The Emergence of Chromosomally Located bla CTX-M-55 in Salmonella From Foodborne Animals in China - PubMed (original) (raw)
The Emergence of Chromosomally Located bla CTX-M-55 in Salmonella From Foodborne Animals in China
Chuan-Zhen Zhang et al. Front Microbiol. 2019.
Abstract
The emergence and increase in prevalence of resistance to cephalosporins amongst isolates of Salmonella from food animals imposes a public health threat. The aim of the present study was to investigate the prevalence and characteristics of CTX-M-producing Salmonella isolates from raw meat and food animals. 27 of 152 (17.76%) Salmonella isolates were ESBL-positive including 21/70 (30%) from food animals and 6/82 (7.32%) from raw meat. CTX-M-55 was the most prevalent ESBL type observed (12/27, 44.44%). 7 of 12 CTX-M-55-positive Salmonella isolates were Salmonella Indiana, 2 were Salmonella Typhimurium, 2 were Salmonella Chester, and the remaining isolate was not typeable. Eight CTX-M-55-positive Salmonella isolates were highly resistant to fluoroquinolones (MICCIP = 64 ug/mL) and co-harbored aac(6')-Ib-cr and oqxAB. Most of the CTX-M-55 positive isolates (11/12) carried bla CTX-M-55 genes on the chromosome, with the remaining isolate carrying this gene on a transferable 280 kb IncHI2 plasmid. A chromosomal bla CTX-M-55 gene from one isolate transferred onto a 250 kb IncHI2 plasmid which was subsequently conjugated into recipient strain J53. PFGE and MLST profiles showed a wide range of strain types were carrying bla CTX-M-55. Our study demonstrates the emergence and prevalence of foodborne Salmonella harboring a chromosomally located bla CTX-M-55 in China. The co-existence of PMQR genes with bla CTX-M-55 in Salmonella isolates suggests co-selection and dissemination of resistance to both fluoroquinolones and cephalosporins in Salmonella via the food chain in China represents a public health concern.
Keywords: Indiana; Salmonella; blaCTX-M-55; chromosomal; transfer.
Figures
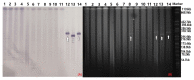
FIGURE 1
PFGE fingerprinting patterns and other characteristics of Salmonella isolates harboring _bla_CTX-M-55 genes.
FIGURE 2
Southern blot hybridization with the _bla_CTX-M-55 probe (A) and S1-PFGE of S1 nuclease-digested genomic DNA (B). The arrow indicates plasmids in the isolates. OYM4 (lane 1), OYM6 (lane 2), OYM8 (lane 3), OYM9 (lane 4), OYM13 (lane 5), OYZ3 (lane 6), OJM1 (lane 7), HZP3 (lane 8), LWP4 (lane 9), OYM10 (lane 10), PJM1 (lane 11), OYZ4 (lane 12), C-PJM1 (lane 13), C-OYZ4 (lane 14), Marker (H9812).
Similar articles
- CTX-M-27 Producing Salmonella enterica Serotypes Typhimurium and Indiana Are Prevalent among Food-Producing Animals in China.
Zhang WH, Lin XY, Xu L, Gu XX, Yang L, Li W, Ren SQ, Liu YH, Zeng ZL, Jiang HX. Zhang WH, et al. Front Microbiol. 2016 Mar 31;7:436. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00436. eCollection 2016. Front Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27065989 Free PMC article. - A Multidrug-resistant Monophasic Salmonella Typhimurium Co-harboring mcr-1, fosA3, bla CTX-M-14 in a Transferable IncHI2 Plasmid from a Healthy Catering Worker in China.
Wang Z, Xu H, Tang Y, Li Q, Jiao X. Wang Z, et al. Infect Drug Resist. 2020 Oct 13;13:3569-3574. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S272272. eCollection 2020. Infect Drug Resist. 2020. PMID: 33116676 Free PMC article. - Genomic Characterization of _mcr_-_1_-Carrying Foodborne Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium and Identification of a Transferable Plasmid Carrying _mcr_-1, bla CTX-M-14 , qnrS2, and oqxAB Genes From Ready-to-Eat Pork Product in China.
Li L, Wan X, Olsen RH, Xiao J, Wang C, Xu X, Meng H, Shi L. Li L, et al. Front Microbiol. 2022 Jun 29;13:903268. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.903268. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35847096 Free PMC article. - bla CTX-M-I group extended spectrum beta lactamase-producing Salmonella typhi from hospitalized patients in Lagos, Nigeria.
Akinyemi KO, Iwalokun BA, Alafe OO, Mudashiru SA, Fakorede C. Akinyemi KO, et al. Infect Drug Resist. 2015 May 11;8:99-106. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S78876. eCollection 2015. Infect Drug Resist. 2015. PMID: 25999745 Free PMC article. - Antimicrobial resistance of Salmonella Indiana from retail chickens in China and emergence of an _mcr-1_-harboring isolate with concurrent resistance to ciprofloxacin, cefotaxime, and colistin.
Hu Y, He Y, Nguyen SV, Liu C, Liu C, Gan X, Wang W, Dong Y, Xu J, Li F, Fanning S. Hu Y, et al. Front Microbiol. 2022 Sep 8;13:955827. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.955827. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36160190 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Prevalence of Extended-Spectrum _β_-Lactamase-Resistant Genes in Escherichia coli Isolates from Central China during 2016-2019.
Wang Z, Lu Q, Mao X, Li L, Dou J, He Q, Shao H, Luo Q. Wang Z, et al. Animals (Basel). 2022 Nov 18;12(22):3191. doi: 10.3390/ani12223191. Animals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36428418 Free PMC article. - High Prevalence and Diversity Characteristics of _bla_NDM, mcr, and _bla_ESBLs Harboring Multidrug-Resistant Escherichia coli From Chicken, Pig, and Cattle in China.
Liu Z, Wang K, Zhang Y, Xia L, Zhao L, Guo C, Liu X, Qin L, Hao Z. Liu Z, et al. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Feb 7;11:755545. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.755545. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35198455 Free PMC article. - Characterizations of _bla_CTX-M-14 and _bla_CTX-M-64 in a clinical isolate of Escherichia coli from China.
Yang M, Liu D, Li X, Xiao C, Mao Y, He J, Feng J, Wang L. Yang M, et al. Front Microbiol. 2023 May 18;14:1158659. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1158659. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37649630 Free PMC article. - High prevalence of blaCTX-M and blaSHV among ESBL producing E. coli isolates from beef cattle in China's Sichuan-Chongqing Circle.
Zhang YL, Huang FY, Gan LL, Yu X, Cai DJ, Fang J, Zhong ZJ, Guo HR, Xie Y, Yi J, Wang ZS, Zuo ZC. Zhang YL, et al. Sci Rep. 2021 Jul 2;11(1):13725. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-93201-z. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34215807 Free PMC article. - Genomic epidemiology of emerging ESBL-producing Salmonella Kentucky bla CTX-M-14b in Europe.
Coipan CE, Westrell T, van Hoek AHAM, Alm E, Kotila S, Berbers B, de Keersmaecker SCJ, Ceyssens PJ, Borg ML, Chattaway M, McCormick J, Dallman TJ, Franz E. Coipan CE, et al. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2020 Dec;9(1):2124-2135. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2020.1821582. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2020. PMID: 32896234 Free PMC article.
References
- Cao Y., Shen Y., Cheng L., Zhang X., Wang C., Wang Y., et al. (2018). Combination of multilocus sequence typing and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis reveals an association of molecular clonality with the emergence of extensive-drug resistance (XDR) in Salmonella. Microbiol. Res. 207 170–176. 10.1016/j.micres.2017.12.001 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources