Interplay Between N 6-Methyladenosine (m6A) and Non-coding RNAs in Cell Development and Cancer - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Interplay Between N 6-Methyladenosine (m6A) and Non-coding RNAs in Cell Development and Cancer
Francesco Fazi et al. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2019.
Abstract
RNA chemical modifications in coding and non-coding RNAs have been known for decades. They are generally installed by specific enzymes and, in some cases, can be read and erased by other specific proteins. The impact of RNA chemical modifications on gene expression regulation and the reversible nature of some of these modifications led to the birth of the word epitranscriptomics, in analogy with the changes that occur on DNA and histones. Among more than 100 different modifications identified so far, most of the epitranscriptomics studies focused on the N 6-methyladenosine (m6A), which is the more abundant internal modification in protein coding RNAs. m6A can control several pathways of gene expression, including spicing, export, stability, and translation. In this review, we describe the interplay between m6A and non-coding RNAs, in particular microRNAs and lncRNAs, with examples of its role in gene expression regulation. Finally, we discuss its relevance in cell development and disease.
Keywords: ESC development; RNA modifications; cell reprogramming; epitranscriptomics; lncRNAs; m6A; microRNAs; non-coding RNAs.
Figures
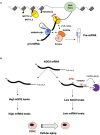
FIGURE 1
Impact of epitranscriptomics on microRNAs biogenesis and function. (A) m6A stimulates microRNA processing by recruiting the Drosha cofactor DGCR8 by the m6A reader HNBRPA2B1 (Alarcón et al., 2015a, b) or, in the case of the miR-126a, by direct interaction with METTL14 (Ma et al., 2017). (B) During aging of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs), AGO2 and, eventually, miRNA levels are decreased by higher m6A modification of AGO2 mRNA. This results in enhanced mRNA decay that is very likely mediated by the YTHDF2 reader (Min et al., 2018).
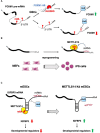
FIGURE 2
Examples of the interplay between non-coding RNAs and epitranscriptomics. (A) In glioblastoma stem-like cells (GSCs) the expression of FOXM1 is increased by the concomitant expression of the antisense transcript FOXM1-AS, which, in turn, promote m6A demethylation by recruiting ALKBH5 (Zhang et al., 2017). (B) m6A RNA methylation is positively regulated by microRNAs, which recruit METTL3 on specific mRNA and promotes reprogramming to pluripotency (Chen et al., 2015). (C) m6A modification decreases the IGFBP3 mRNA levels by inhibiting the binding of HuR and promoting the interaction with microRNAs. IGFBP3 protein positively regulates the stability of different developmental regulators. This mechanism ensures low level of IGFBP3 in mESCs (Wang Y. et al., 2014).
Similar articles
- The functions of N6-methyladenosine modification in lncRNAs.
He RZ, Jiang J, Luo DX. He RZ, et al. Genes Dis. 2020 Mar 19;7(4):598-605. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2020.03.005. eCollection 2020 Dec. Genes Dis. 2020. PMID: 33335959 Free PMC article. Review. - N6-Methyladenosine (m6A): A Promising New Molecular Target in Acute Myeloid Leukemia.
Ianniello Z, Paiardini A, Fatica A. Ianniello Z, et al. Front Oncol. 2019 Apr 9;9:251. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00251. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31024852 Free PMC article. Review. - Environmental exposures and RNA N6-Methyladenosine modified long Non-Coding RNAs.
Cayir A. Cayir A. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2020 Sep;50(8):641-649. doi: 10.1080/10408444.2020.1812511. Epub 2020 Sep 14. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2020. PMID: 32924714 Review. - Role of N6-Methyladenosine RNA Modification in Cardiovascular Disease.
Song D, Hou J, Wu J, Wang J. Song D, et al. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 May 7;8:659628. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.659628. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 34026872 Free PMC article. Review. - The Dark Side of the Epitranscriptome: Chemical Modifications in Long Non-Coding RNAs.
Jacob R, Zander S, Gutschner T. Jacob R, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Nov 10;18(11):2387. doi: 10.3390/ijms18112387. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 29125541 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Comprehensive Analysis and Prognosis Prediction of N6-Methyladenosine-Related lncRNAs in Immune Microenvironment Infiltration of Gastric Cancer.
Huang J, Chen W, Chen C, Jie Z, Xiao T. Huang J, et al. Int J Gen Med. 2022 Mar 8;15:2629-2643. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S349399. eCollection 2022. Int J Gen Med. 2022. PMID: 35300127 Free PMC article. - Regulatory role of RNA N6-methyladenosine modifications during skeletal muscle development.
Yu B, Liu J, Zhang J, Mu T, Feng X, Ma R, Gu Y. Yu B, et al. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Aug 5;10:929183. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.929183. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35990615 Free PMC article. Review. - Identification and validation of lncRNAs involved in m6A regulation for patients with ovarian cancer.
Zheng J, Guo J, Cao B, Zhou Y, Tong J. Zheng J, et al. Cancer Cell Int. 2021 Jul 8;21(1):363. doi: 10.1186/s12935-021-02076-7. Cancer Cell Int. 2021. PMID: 34238292 Free PMC article. - WTAP and m6A-modified circRNAs modulation during stress response in acute myeloid leukemia progenitor cells.
Iaiza A, Mazzanti G, Goeman F, Cesaro B, Cortile C, Corleone G, Tito C, Liccardo F, De Angelis L, Petrozza V, Masciarelli S, Blandino G, Fanciulli M, Fatica A, Fontemaggi G, Fazi F. Iaiza A, et al. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024 Jun 23;81(1):276. doi: 10.1007/s00018-024-05299-9. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 38909325 Free PMC article. - N6-methyladenosine modification of circMARK2 enhances cytoplasmic export and stabilizes LIN28B, contributing to the progression of Wilms tumor.
Shu G, Zhao Z, Zhao T, Deng C, Zhu J, Han Y, Chen M, Jing J, Bai G, Li D, Li F, He J, Fu W, Liu G. Shu G, et al. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024 Jul 11;43(1):191. doi: 10.1186/s13046-024-03113-9. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38987793 Free PMC article. Retracted.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources