Study protocol: multicenter double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial of rituximab for the treatment of childhood-onset early-stage uncomplicated frequently relapsing or steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome (JSKDC10 trial) - PubMed (original) (raw)
Study protocol: multicenter double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial of rituximab for the treatment of childhood-onset early-stage uncomplicated frequently relapsing or steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome (JSKDC10 trial)
China Nagano et al. BMC Nephrol. 2019.
Abstract
Background: Eighty percent of children with idiopathic nephrotic syndrome respond well to steroid therapy, but up to 50% of patients with steroid-sensitive nephrotic syndrome exhibit frequently relapsing (FRNS) or steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome (SDNS). Several studies identified the chimeric anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody rituximab as an effective treatment for patients with complicated FRNS/SDNS. Recent studies suggested that rituximab could also be a first-line treatment for early-stage uncomplicated FRNS/SDNS, although further studies are required to confirm its efficacy and safety.
Methods/design: We are conducting a multicenter, double-blind, randomized placebo controlled trial to investigate the efficacy and safety of rituximab for the treatment of childhood-onset early-stage uncomplicated FRNS/SDNS. Patients will be allocated to receive two 375 mg/m2 doses (maximum dose: 500 mg) of either rituximab or placebo. Investigators are permitted to request the disclosure of a subject's allocation code if he or she exhibits treatment failure. Additionally, if placebo-treated subjects display early relapse (a sign of treatment failure), they have the option to receive rituximab in an unblinded phase. The primary endpoint is relapse-free survival during the observation period.
Discussion: The results will provide important data on the use of rituximab for patients with uncomplicated FRNS/SDNS. In the future, rituximab treatment will enable most patients with uncomplicated FRNS/SDNS to discontinue or reduce steroid therapy without relapse, and it is possible that rituximab could represent an immunosuppressive therapy for these diseases.
Trial registration: This trial was prospectively registered to the JMACCT Clinical Trials Registry on September 6, 2018 (Trial ID: JMA-IIA00380 ).
Keywords: Frequently relapsing nephrotic syndrome; Rituximab; Steroid-sensitive nephrotic syndrome.
Conflict of interest statement
Mayumi Sako received a consulting fee from Zenyaku Kogyo Co. Ltd. Kenji Ishikura received a grant from Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. and Novartis Pharma K.K., and a lecture fee from Zenyaku Kogyo Co. Ltd. and Novartis Pharma K.K. Koichi Kamei has received lecture fees from Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. Koichi Nakanishi received lecture fees from Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. and Novartis Pharma K.K. Kandai Nozu received lecture fees from Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. Kazumoto Iijima received a grant from Zenyaku Kogyo Co. Ltd. and lecture and/or consulting fees from Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Zenyaku Kogyo Co. Ltd., Takeda Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Novartis Pharma K.K. and Kyowa Hakko Kirin Co. Ltd.
Figures
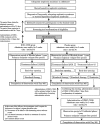
Fig. 1
Flow diagram of the clinical trial set-up. The trial is a multicenter, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study. After obtaining informed consent, randomization will be conducted. If subjects in the placebo group wish to receive IDEC-C2B8 after the initial phase, they will receive the drug in an unblinded phase
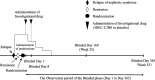
Fig. 2
Dosage regimen (blinded period). Investigators will administer the first dose of the investigational drug within 14 days after the date of randomization (the date the first dose of the investigational drug is administered is set as Blinded Day 1). The investigational drug will be administered via two 375-mg/m2 doses (maximum dose: 500 mg) separated by 1 week (Blinded Days 1 and 8)
Fig. 3
Dosage regimen (unblinded period). Investigators will administer the first dose of IDEC-C2B8 within 14 days after the date of allocation (the date the first dose of IDEC-C2B8 is administered is set as Unblinded Day 1). IDEC-C2B8 will be administered via two 375-mg/m2 doses (maximum dose: 500 mg) separated by 1 week (Unblinded Days 1 and 8)
Similar articles
- Study protocol: mycophenolate mofetil as maintenance therapy after rituximab treatment for childhood-onset, complicated, frequently-relapsing nephrotic syndrome or steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome: a multicenter double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial (JSKDC07).
Horinouchi T, Sako M, Nakanishi K, Ishikura K, Ito S, Nakamura H, Oba MS, Nozu K, Iijima K. Horinouchi T, et al. BMC Nephrol. 2018 Nov 1;19(1):302. doi: 10.1186/s12882-018-1099-7. BMC Nephrol. 2018. PMID: 30382824 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Rituximab for childhood-onset, complicated, frequently relapsing nephrotic syndrome or steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome: a multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled trial.
Iijima K, Sako M, Nozu K, Mori R, Tuchida N, Kamei K, Miura K, Aya K, Nakanishi K, Ohtomo Y, Takahashi S, Tanaka R, Kaito H, Nakamura H, Ishikura K, Ito S, Ohashi Y; Rituximab for Childhood-onset Refractory Nephrotic Syndrome (RCRNS) Study Group. Iijima K, et al. Lancet. 2014 Oct 4;384(9950):1273-81. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60541-9. Epub 2014 Jun 22. Lancet. 2014. PMID: 24965823 Clinical Trial. - Long-term outcome of childhood-onset complicated nephrotic syndrome after a multicenter, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial of rituximab.
Kamei K, Ishikura K, Sako M, Aya K, Tanaka R, Nozu K, Kaito H, Nakanishi K, Ohtomo Y, Miura K, Takahashi S, Morimoto T, Kubota W, Ito S, Nakamura H, Iijima K; Rituximab for Childhood-Onset Refractory Nephrotic Syndrome (RCRNS) Study Group. Kamei K, et al. Pediatr Nephrol. 2017 Nov;32(11):2071-2078. doi: 10.1007/s00467-017-3718-0. Epub 2017 Jun 29. Pediatr Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 28664242 Clinical Trial. - Rituximab in steroid-sensitive nephrotic syndrome: lessons from clinical trials.
Iijima K, Sako M, Kamei K, Nozu K. Iijima K, et al. Pediatr Nephrol. 2018 Sep;33(9):1449-1455. doi: 10.1007/s00467-017-3746-9. Epub 2017 Jul 17. Pediatr Nephrol. 2018. PMID: 28717938 Free PMC article. Review. - Rituximab for nephrotic syndrome in children.
Iijima K, Sako M, Nozu K. Iijima K, et al. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2017 Apr;21(2):193-202. doi: 10.1007/s10157-016-1313-5. Epub 2016 Jul 15. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 27422620 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Timing and selection of steroid-sparing agents for children with early-stage steroid-sensitive nephrotic syndrome.
Fujinaga S. Fujinaga S. Pediatr Nephrol. 2024 Aug;39(8):2539. doi: 10.1007/s00467-024-06326-4. Epub 2024 Feb 27. Pediatr Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 38411639 No abstract available. - [Efficacy and safety of low-dose rituximab in treatment of pediatric nephrotic syndrome: a prospective randomized controlled trial].
Zhu Y, Wu L, Wang Y, Zhu YF, Peng Y, Fang SH, Zhang LD, Deng F. Zhu Y, et al. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2023 Jun 15;25(6):606-611. doi: 10.7499/j.issn.1008-8830.2301026. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 37382130 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. Chinese. - Non-corticosteroid immunosuppressive medications for steroid-sensitive nephrotic syndrome in children.
Larkins NG, Hahn D, Liu ID, Willis NS, Craig JC, Hodson EM. Larkins NG, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Nov 8;11(11):CD002290. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002290.pub6. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39513526 Review. - Optimizing the corticosteroid dose in steroid-sensitive nephrotic syndrome.
Christian MT, Maxted AP. Christian MT, et al. Pediatr Nephrol. 2022 Jan;37(1):37-47. doi: 10.1007/s00467-021-04985-1. Epub 2021 Feb 20. Pediatr Nephrol. 2022. PMID: 33611671 Free PMC article. Review. - Necrotizing Fasciitis: A Side Effect of Rituximab Administration in Steroid-Dependent Nephrotic Syndrome.
Safdar OY, Basunbul LI, Alhazmi LS, Almughamisi SA, Habib LA, Basaeed AJ, Kalaktawi NM, Alharithi ET, Aljaaly HA, Alzahrani WA. Safdar OY, et al. Int Med Case Rep J. 2022 Oct 18;15:587-592. doi: 10.2147/IMCRJ.S347389. eCollection 2022. Int Med Case Rep J. 2022. PMID: 36281444 Free PMC article.
References
- Kikunaga Kaori, Ishikura Kenji, Terano Chikako, Sato Mai, Komaki Fumiyo, Hamasaki Yuko, Sasaki Satoshi, Iijima Kazumoto, Yoshikawa Norishige, Nakanishi Koichi, Nakazato Hitoshi, Matsuyama Takeshi, Ando Takashi, Ito Shuichi, Honda Masataka. High incidence of idiopathic nephrotic syndrome in East Asian children: a nationwide survey in Japan (JP-SHINE study) Clinical and Experimental Nephrology. 2016;21(4):651–657. doi: 10.1007/s10157-016-1319-z. - DOI - PubMed
- Iijima K, Sako M, Nozu K, Mori R, Tuchida N, Kamei K, et al. Rituximab for childhood-onset, complicated, frequently relapsing nephrotic syndrome or steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome: a multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2014;384(9950):1273–1281. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60541-9. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources