A pan-coronavirus fusion inhibitor targeting the HR1 domain of human coronavirus spike - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2019 Apr 10;5(4):eaav4580.
doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aav4580. eCollection 2019 Apr.
Lei Yan 2, Wei Xu 1, Anurodh Shankar Agrawal 3, Abdullah Algaissi 3 4, Chien-Te K Tseng 3, Qian Wang 1, Lanying Du 5, Wenjie Tan 6, Ian A Wilson 2 7, Shibo Jiang 1 5, Bei Yang 2, Lu Lu 1
Affiliations
- PMID: 30989115
- PMCID: PMC6457931
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aav4580
A pan-coronavirus fusion inhibitor targeting the HR1 domain of human coronavirus spike
Shuai Xia et al. Sci Adv. 2019.
Abstract
Continuously emerging highly pathogenic human coronaviruses (HCoVs) remain a major threat to human health, as illustrated in past SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV outbreaks. The development of a drug with broad-spectrum HCoV inhibitory activity would address this urgent unmet medical need. Although previous studies have suggested that the HR1 of HCoV spike (S) protein is an important target site for inhibition against specific HCoVs, whether this conserved region could serve as a target for the development of broad-spectrum pan-CoV inhibitor remains controversial. Here, we found that peptide OC43-HR2P, derived from the HR2 domain of HCoV-OC43, exhibited broad fusion inhibitory activity against multiple HCoVs. EK1, the optimized form of OC43-HR2P, showed substantially improved pan-CoV fusion inhibitory activity and pharmaceutical properties. Crystal structures indicated that EK1 can form a stable six-helix bundle structure with both short α-HCoV and long β-HCoV HR1s, further supporting the role of HR1 region as a viable pan-CoV target site.
Figures
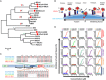
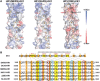
Fig. 1. HR1P and HR2P fusion inhibitory activity.
(A) Maximum likelihood trees created with the S sequence of representative CoVs from all four genogroups. HCoVs are denoted with filled red circles. (B) The antiviral mechanism of HR2P peptides. (C) Schematic representation of HCoV S protein. SP, signal peptide; FP, fusion peptide; HR, heptad repeat domain (HR1 and HR2); TM, transmembrane domain; CP, cytoplasmic domain. Corresponding sequences of the designed peptides (HR1Ps and HR2Ps). (D) HR2P peptides potently inhibit cell-cell fusion mediated by the S proteins of MERS-CoV, SARS-CoV, 229E, NL63, and OC43. Data are means ± SD of triplicate samples from a representative experiment.
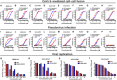
Fig. 2. EK1 is effective against viral infection mediated by S protein of multiple HCoVs.
(A to H) Inhibitory activity of EK1 in cell-cell fusion mediated by the S proteins of MERS-CoV (A), SARS-CoV (B), 229E (C), NL63 (D), OC43 (E), Rs3367 (F), WIV1 (G), and SHC014 (H). (I to P) Inhibitory activity of EK1 in pseudovirus infection assays against MERS-CoV (I), SARS-CoV (J), 229E (K), NL63 (L), OC43 (M), Rs3367 (N), WIV1 (O), and VSV (P). (Q to T) Inhibitory activity of EK1 on live HCoV replication for MERS-CoV (Q), OC43 (R), 229E (S), and NL63 (T). Data are means ± SD of triplicate samples from a representative experiment.
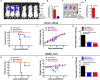
Fig. 3. In vivo prophylactic and therapeutic efficacy of EK1 in mice against OC43 and MERS-CoV infection.
(A and B) Imaging of mice treated with Cy5-EK1 or PBS by the IVIS Lumina K Series III from PerkinElmer and the statistical analysis. (C and D) Imaging of lungs from those mice with the statistical analysis. (E to G) Anti–OC43 efficacy of EK1 in vivo. Survival curves of 3-day-old suckling mice challenged with OC43. (E) Newborn mice were treated with EK1 (5 mg/kg in PBS) or PBS 30 min before or after challenge with OC43 (102 TCID50). (F) Body weight change of newborn mice treated with EK1 or PBS 30 min before and after OC43 challenge. (G) Viral titer in mouse brain of each group. (H to J) Anti–MERS-CoV efficacy of EK1 in vivo. Survival curves of mice challenged with MERS-CoV. (H) Mice expressing human DPP4 were treated with 200 μg EK1 in PBS or PBS 30 min before or after challenge with MERS-CoV (104 TCID50). (I) Body weight change of each group of mice. (J) Viral titer in mouse lungs of each group. SD of triplicate samples from a representative experiment; *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001.
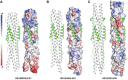
Fig. 4. Interaction of EK1 with HCoV.
Side-by-side ribbon diagram and electrostatic surface representations illustrate that EK1 snugly fits into the hydrophobic groves formed between two adjacent HR1 helices of the 3HR1 core from MERS-CoV (A), SARS-CoV (B), and 229E (C). The EK1 peptide is shown as a green on white ribbon (left) and electrostatic (right) representations of corresponding HCoV 3HR1 cores. Hydrophobic surfaces are in whitish gray, basic in blue, and acidic in red.
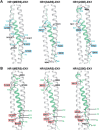
Fig. 5. Hydrophobic packing between EK1 and 3HR1 hydrophobic cores are largely conserved across different EK1-HR1 complexes.
(A) The 3HR1 cores are shown as electrostatic surfaces. At the positions where the hydrophobic surface on the 3HR1 core is deeply concave (pockets), EK1 residues that bury over 70% of their side-chain solvent accessible surface (SAS) into these pockets are shown as orange stick models. At the locations where the hydrophobic surface on the 3HR1 core is relatively flat (ridges), EK1 residues that pack 50 to 70% of their side-chain SAS against these ridges are shown as light yellow stick models. EK1 residues are labeled, where those labeled in red form both hydrophobic and hydrophilic interactions with 3HR1 cores. (B) HR1 residues involved in interactions with EK1 are conserved across different HCoVs. EK1 and HR1 residues linked with dashed lines locate to the same layers on the 3HR1 triple helix. Burying EK1 residues are shaded orange, and ridge-packing EK1 residues are shaded light yellow. HR1 residues that mediate assembly of the 3HR1 cores are shaded orange, while those involved in ridge packing are shaded yellow. HR1 residues that mediate conserved side chain–to–side chain and side chain–to–main chain hydrophilic interactions with EK1 residues are highlighted with cyan and red boxes, respectively.
Fig. 6. Highly conserved hydrophilic interactions between EK1 and 3HR1 cores.
(A) Side chain–to–side chain hydrophilic interactions between EK1 and HR1. Side chains of EK1 and HR1 residues involved in these interactions are shown as cyan and gray stick models, respectively, and are similarly color-coded. At least four pairs of this hydrophilic interaction are conserved across different EK1-HR1 complexes: Y30EK1 forms similar polar interactions with Q1009MERS (left), Q917SARS (middle), or T817229E (right); E27EK1 forms similar polar interactions with Q1009MERS (left), Q917SARS (middle), or S820229E (right); E15EK1 forms salt bridges with K1021MERS (left), K929SARS (middle), or K832229E (right); and T8EK1 makes similar interactions with N1028MERS (left), Q936SARS (middle), or Q839229E (right). The conserved HR1 residues mentioned above are highlighted with cyan boxes. (B) Main chain–to–side chain hydrophilic interactions between EK1 and HR1. EK1 and HR1 residues involved in these interactions are shown as green and gray stick models, respectively. The main-chain atoms of HR1 residues are not shown for clarity. Similar to the side chain–to–side chain interactions, main chain–to–side chain interactions are also highly conserved across different EK1-HR1 complexes. The HR1 residues involved in conserved interactions are highlighted with red boxes.
Similar articles
- Peptide-Based Membrane Fusion Inhibitors Targeting HCoV-229E Spike Protein HR1 and HR2 Domains.
Xia S, Xu W, Wang Q, Wang C, Hua C, Li W, Lu L, Jiang S. Xia S, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Feb 6;19(2):487. doi: 10.3390/ijms19020487. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29415501 Free PMC article. - Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 (previously 2019-nCoV) infection by a highly potent pan-coronavirus fusion inhibitor targeting its spike protein that harbors a high capacity to mediate membrane fusion.
Xia S, Liu M, Wang C, Xu W, Lan Q, Feng S, Qi F, Bao L, Du L, Liu S, Qin C, Sun F, Shi Z, Zhu Y, Jiang S, Lu L. Xia S, et al. Cell Res. 2020 Apr;30(4):343-355. doi: 10.1038/s41422-020-0305-x. Epub 2020 Mar 30. Cell Res. 2020. PMID: 32231345 Free PMC article. - A Modified Fibronectin Type III Domain-Conjugated, Long-Acting Pan-Coronavirus Fusion Inhibitor with Extended Half-Life.
Duan Q, Xia S, Jiao F, Wang Q, Wang R, Lu L, Jiang S, Xu W. Duan Q, et al. Viruses. 2022 Mar 22;14(4):655. doi: 10.3390/v14040655. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35458385 Free PMC article. - [Development of peptidic MERS-CoV entry inhibitors].
Xia S, Wang Q, Liu SW, Lu L, Jiang SB. Xia S, et al. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2015 Dec;50(12):1513-9. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2015. PMID: 27169270 Review. Chinese. - Active site-based analysis of structural proteins for drug targets in different human Coronaviruses.
Ahmadi K, Zahedifard F, Mafakher L, Ali Einakian M, Ghaedi T, Kavousipour S, Faezi S, Karmostaji A, Sharifi-Sarasiabi K, Gouklani H, Hassaniazad M. Ahmadi K, et al. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2022 Apr;99(4):585-602. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.14004. Epub 2022 Feb 1. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2022. PMID: 34914204 Review.
Cited by
- Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 Entry: Current and Future Opportunities.
Xiu S, Dick A, Ju H, Mirzaie S, Abdi F, Cocklin S, Zhan P, Liu X. Xiu S, et al. J Med Chem. 2020 Nov 12;63(21):12256-12274. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c00502. Epub 2020 Jun 25. J Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32539378 Free PMC article. Review. - Effects of Single α-to-β Residue Replacements on Recognition of an Extended Segment in a Viral Fusion Protein.
Outlaw VK, Kreitler DF, Stelitano D, Porotto M, Moscona A, Gellman SH. Outlaw VK, et al. ACS Infect Dis. 2020 Aug 14;6(8):2017-2022. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.0c00385. Epub 2020 Jul 27. ACS Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32692914 Free PMC article. - Unlocking COVID therapeutic targets: A structure-based rationale against SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV Spike.
Trigueiro-Louro J, Correia V, Figueiredo-Nunes I, Gíria M, Rebelo-de-Andrade H. Trigueiro-Louro J, et al. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2020 Jul 31;18:2117-2131. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2020.07.017. eCollection 2020. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2020. PMID: 32913581 Free PMC article. - The recent outbreaks of human coronaviruses: A medicinal chemistry perspective.
Pillaiyar T, Wendt LL, Manickam M, Easwaran M. Pillaiyar T, et al. Med Res Rev. 2021 Jan;41(1):72-135. doi: 10.1002/med.21724. Epub 2020 Aug 27. Med Res Rev. 2021. PMID: 32852058 Free PMC article. Review. - Clinical and Analytical Performance of an Automated Serological Test That Identifies S1/S2-Neutralizing IgG in COVID-19 Patients Semiquantitatively.
Bonelli F, Sarasini A, Zierold C, Calleri M, Bonetti A, Vismara C, Blocki FA, Pallavicini L, Chinali A, Campisi D, Percivalle E, DiNapoli AP, Perno CF, Baldanti F. Bonelli F, et al. J Clin Microbiol. 2020 Aug 24;58(9):e01224-20. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01224-20. Print 2020 Aug 24. J Clin Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32580948 Free PMC article.
References
- Woo P. C. Y., Lau S. K. P., Lam C. S. F., Lau C. C. Y., Tsang A. K. L., Lau J. H. N., Bai R., Teng J. L. L., Tsang C. C. C., Wang M., Zheng B.-J., Chan K.-H., Yuen K.-Y., Discovery of seven novel mammalian and avian coronaviruses in the genus Deltacoronavirus supports bat coronaviruses as the gene source of Alphacoronavirus and Betacoronavirus and avian coronaviruses as the gene source of Gammacoronavirus and Deltacoronavirus. J. Virol. 86, 3995–4008 (2012). - PMC - PubMed
- Morfopoulou S., Brown J. R., Davies E. G., Anderson G., Virasami A., Qasim W., Chong W. K., Hubank M., Plagnol V., Desforges M., Jacques T. S., Talbot P. J., Breuer J., Human coronavirus OC43 associated with fatal encephalitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 375, 497–498 (2016). - PubMed
- Mayer K., Nellessen C., Hahn-Ast C., Schumacher M., Pietzonka S., Eis-Hübinger A. M., Drosten C., Brossart P., Wolf D., Fatal outcome of human coronavirus NL63 infection despite successful viral elimination by IFN-alpha in a patient with newly diagnosed ALL. Eur. J. Haematol. 97, 208–210 (2016). - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous