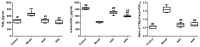UPLC-Q-TOF/MS-Based Plasma Metabolomics to Evaluate the Effects of Aspirin Eugenol Ester on Blood Stasis in Rats - PubMed (original) (raw)
UPLC-Q-TOF/MS-Based Plasma Metabolomics to Evaluate the Effects of Aspirin Eugenol Ester on Blood Stasis in Rats
Dongshuai Shen et al. Molecules. 2019.
Abstract
Aspirin eugenol ester (AEE) is a novel compound that is formed from the esterification of aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid (ASA)) and eugenol. This study aimed to investigate the effects of AEE on blood stasis in rats and to characterize the underlying mechanisms using a plasma metabolomic study. The results indicate that AEE and ASA could modulate whole blood viscosity (WBV), plasma viscosity (PV), blood coagulation parameters, platelet count, platelet aggregation, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), creatinine (CR) and the levels of thromboxane A2 (TXA2) and 6-keto prostaglandin F1α (6-keto-PGF1α). The metabolic profiles of the plasma samples from all groups were clearly separated in the score plots. Nineteen potential metabolites were selected and identified, and disordered levels of these metabolites could be regulated by AEE and ASA. Pathway analysis showed that the mechanism of action of AEE on blood stasis might be principally related to the metabolism of amino acid, fatty acid, energy and glycerophospholipid. The above results indicate that AEE protected the rats against blood stasis, and that this effect might have been caused by the anticoagulation activity of AEE and its abilities to maintain a balance between TXA2 and PGI2, reduce blood viscosity, inhibit platelet aggregation and normalize the plasma metabolic profile.
Keywords: AEE; UPLC-Q-TOF/MS; aspirin; blood stasis; metabolomics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Figure 1
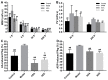
Results of blood viscosity and platelet aggregation in different groups. (A,B) Effects of AEE on WBV and PV. (C,D) Effects of AEE on AA and ADP-induced platelet aggregation. ASA: aspirin; AEE: aspirin eugenol ester; WBV: whole blood viscosity; PV: plasma viscosity; PAg: platelet aggregation. Compared with the model group, # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01; compared with the ASA group, ▲ p < 0.05.
Figure 2
Effects of AEE on TXB2 and 6-keto-PGF1α levels. TXB2: thromboxane B2. Compared with the model group, ## p < 0.01; compared with the ASA group, ▲▲ p < 0.01.
Figure 3
The effect of AEE on the metabolomic profile of plasma from rats with blood stasis. The OPLS-DA score plots of different groups in positive and negative modes. (A) Control group versus model group, ESI+: R2X = 0.706, R2Y = 0.998 and Q2 = 0.967; ESI-: R2X = 0.522, R2Y = 0.978 and Q2 = 0.936. (B) ASA group versus model group, ESI+: R2X = 0.344, R2Y = 0.996 and Q2 = 0.944; ESI-: R2X = 0.363, R2Y = 0.995 and Q2 = 0.93. (C) AEE group versus model group, ESI+: R2X = 0.475, R2Y = 0.984 and Q2 = 0.928; ESI-: R2X = 0.494, R2Y = 0.976 and Q2 = 0.912.
Figure 4
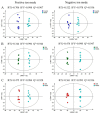
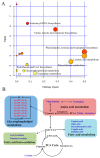
Disturbed pathways in response to blood stasis and AEE treatment. (A) Summary of pathway analysis from MetaboAnalyst. All of the matched pathways are displayed as circles. The color and size of each circle are based on its -log (p) value and pathway impact value, respectively. The x-axis represents the pathway impact value that was calculated from the pathway topological analysis, and the y-axis represents the -log (p) value that was obtained from the pathway enrichment analysis. The metabolic pathway with a high pathway impact value and -log (p) value shows that the identified metabolites had a key position and influence on this pathway. (B) The potential metabolic network that was disrupted in rats with blood stasis and was altered by AEE treatment.
Figure 5
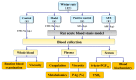
Study design of this experiment. i.g.: intragastric administration; PAg%: platelet aggregation rate.
Similar articles
- Evaluation on antithrombotic effect of aspirin eugenol ester from the view of platelet aggregation, hemorheology, TXB2/6-keto-PGF1α and blood biochemistry in rat model.
Ma N, Liu XW, Yang YJ, Shen DS, Zhao XL, Mohamed I, Kong XJ, Li JY. Ma N, et al. BMC Vet Res. 2016 Jun 14;12(1):108. doi: 10.1186/s12917-016-0738-0. BMC Vet Res. 2016. PMID: 27296110 Free PMC article. - UPLC-Q-TOF/MS-based urine and plasma metabonomics study on the ameliorative effects of aspirin eugenol ester in hyperlipidemia rats.
Ma N, Karam I, Liu XW, Kong XJ, Qin Z, Li SH, Jiao ZH, Dong PC, Yang YJ, Li JY. Ma N, et al. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2017 Oct 1;332:40-51. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2017.07.013. Epub 2017 Jul 18. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28733207 - Feces and liver tissue metabonomics studies on the regulatory effect of aspirin eugenol eater in hyperlipidemic rats.
Ma N, Liu X, Kong X, Li S, Jiao Z, Qin Z, Dong P, Yang Y, Li J. Ma N, et al. Lipids Health Dis. 2017 Dec 11;16(1):240. doi: 10.1186/s12944-017-0633-0. Lipids Health Dis. 2017. PMID: 29228968 Free PMC article. - Acetylsalicylic acid and the balance between prostacyclin and thromboxane A2.
Viinikka L. Viinikka L. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1990;201:103-8. doi: 10.3109/00365519009085806. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1990. PMID: 2244178 Review. - Thromboxane A2, prostacyclin and aspirin: effects on vascular tone and platelet aggregation.
Smith JB, Araki H, Lefer AM. Smith JB, et al. Circulation. 1980 Dec;62(6 Pt 2):V19-25. Circulation. 1980. PMID: 7002350 Review.
Cited by
- Combined Lipidomics and Network Pharmacology Study of Protective Effects of Salvia miltiorrhiza against Blood Stasis Syndrome.
Jin Y, Xie Z, Li S, Zeng X, Wang L, Hu P, Zhang H, Xiao X. Jin Y, et al. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Mar 19;2021:5526778. doi: 10.1155/2021/5526778. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 33790973 Free PMC article. - The vaginal metabolomics profile with features of polycystic ovary syndrome: a pilot investigation in China.
Xuan Y, Hong X, Zhou X, Yan T, Qin P, Peng D, Wang B. Xuan Y, et al. PeerJ. 2024 Oct 8;12:e18194. doi: 10.7717/peerj.18194. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 39399434 Free PMC article. - The Role of Amino Acids in Endothelial Biology and Function.
Li M, Wu Y, Ye L. Li M, et al. Cells. 2022 Apr 18;11(8):1372. doi: 10.3390/cells11081372. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35456051 Free PMC article. Review. - Role of Fibrinogen in Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus with Diabetic Neuropathy and its Preliminary Mechanism.
Gu WL, Li ZH, Zhang SQ, Ao P, Zhu XB, Zhao X, Zhang XY, Zhang DF, Huang XJ, Jiang Y, Wei L. Gu WL, et al. Protein Pept Lett. 2023;30(6):486-497. doi: 10.2174/0929866530666230509140515. Protein Pept Lett. 2023. PMID: 37165590 Free PMC article. - The Protective Effect of Aspirin Eugenol Ester on Paraquat-Induced Acute Liver Injury Rats.
Zhang ZD, Yang YJ, Liu XW, Qin Z, Li SH, Li JY. Zhang ZD, et al. Front Med (Lausanne). 2020 Dec 17;7:589011. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2020.589011. eCollection 2020. Front Med (Lausanne). 2020. PMID: 33392217 Free PMC article.
References
- Mchedlishvili G. Disturbed blood flow structuring as critical factor of hemorheological disorders in microcirculation. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 1998;19:315–325. - PubMed
- Meng J.M. Standardization in clinimetrics for syndromatic diagnosis of cerebrovascular diseases in traditional Chinese medicine. Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 1988;8:173–175. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical