Efficacy of a nutraceutical combination on lipid metabolism in patients with metabolic syndrome: a multicenter, double blind, randomized, placebo controlled trial - PubMed (original) (raw)
Randomized Controlled Trial
doi: 10.1186/s12944-019-1002-y.
Valeria Fazio [ 2](#full-view-affiliation-2 "Department of Clinical Medicine and Surgery, ESH Excellence Centre of Hypertension, "Federico II" University of Naples Medical School, Naples, Italy."), Marco Gentile [ 2](#full-view-affiliation-2 "Department of Clinical Medicine and Surgery, ESH Excellence Centre of Hypertension, "Federico II" University of Naples Medical School, Naples, Italy."), Giuseppe Schillaci 3, Giacomo Pucci 3, Francesca Battista 3, Valentina Mercurio [ 4](#full-view-affiliation-4 "Department of Translational Medical Sciences, "Federico II" University of Naples Medical School, Naples, Italy."), Giorgio Bosso [ 4](#full-view-affiliation-4 "Department of Translational Medical Sciences, "Federico II" University of Naples Medical School, Naples, Italy."), Domenico Bonaduce [ 4](#full-view-affiliation-4 "Department of Translational Medical Sciences, "Federico II" University of Naples Medical School, Naples, Italy."), Nadia Brambilla 5, Cristina Vitalini 5, Massimo D'Amato 5, Giampaolo Giacovelli 5
Affiliations
- PMID: 30885221
- PMCID: PMC6421674
- DOI: 10.1186/s12944-019-1002-y
Randomized Controlled Trial
Efficacy of a nutraceutical combination on lipid metabolism in patients with metabolic syndrome: a multicenter, double blind, randomized, placebo controlled trial
Ferruccio Galletti et al. Lipids Health Dis. 2019.
Abstract
Background: Nutraceuticals represent a new therapeutic frontier in the treatment of metabolic syndrom (MetS) and related cardiovascular risk factors. The aim of this study was to evaluate the potential beneficial effects of Armolipid Plus (AP) (berberine 500 mg, red yest rice, monacolin K 3 mg and policosanol 10 mg) on insulin resistance, lipid profile, particularly on small and dense LDL cholesterol (sdLDL-C), representing the most atherogenic components, as well as its effects on high sensitivity C-reactive protein, a notable marker of cardiovascular risk, blood pressure and cardiac remodeling in subjects affected by MetS, with left ventricular hypertrophy.
Methods: The study was a prospective, multi-center, randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled trial. One hundred and fifty eight patients, aged between 28 and 76 years old, were enrolled and randomized to receive either one tablet of AP or placebo (PL) once daily for 24 weeks. Anthropometric and vital parameters, total cholesterol (tot-C), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), triglyceridemia (TG), non-HDL cholesterol (NHDL-C) and sdLDL-C were evaluated.
Results: After 24 weeks of treatment, the analysis performed on 141 subjects (71 in AP arm and 70 in PL arm), showed a significant improvement of lipid profile in the AP group, with reduction in tot-C (- 13.2 mg/dl), LDL-C (- 13.9 mg/dl) and NHDL-C (- 15.3 mg/dl) and increase in HDL-C (+ 2.0 mg/dl). These changes were equally significant compared with placebo (tot-C: AP - 13.2 mg/dL vs PL + 2.7 mg/dL, p < 0.01; LDL-C: AP -13.9 mg/dl vs PL + 1.5 mg/dl, p < 0.01; NHDL-C: AP -15.3 mg/dl vs PL + 2.8 mg/dl, p < 0.01), Although no significant difference was observed between the two arms in the reduction of HDL-C nevertheless it increased significantly in the AP group (AP + 2 mg/dL p < 0.05, PL 0.13 mg/dL).
Conclusion: The results of this study, applicable to a specific local population show that, in a population of subjects affected by MetS, treatment with AP improves the lipid profile and the most atherogenic factors, thus suggesting a reduction in the risk of development and progression of atherosclerosis, particularly in subjects with high atherogenic risk, due to the presence of sdLDL-C.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The Institutional Ethics Committee of each site approved the study protocol before initiating any trial related activity, and written informed consent was obtained from each patient. The study was conducted in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Consent for publication
None of the authors has financial relations (personal and institutional) that might be a potential conflict of interest.
All co-authors have read and approved the submission of this manuscript; the content of the manuscript has not been published and is not being considered for publication elsewhere.
Competing interest
The study was sponsored by Rottapharm SpA, Monza Italy.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
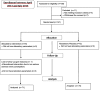
Fig. 1
Study flow diagram
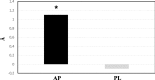
Fig. 2
Changes in sdLDL-C size at wk. 24. * = p < 0.05 24 wks vs Baseline
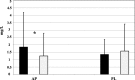
Fig. 3
CRP-Hs levels after 24 weeks of treatment.  = AP,
= AP,  = PL Treatment. * = p < 0.05 24 wks vs Baseline
= PL Treatment. * = p < 0.05 24 wks vs Baseline
Similar articles
- Nutraceutical approach to moderate cardiometabolic risk: results of a randomized, double-blind and crossover study with Armolipid Plus.
Ruscica M, Gomaraschi M, Mombelli G, Macchi C, Bosisio R, Pazzucconi F, Pavanello C, Calabresi L, Arnoldi A, Sirtori CR, Magni P. Ruscica M, et al. J Clin Lipidol. 2014 Jan-Feb;8(1):61-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jacl.2013.11.003. Epub 2013 Nov 11. J Clin Lipidol. 2014. PMID: 24528686 Clinical Trial. - A nutraceutical combination reduces left ventricular mass in subjects with metabolic syndrome and left ventricular hypertrophy: A multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.
Mercurio V, Pucci G, Bosso G, Fazio V, Battista F, Iannuzzi A, Brambilla N, Vitalini C, D'Amato M, Giacovelli G, Vaudo G, Schillaci G, Galletti F, Bonaduce D. Mercurio V, et al. Clin Nutr. 2020 May;39(5):1379-1384. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2019.06.026. Epub 2019 Jul 19. Clin Nutr. 2020. PMID: 31371114 Clinical Trial. - Nutraceutical approach for the management of cardiovascular risk - a combination containing the probiotic Bifidobacterium longum BB536 and red yeast rice extract: results from a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study.
Ruscica M, Pavanello C, Gandini S, Macchi C, Botta M, Dall'Orto D, Del Puppo M, Bertolotti M, Bosisio R, Mombelli G, Sirtori CR, Calabresi L, Magni P. Ruscica M, et al. Nutr J. 2019 Feb 22;18(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s12937-019-0438-2. Nutr J. 2019. PMID: 30795775 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Pitavastatin: novel effects on lipid parameters.
Chapman MJ. Chapman MJ. Atheroscler Suppl. 2011 Nov;12(3):277-84. doi: 10.1016/S1567-5688(11)70887-X. Atheroscler Suppl. 2011. PMID: 22152282 Review. - The effects of a nutraceutical combination on plasma lipids and glucose: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.
Pirro M, Mannarino MR, Bianconi V, Simental-Mendía LE, Bagaglia F, Mannarino E, Sahebkar A. Pirro M, et al. Pharmacol Res. 2016 Aug;110:76-88. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2016.04.021. Epub 2016 May 6. Pharmacol Res. 2016. PMID: 27157250 Review.
Cited by
- The Role of Nutraceutical Supplements, Monacolin K and Astaxanthin, and Diet in Blood Cholesterol Homeostasis in Patients with Myopathy.
Villano I, La Marra M, Allocca S, Ilardi CR, Polito R, Porro C, Chieffi S, Messina G, Monda V, Di Maio G, Messina A. Villano I, et al. Biomolecules. 2022 Aug 14;12(8):1118. doi: 10.3390/biom12081118. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36009012 Free PMC article. - Novel Pharmaceutical and Nutraceutical-Based Approaches for Cardiovascular Diseases Prevention Targeting Atherogenic Small Dense LDL.
Vekic J, Zeljkovic A, Stefanovic A, Bogavac-Stanojevic N, Ilias I, Silva-Nunes J, Stoian AP, Janez A, Rizzo M. Vekic J, et al. Pharmaceutics. 2022 Apr 9;14(4):825. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14040825. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35456658 Free PMC article. Review. - Phenolic Compounds of Propolis Alleviate Lipid Metabolism Disorder.
Kong L, Zhang Y, Feng Z, Dong J, Zhang H. Kong L, et al. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Feb 20;2021:7615830. doi: 10.1155/2021/7615830. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 33688365 Free PMC article. - Efficacy and Safety of Armolipid Plus®: An Updated PRISMA Compliant Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Clinical Trials.
Cicero AFG, Kennedy C, Knežević T, Bove M, Georges CMG, Šatrauskienė A, Toth PP, Fogacci F. Cicero AFG, et al. Nutrients. 2021 Feb 16;13(2):638. doi: 10.3390/nu13020638. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 33669333 Free PMC article. - The beneficial effects of nutraceuticals and natural products on small dense LDL levels, LDL particle number and LDL particle size: a clinical review.
Talebi S, Bagherniya M, Atkin SL, Askari G, Orafai HM, Sahebkar A. Talebi S, et al. Lipids Health Dis. 2020 Apr 11;19(1):66. doi: 10.1186/s12944-020-01250-6. Lipids Health Dis. 2020. PMID: 32276631 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Lamarche B, Tchernof A, Moorjani S, Cantin B, Dagenais GR, Lupien PJ, Despres JP. Small, dense low-density lipoprotein particles as a predictor of the risk of ischemic heart disease in men. Prospective results from the Quebec cardiovascular study. Circulation. 1997;95:69–75. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.95.1.69. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous