mice via regulating NF‐κB. qRT‐PCR analysis of TREM‐1 mRNA in HFD‐fed mice injected with supernatant in cell culture of shTREMs (Lv‐shTREMs) that knockdown of TREM‐1. Western blot analysis of TREM‐1 protein in HFD‐fed mice injected with supernatant in cell culture of shTREMs (Lv‐shTREMs) that knockdown of TREM‐1. The effect of NF‐κB inhibitor PDTC and Lv‐shTREMs on expression of p65 and p‐p65 in HFD‐fed mice was detected by Western blot analysis. qRT‐PCR analysis of IL‐1β, IL‐6, TNF‐α, IFN‐γ, MCP‐1 and MIP‐1α mRNA in HFD‐fed mice injected with Lv‐shTREMs that knockdown of TREM‐1. H&E staining analysis of the effect of NF‐κB inhibitor PDTC and Lv‐shTREMs on tissue morphology and architecture in HFD‐fed mice. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001. GAPDH, glyceraldehyde 3‐phosphate dehydrogenase; HFD, high‐fat diet; H&E, hematoxylin and eosin; IFN‐γ, interferon‐γ; IL, interleukin; Lv, lentiviral vector; MCP‐1, monocyte chemoattractant protein‐1; MIP‐1α, macrophage inflammatory protein‐1α; mRNA, messenger RNA; PDTC, pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate; PMH, primary mouse hepatocytes; qRT‐PCR, quantitative reverse‐transcription polymerase chain reaction; shTREM, short hairpin RNAs of TREM‐1; TNF‐α, tumor necrosis factor‐α; TREM‐1, triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells‐1
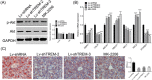
Figure 5
Knockdown of TREM‐1 alleviates lipid accumulation in HFD‐fed mice via regulating PI3K/AKT. The effect of AKT inhibitor MK‐2206 and Lv‐shTREMs on expression of AKT and p‐AKT in HFD‐fed mice was detected by Western blot analysis. qRT‐PCR analysis of MSR1, LDLR, ABCA1, ABCG1, NPC1/2 and STARD4 mRNA in HFD‐fed mice injected with Lv‐shTREMs that knockdown of TREM‐1.Oil Red O staining of liver tissues of HFD‐fed mice treated with MK‐2206 and Lv‐shTREMs. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001. ABCA1, ATP‐binding cassette transporter‐1; ABCG1, ATP‐binding cassette sub‐family G member 1; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde 3‐phosphate dehydrogenase; HFD, high‐fat diet; LDLR, low‐density lipoprotein receptor; Lv, lentiviral vector; mRNA, messenger RNA; MSR1, macrophage scavenger receptor 1; NPC1, Niemann‐Pick disease, type C1; NPC2, NPC intracellular cholesterol transporter 2; qRT‐PCR, quantitative reverse‐transcription polymerase chain reaction; shTREM, short hairpin RNAs of TREM‐1; STARD4, StAR‐related lipid transfer protein 4; TREM‐1, triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells‐1
Similar articles
- Allyl isothiocyanate ameliorates lipid accumulation and inflammation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease via the Sirt1/AMPK and NF-κB signaling pathways.
Li CX, Gao JG, Wan XY, Chen Y, Xu CF, Feng ZM, Zeng H, Lin YM, Ma H, Xu P, Yu CH, Li YM. Li CX, et al. World J Gastroenterol. 2019 Sep 14;25(34):5120-5133. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i34.5120. World J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 31558861 Free PMC article. - Antrodia cinnamomea and its compound dehydroeburicoic acid attenuate nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by upregulating ALDH2 activity.
Cao YN, Yue SS, Wang AY, Xu L, Hu YT, Qiao X, Wu TY, Ye M, Wu YC, Qi R. Cao YN, et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Jun 28;292:115146. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115146. Epub 2022 Mar 16. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35304272 - Systemic Overexpression of GDF5 in Adipocytes but Not Hepatocytes Alleviates High-Fat Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver in Mice.
Yang Y, Zhang W, Wu X, Wu J, Sun C, Luo F, Pei Z. Yang Y, et al. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021 Jan 15;2021:8894685. doi: 10.1155/2021/8894685. eCollection 2021. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 33542911 Free PMC article. - Psoralea corylifolia L. extract ameliorates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in free-fatty-acid-incubated HEPG2 cells and in high-fat diet-fed mice.
Hong Y, Choi SI, Hong E, Kim GH. Hong Y, et al. J Food Sci. 2020 Jul;85(7):2216-2226. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.15166. Epub 2020 Jun 24. J Food Sci. 2020. PMID: 32579753
Cited by
- Soluble TREM-1, as a new ligand for the membrane receptor Robo2, promotes hepatic stellate cells activation and liver fibrosis.
Liu T, Chen S, Xie X, Liu H, Wang Y, Qi S, Shi L, Zhou X, Zhang J, Wang S, Wang Y, Chen S, Dou S, Jiang X, Cui R, Jiang H. Liu T, et al. J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Dec;25(24):11113-11127. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17033. Epub 2021 Nov 9. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34750987 Free PMC article. - TREM-1 deficiency attenuates the inflammatory responses in LPS-induced murine endometritis.
Zhu H, Li W, Wang Z, Chen J, Ding M, Han L. Zhu H, et al. Microb Biotechnol. 2019 Nov;12(6):1337-1345. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.13467. Epub 2019 Jul 31. Microb Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 31365951 Free PMC article. - NF-κB p65 regulates hepatic lipogenesis by promoting nuclear entry of ChREBP in response to a high carbohydrate diet.
Daniel PV, Dogra S, Rawat P, Choubey A, Khan AS, Rajak S, Kamthan M, Mondal P. Daniel PV, et al. J Biol Chem. 2021 Jan-Jun;296:100714. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100714. Epub 2021 Apr 27. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33930463 Free PMC article. - Transcriptomics Reveals Discordant Lipid Metabolism Effects between In Vitro Models Exposed to Elafibranor and Liver Samples of NAFLD Patients after Bariatric Surgery.
Boeckmans J, Gatzios A, Heymans A, Rombaut M, Rogiers V, De Kock J, Vanhaecke T, Rodrigues RM. Boeckmans J, et al. Cells. 2022 Mar 4;11(5):893. doi: 10.3390/cells11050893. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35269515 Free PMC article. - HIV and HCV augments inflammatory responses through increased TREM-1 expression and signaling in Kupffer and Myeloid cells.
Hyun J, McMahon RS, Lang AL, Edwards JS, Badilla AD, Greene ME, Stone GW, Pallikkuth S, Stevenson M, Dykxhoorn DM, Kottilil S, Pahwa S, Thomas E. Hyun J, et al. PLoS Pathog. 2019 Jul 1;15(7):e1007883. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007883. eCollection 2019 Jul. PLoS Pathog. 2019. PMID: 31260499 Free PMC article.
References
- French SW, Takahashi H, Wong K, Mendenhall CL. Ito cell activation induced by chronic ethanol feeding in the presence of different dietary fats. Alcohol Alcohol Suppl. 1991;1:357‐361. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources