Magnitude of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Eastern Perspective - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Magnitude of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Eastern Perspective
Becky Ching-Yeung Yu et al. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2019 Jul-Aug.
Abstract
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is currently the most common chronic liver disease worldwide, affecting a quarter of the global adult population. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, the more active form of NAFLD with active hepatic necroinflammation and faster fibrosis progression, has become one of the leading indications for liver transplantation and an important cause of hepatocellular carcinoma in Western countries. Epidemiological studies suggest that NAFLD is almost equally prevalent in Asia as in the West, but severe liver complications appear to be less common. In this article, we review the epidemiology, clinical characteristics, risk factors and clinical outcomes of NAFLD in Asia. We highlight the issue of NAFLD in the nonobese population and discuss whether it is a unique phenomenon in Asia. Because of the rapidly changing epidemiology and natural history, future studies should continue to monitor the magnitude of NAFLD in Asia and define the best policy to control this new epidemic.
Keywords: Asia; BMI, body mass index; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; HSD17B13, hydroxysteroid 17-beta dehydrogenase 13; NAFL, nonalcoholic fatty liver; NAFLD, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; NASH, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis; PNPLA3, patatin-like phospholipase domain–containing protein 3; TM6SF2, transmembrane 6 superfamily 2; epidemiology; metabolic syndrome; non-alcoholic steatohepatitis; obesity.
Figures
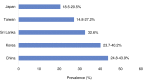
Figure 1
Prevalence of NAFLD in Asian countries. The figures were modified from Younossi et al.
References
- Younossi Z.M., Koenig A.B., Abdelatif D., Fazel Y., Henry L., Wymer M. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-Meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology. 2016;64:73–84. - PubMed
- Wong V.W., Chan W.K., Chitturi S. Asia-pacific working party on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease guidelines 2017-Part 1: definition, risk factors and assessment. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;33:70–85. - PubMed
- Wong V.W., Wong G.L., Choi P.C. Disease progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a prospective study with paired liver biopsies at 3 years. Gut. 2010;59:969–974. - PubMed
- Fan J.G., Kim S.U., Wong V.W. New trends on obesity and NAFLD in Asia. J Hepatol. 2017;67:862–873. - PubMed
- Kojima S., Watanabe N., Numata M., Ogawa T., Matsuzaki S. Increase in the prevalence of fatty liver in Japan over the past 12 years: analysis of clinical background. J Gastroenterol. 2003;38:954–961. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources