Class effect for SGLT-2 inhibitors: a tale of 9 drugs - PubMed (original) (raw)
Class effect for SGLT-2 inhibitors: a tale of 9 drugs
Dario Giugliano et al. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2019.
Abstract
The definition of class effect for SGLT-2 inhibitors may be based on three concepts: a similar chemical structure, a similar mechanism of action and similar pharmacological effects. We have also assumed that a class effect does exist when an effect on a particular outcome is present and is significant for each drug within the class of SGLT-2 inhibitors. For major cardiovascular events (MACE), there is no class effect for SGLT-2 inhibitors, as the 7% reduction of MACE risk observed with dapagliflozin in the DECLARE trial was not significant; on the other hand, a class effect is evident for both heart failure and diabetic kidney disease, as in all four trials so far completed (EMPAREG-OUTCOME, CANVAS, DECLARE, CREDENCE) the risk of hospitalization for heart failure and progression of diabetic kidney disease was significantly reduced by all SGLT-2 inhibitors.
Keywords: Class effect; Diabetic kidney disease; Heart failure; MACE; SGLT-2 inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
D.G. received honoraria for speaking at meetings from Novartis, Sanofi, Lilly, AstraZeneca, and Novo Nordisk. K.E. received honoraria for speaking at meetings from Novartis, Sanofi, Lilly, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Novo Nordisk.
Figures
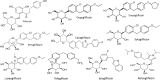
Fig. 1
The class of SGLT-2 inhibitors with its founder phlorizin. Phlorizin-based analogs can be divided into _O_-glucoside analogs (the sugar group is bonded to another group via a glycoside bond, such the founder phlorizin and remogliflozin) or _C_-glucoside analogs (such as dapagliflozin and the many others); the latter have greater pharmacokinetic stability and selectivity for SGLT2. Inhibitor affinity is the result of a synergistic relationship between binding sites for sugar and the aglycone, with alterations in the sugar resulting in surprising differences in selectivity. All the nine SGLT-2 inhibitors showed in the figure are available in different parts of the world
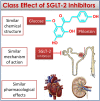
Fig. 2
The three concepts that must be fulfilled for the definition of a class effect. Similar chemical structure, similar mechanism of action, similar pharmacological effects at the level of target organs; to all that, it must be added the statistical significance of the effect in each trial
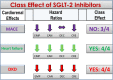
Fig. 3
Class effects for the cardiorenal outcomes of SGLT-2 inhibitors. A class effect is not evident for MACE (only three trials demonstrated a significant reduction of the MACE risk), but is evident for heart failure (reduced risk of hospitalization for heart failure) and DKD progression (reduced decline of eGFR, renal death, or requirement for renal replacement therapy). MACE, major cardiovascular events; DKD, diabetic kidney disease; EMP, EMPAREG-OUTCOME; CAN, CANVAS; DEC, DECLARE; CRE, CREDENCE
Similar articles
- [Outcome studies on SGLT-2 inhibitors].
Seufert J, Laubner K. Seufert J, et al. Internist (Berl). 2019 Sep;60(9):903-911. doi: 10.1007/s00108-019-0656-x. Internist (Berl). 2019. PMID: 31375850 Review. German. - Preventing major adverse cardiovascular events by SGLT-2 inhibition in patients with type 2 diabetes: the role of kidney.
Giugliano D, De Nicola L, Maiorino MI, Bellastella G, Garofalo C, Chiodini P, Ceriello A, Esposito K. Giugliano D, et al. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2020 Mar 19;19(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s12933-020-01010-x. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2020. PMID: 32192503 Free PMC article. - Exploring the heterogeneity of the effects of SGLT-2 inhibitors in cardiovascular outcome trials.
Mannucci E, Dicembrini I, Nreu B, Monami M. Mannucci E, et al. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2020 Jan 3;30(1):71-76. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2019.07.018. Epub 2019 Aug 5. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2020. PMID: 31757568 Review. - An Exploratory Study of Dapagliflozin for the Attenuation of Albuminuria in Patients with Heart Failure and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (DAPPER).
Yoshihara F, Imazu M, Hamasaki T, Anzai T, Yasuda S, Ito S, Yamamoto H, Hashimura K, Yasumura Y, Mori K, Watanabe M, Asakura M, Kitakaze M; DAPPER investigators and study coordinators. Yoshihara F, et al. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2018 Apr;32(2):183-190. doi: 10.1007/s10557-018-6782-1. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2018. PMID: 29589153 - Cardiovascular effects of SGLT-2 inhibitors: What we have learned from cardiovascular outcome trials and what we still need to understand.
Cavallari I, Maddaloni E. Cavallari I, et al. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2019 May;35(4):e3124. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.3124. Epub 2019 Jan 16. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2019. PMID: 30604504
Cited by
- Systematic Review of Cardiovascular Outcome Trials Using New Antidiabetic Agents in CKD Stratified by Estimated GFR.
Arshad A, Sarween N, Sharif A. Arshad A, et al. Kidney Int Rep. 2021 Jul 1;6(9):2415-2424. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2021.06.029. eCollection 2021 Sep. Kidney Int Rep. 2021. PMID: 34514202 Free PMC article. - Impact of prescription length supply policy on patient medication adherence in Thailand.
Jarujumrus I, Taychakhoonavudh S. Jarujumrus I, et al. BMC Health Serv Res. 2023 May 24;23(1):533. doi: 10.1186/s12913-023-09530-4. BMC Health Serv Res. 2023. PMID: 37226134 Free PMC article. - Sodium-Glucose Co-transporter-2 Inhibitors and Nephroprotection in Diabetic Patients: More Than a Challenge.
Provenzano M, Pelle MC, Zaffina I, Tassone B, Pujia R, Ricchio M, Serra R, Sciacqua A, Michael A, Andreucci M, Arturi F. Provenzano M, et al. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 Jun 4;8:654557. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.654557. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34150796 Free PMC article. Review. - The Impact of the Novel Sodium-Dependent Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitor, Enavogliflozin, on Cardiac Reverse Remodeling in Heart Failure Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Case Series.
Yang T, Jang Y, Chung WJ. Yang T, et al. Int J Heart Fail. 2024 Oct 28;6(4):176-178. doi: 10.36628/ijhf.2024.0018. eCollection 2024 Oct. Int J Heart Fail. 2024. PMID: 39513017 Free PMC article. No abstract available. - Generalizability of sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors cardiovascular outcome trials to the type 2 diabetes population: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Castellana M, Procino F, Sardone R, Trimboli P, Giannelli G. Castellana M, et al. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2020 Jun 13;19(1):87. doi: 10.1186/s12933-020-01067-8. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2020. PMID: 32534590 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical