Quality and Authenticity Control of Functional Red Yeast Rice-A Review - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Quality and Authenticity Control of Functional Red Yeast Rice-A Review
Jiawen Song et al. Molecules. 2019.
Abstract
Red yeast rice (RYR) is made by fermenting the rice with Monascus. It is commonly used in food colorants, dyeing, and wine making in China and its neighboring countries. Nowadays RYR has two forms on the market: common RYR is used for food products, the other form is functional RYR for medicine. However, some researchers reported that commercial lovastatin (structure is consistent with monacolin K) is illegally added to common RYR to meet drug quality standards, so as to imitate functional RYR and sell the imitation at a higher price. Based on current detection methods, it is impossible to accurately distinguish whether functional RYR is adulterated. Therefore, it is especially important to find a way to authenticate functional RYR. In the current review, the advances in history, applications, components (especially monacolins, monacolins detection methods), quality standards, authentication methods and perspectives for the future study of RYR are systematically reviewed.
Keywords: authentication methods; detection methods; functional RYR; monacolin K; quality standards.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
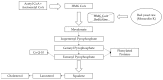
Figure 1
The two structures of monacolin K. (a) the lactone form; (b) the acid form.
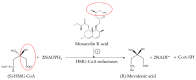
Figure 2
RYR effects on cholesterol biosynthesis.
Figure 3
The HMG-CoA reductase reaction and the competitive inhibition of monacolin K acid.
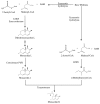
Figure 4
The biosynthetic pathway of Monacolin K. Abbreviations: SAM, S_-Adenosyl methionine; R, 2-[(2_R,4_R_)-4-hydroxy-6-oxo-2-tetrahydropyranyl]-ethyl.
Similar articles
- Chemical profiling and quantification of monacolins and citrinin in red yeast rice commercial raw materials and dietary supplements using liquid chromatography-accurate QToF mass spectrometry: Chemometrics application.
Avula B, Cohen PA, Wang YH, Sagi S, Feng W, Wang M, Zweigenbaum J, Shuangcheng M, Khan IA. Avula B, et al. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2014 Nov;100:243-253. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2014.07.039. Epub 2014 Aug 9. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2014. PMID: 25168220 - Stable isotope ratio analysis for authentication of red yeast rice.
Perini M, Carbone G, Camin F. Perini M, et al. Talanta. 2017 Nov 1;174:228-233. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2017.05.057. Epub 2017 May 23. Talanta. 2017. PMID: 28738573 - Marked variability of monacolin levels in commercial red yeast rice products: buyer beware!
Gordon RY, Cooperman T, Obermeyer W, Becker DJ. Gordon RY, et al. Arch Intern Med. 2010 Oct 25;170(19):1722-7. doi: 10.1001/archinternmed.2010.382. Arch Intern Med. 2010. PMID: 20975018 - Functional food red yeast rice (RYR) for metabolic syndrome amelioration: a review on pros and cons.
Patel S. Patel S. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016 May;32(5):87. doi: 10.1007/s11274-016-2035-2. Epub 2016 Apr 2. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 27038957 Review. - Red yeast rice for the treatment of dyslipidemia.
Burke FM. Burke FM. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2015 Apr;17(4):495. doi: 10.1007/s11883-015-0495-8. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2015. PMID: 25728312 Review.
Cited by
- Quality Control and Safety Assessment of Online-Purchased Food Supplements Containing Red Yeast Rice (RYR).
Vanhee C, Jacobs B, Canfyn M, Malysheva SV, Willocx M, Masquelier J, Van Hoorde K. Vanhee C, et al. Foods. 2024 Jun 18;13(12):1919. doi: 10.3390/foods13121919. Foods. 2024. PMID: 38928859 Free PMC article. - Phytochemical Profiles and Biological Studies of Selected Botanical Dietary Supplements Used in the United States.
Salinas-Arellano ED, Castro-Dionicio IY, Jeyaraj JG, Mirtallo Ezzone NP, Carcache de Blanco EJ. Salinas-Arellano ED, et al. Prog Chem Org Nat Prod. 2023;122:1-162. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-26768-0_1. Prog Chem Org Nat Prod. 2023. PMID: 37392311 - Red Yeast Rice for the Improvement of Lipid Profiles in Mild-to-Moderate Hypercholesterolemia: A Narrative Review.
Cicero AFG, Fogacci F, Stoian AP, Toth PP. Cicero AFG, et al. Nutrients. 2023 May 12;15(10):2288. doi: 10.3390/nu15102288. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37242171 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Ozlem T., Sebile A. A review on the red yeast rice (Monascus purpureus) Turk. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2004;2:37–49.
- Chen W., He Y., Zhou Y., Shao Y., Feng Y., Li M., Chen F. Edible Filamentous Fungi from the Species Monascus: Early Traditional Fermentations, Modern Molecular Biology, and Future Genomics. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2015;14:555–567. doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.12145. - DOI
- Lin F. Textual research on Gutian as place where red yeast rice originated. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs. 2017;48:2793–2800.
- Rojsuntornkitti K., Jittrepotch N., Kongbangkerd T., Kraboun K. Substitution of nitrite by Chinese red broken rice powder in Thaitraditional fermented pork sausage (Nham) Int. Food Res. J. 2010;17:153–161.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous