Association of serum magnesium with type 2 diabetes mellitus and diabetic retinopathy - PubMed (original) (raw)
Association of serum magnesium with type 2 diabetes mellitus and diabetic retinopathy
Pratyush Kumar et al. J Family Med Prim Care. 2019 May.
Abstract
Introduction and objective: The rising burden of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) globally has led to huge morbidity and socioeconomic impact in developing countries. In India, too, it has become a silent epidemic and it is estimated that there are over 60 million diabetics. Although in recent years, a lot of research papers have come up on the management of diabetes, latest treatment modalities may not be affordable to all. So, it becomes imperative to prioritize research on prevention and primary care. Magnesium is an intracellular cation and coenzyme for various reactions of the glycolytic pathway. Hypomagnesemia has been shown to precipitate hyperglycemia and has, therefore, been implicated in insulin resistance and its microvascular complications. Poor glycemic control has been associated with retinopathy. Hence, we evaluated association of serum magnesium with T2DM and diabetic retinopathy.
Materials and methods: In a cross-sectional study in North India, 250 consenting adult patients from outpatient department of family medicine of our hospital were recruited. Critically ill patients and those on magnesium supplements were excluded. Clinicolaboratory profile was evaluated. Patients were divided based on serum magnesium level ≤ 1.7 mg/dL (group 1) and > 1.7 mg/dL (group 2). Glycemic control and proportion of diabetic retinopathy were compared between these two groups by using univariate regression analysis.
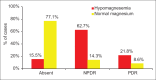
Results: Out of 250 patients, 110 patients (44%) were found to have hypomagnesemia. Glycemia by fasting blood sugar (P = 0.02), post-Prandial blood sugar (P = 0.04), and HbA1C(P = 0.01) was poorly controlled in hypomagnesemia group. In group 1, 62.7% had non proliferative diabetic retinopathy and 21.8% had proliferative diabetic retinopathy, whereas in group 2, 14.3% had nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy and 8.6% had proliferative diabetic retinopathy (P < 0.001).
Conclusions: Magnesium deficiency is associated with increased risk of diabetic retinopathy and poor glycemic control. Dietary supplementation may be advised to prevent such complications and improve glycemic control.
Keywords: Diabetes; T2dm; magnesium; retinopathy.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Figure 1
Correlation between Retinopathy and Hypomagnesemia
Similar articles
- Hypomagnesemia in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.
Kumar SR, Kumar KGS, Gayathri R. Kumar SR, et al. J Assoc Physicians India. 2024 Jul;72(7):25-28. doi: 10.59556/japi.72.0410. J Assoc Physicians India. 2024. PMID: 38990583 - Unveiling the Role of Magnesium: Insights into Insulin Resistance and Glycemic Control in Type 2 Diabetes.
Ram VS, Vishnoi A, Sharma M, Jaison A, Singh N. Ram VS, et al. EJIFCC. 2024 Oct 30;35(3):189-194. eCollection 2024 Oct. EJIFCC. 2024. PMID: 39507571 Free PMC article. - Association Between Serum Magnesium and Glycemic Control, Lipid Profile and Diabetic Retinopathy in Type 1 Diabetes.
Inácio I, Azevedo T, Balsa AM, Ferreira S, Rosinha P, Alves M, Dantas R, Guimarães J. Inácio I, et al. Cureus. 2022 Jan 11;14(1):e21128. doi: 10.7759/cureus.21128. eCollection 2022 Jan. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 35165581 Free PMC article. - Management of Patients with Newly Diagnosed Diabetic Mellitus: Ophthalmologic Outcomes in Intensive versus Conventional Glycemic Control.
Lam PY, Chow SC, Lam WC, Chow LLW, Fung NSK. Lam PY, et al. Clin Ophthalmol. 2021 Jun 25;15:2767-2785. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S301317. eCollection 2021. Clin Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 34234400 Free PMC article. Review. - Magnesium and diabetes: a review.
White JR Jr, Campbell RK. White JR Jr, et al. Ann Pharmacother. 1993 Jun;27(6):775-80. doi: 10.1177/106002809302700619. Ann Pharmacother. 1993. PMID: 8329802 Review.
Cited by
- Beneficial effects of adding magnesium to desalinated drinking water on metabolic and insulin resistance parameters among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized controlled clinical trial.
Albaker WI, Al-Hariri MT, Al Elq AH, Alomair NA, Alamoudi AS, Voutchkov N, Ihm S, Namazi MA, Alsayyah AA, AlRubaish FA, Alohli FT, Zainuddin FA, Alobaidi AA, Almuzain FA, Elamin MO, Alamoudi NB, Alamer MA, Alghamdi AA, AlRubaish NA. Albaker WI, et al. NPJ Clean Water. 2022;5(1):63. doi: 10.1038/s41545-022-00207-9. Epub 2022 Nov 12. NPJ Clean Water. 2022. PMID: 36408199 Free PMC article. - High Fasting Blood Sugar and Increased Waist Circumference as Risk Factors for Diabetic Retinopathy in Type 2 Diabetes Patients Older than 45 Years.
Ranganathan RS, K EV, R S, Manimozhian N. Ranganathan RS, et al. Cureus. 2022 Aug 23;14(8):e28291. doi: 10.7759/cureus.28291. eCollection 2022 Aug. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36158357 Free PMC article. - Assessment of Electrolyte Imbalance and Associated Factors Among Adult Diabetic Patients Attending the University of Gondar Comprehensive Specialized Hospital, Ethiopia: A Comparative Cross-Sectional Study.
Eshetu B, Worede A, Fentie A, Chane E, Fetene G, Wondifraw H, Shimelis M, Girma M, Hadgu R, Demeke K, Fasil A. Eshetu B, et al. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2023 Apr 26;16:1207-1220. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S404788. eCollection 2023. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2023. PMID: 37131504 Free PMC article. - Possibility of magnesium supplementation for supportive treatment in patients with COVID-19.
Tang CF, Ding H, Jiao RQ, Wu XX, Kong LD. Tang CF, et al. Eur J Pharmacol. 2020 Nov 5;886:173546. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173546. Epub 2020 Sep 12. Eur J Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32931782 Free PMC article. Review. - Hypomagnesemia and Poor Glycemic Control among Type 2 Diabetic Patients: A Cross-Sectional Study.
Hamarshih M, Hamshari S, Nazzal Z, Snobar F, Mletat R, Abu-Mazen O, Maraqa B. Hamarshih M, et al. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2022 Nov-Dec;26(6):575-580. doi: 10.4103/ijem.ijem_213_22. Epub 2023 Feb 7. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2022. PMID: 39005513 Free PMC article.
References
- Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2014;38(Suppl 1):S8–16. - PubMed
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas. 6th ed. Brussels, Belgium: International Diabetes Federation; 2013. Available from: http://www.idf.org/diabetesatlas . - PubMed
- Wild S, Roglic G, Green A, Sicree R, King H. Global prevalence of diabetes-estimates for the year 2000 and projections for 2030. Diabetes Care. 2004;27:1047–53. - PubMed
- Whiting DR, Guariguata L, Weil C, Shaw J. IDF diabetes atlas: Global estimates of the prevalence of diabetes for 2011 and 2030. Diab Res ClinPract. 2011;94:311–21. - PubMed
- Ramachandran A, Ma RC, Snehalatha C. Diabetes in Asia. Lancet. 2010;375:408–18. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous