Genome-Wide Association Study of Diabetic Kidney Disease Highlights Biology Involved in Glomerular Basement Membrane Collagen - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2019 Oct;30(10):2000-2016.
doi: 10.1681/ASN.2019030218. Epub 2019 Sep 19.
Jennifer N Todd 2 3 4, Niina Sandholm 5 6 7, Joanne B Cole 2 3 4, Wei-Min Chen 8, Darrell Andrews 9, Marcus G Pezzolesi 10, Paul M McKeigue 11, Linda T Hiraki 12, Chengxiang Qiu 13, Viji Nair 14, Chen Di Liao 12, Jing Jing Cao 12, Erkka Valo 5 6 7, Suna Onengut-Gumuscu 8, Adam M Smiles 15, Stuart J McGurnaghan 16, Jani K Haukka 5 6 7, Valma Harjutsalo 5 6 7 17, Eoin P Brennan 9, Natalie van Zuydam 18 19, Emma Ahlqvist 20, Ross Doyle 9, Tarunveer S Ahluwalia 21, Maria Lajer 21, Maria F Hughes 9, Jihwan Park 13, Jan Skupien 15, Athina Spiliopoulou 11, Andrew Liu 22, Rajasree Menon 14 23, Carine M Boustany-Kari 24, Hyun M Kang 23 25, Robert G Nelson 26, Ronald Klein 27, Barbara E Klein 27, Kristine E Lee 27, Xiaoyu Gao 28, Michael Mauer 29, Silvia Maestroni 30, Maria Luiza Caramori 29, Ian H de Boer 31, Rachel G Miller 32, Jingchuan Guo 32, Andrew P Boright 12, David Tregouet 33 34, Beata Gyorgy 33 34, Janet K Snell-Bergeon 35, David M Maahs 36, Shelley B Bull 37, Angelo J Canty 38, Colin N A Palmer 39, Lars Stechemesser 40, Bernhard Paulweber 40, Raimund Weitgasser 40 41, Jelizaveta Sokolovska 42, Vita Rovīte 43, Valdis Pīrāgs 42 44, Edita Prakapiene 45, Lina Radzeviciene 46, Rasa Verkauskiene 46, Nicolae Mircea Panduru 6 47, Leif C Groop 20 48, Mark I McCarthy 18 19 49 50, Harvest F Gu 51 52, Anna Möllsten 53, Henrik Falhammar 54 55, Kerstin Brismar 54 55, Finian Martin 9, Peter Rossing 21 56, Tina Costacou 32, Gianpaolo Zerbini 30, Michel Marre 57 58 59 60, Samy Hadjadj 61 62 63, Amy J McKnight 64, Carol Forsblom 5 7 7, Gareth McKay 64, Catherine Godson 9, A Peter Maxwell 64, Matthias Kretzler 14 23, Katalin Susztak 13, Helen M Colhoun 16, Andrzej Krolewski 15, Andrew D Paterson 12, Per-Henrik Groop 5 6 7 65, Stephen S Rich 8, Joel N Hirschhorn 2 3, Jose C Florez 66 4 67 68; SUMMIT Consortium, DCCT/EDIC Research Group, GENIE Consortium
Affiliations
- PMID: 31537649
- PMCID: PMC6779358
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2019030218
Genome-Wide Association Study of Diabetic Kidney Disease Highlights Biology Involved in Glomerular Basement Membrane Collagen
Rany M Salem et al. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2019 Oct.
Abstract
Background: Although diabetic kidney disease demonstrates both familial clustering and single nucleotide polymorphism heritability, the specific genetic factors influencing risk remain largely unknown.
Methods: To identify genetic variants predisposing to diabetic kidney disease, we performed genome-wide association study (GWAS) analyses. Through collaboration with the Diabetes Nephropathy Collaborative Research Initiative, we assembled a large collection of type 1 diabetes cohorts with harmonized diabetic kidney disease phenotypes. We used a spectrum of ten diabetic kidney disease definitions based on albuminuria and renal function.
Results: Our GWAS meta-analysis included association results for up to 19,406 individuals of European descent with type 1 diabetes. We identified 16 genome-wide significant risk loci. The variant with the strongest association (rs55703767) is a common missense mutation in the collagen type IV alpha 3 chain (COL4A3) gene, which encodes a major structural component of the glomerular basement membrane (GBM). Mutations in COL4A3 are implicated in heritable nephropathies, including the progressive inherited nephropathy Alport syndrome. The rs55703767 minor allele (Asp326Tyr) is protective against several definitions of diabetic kidney disease, including albuminuria and ESKD, and demonstrated a significant association with GBM width; protective allele carriers had thinner GBM before any signs of kidney disease, and its effect was dependent on glycemia. Three other loci are in or near genes with known or suggestive involvement in this condition (BMP7) or renal biology (COLEC11 and DDR1).
Conclusions: The 16 diabetic kidney disease-associated loci may provide novel insights into the pathogenesis of this condition and help identify potential biologic targets for prevention and treatment.
Keywords: diabetes; diabetic nephropathy; end-stage renal disease; genetic renal disease; human genetics; kidney disease.
Copyright © 2019 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures
Graphical abstract
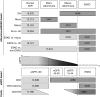
Figure 1.
Phenotypic analysis of DKD. Schematic diagram of outcomes analyzed in this study. Numbers indicate the total number of cases (darker gray) and controls (lighter gray) included in the meta-analyses for each phenotype. ESKD defined as eGFR<15 ml/min per 1.73 m2 or undergoing dialysis or having renal transplant.
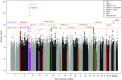
Figure 2.
Genome-wide association testing of all ten phenotypic comparisons. Multiphenotype Manhattan plot shows lowest P value at each marker for each of the ten phenotypic comparisons, under the standard and fully-adjusted model. Significance of SNPs (−log10[P value], y axis) is plotted against genomic location (x axis). Loci surpassing genome-wide significance (red line) and/or study-wide significance (blue line) are colored by phenotype.
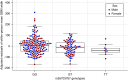
Figure 3.
Adjusted residuals of GBM width by rs55703767 genotype and sex. Box and whisker plot of residuals of mean GBM width after adjusting for age, sex, and diabetes duration, stratified by GG, GT, or TT genotype at rs55703767, with overlay of individual data points for both women (pink) and men (blue).
Figure 4.
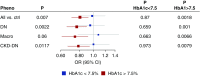
Association at rs55703767 (COL4A3) stratified by HbA1c below or above 7.5%, for the phenotypes reaching genome-wide significance in the combined meta-analysis. Analysis included 1344 individuals with time-weighted mean HbA1c <7.5% (58 mmol/mol), and 2977 with mean HbA1c ≥7.5% from the FinnDiane study; the individuals had median 19 HbA1c measurements (range 1–129).
Figure 5.
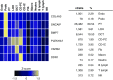
Single-cell RNA-sequencing in mouse kidney shows COL4A3, SNCAIP, and BMP7 are specifically expressed in podocytes. Mean expression values of the genes were calculated in each cluster. The color scheme is on the basis of z-score distribution; the map shows genes with _z_-score >2. In the heatmap, each row represents one gene and each column is a single cell type. Percentages of assigned cell types are summarized in the right panel. CD-IC, collecting duct intercalated cell; CD-PC, collecting duct principal cell; CD-Trans, collecting duct transitional cell; DCT, distal convoluted tubule; Endo, containing endothelial, vascular, and descending loop of Henle; Fib, fibroblast; LOH, ascending loop of Henle; Lymph, lymphocyte; Macro, macrophage; Neutro, neutrophil; NK, natural killer cell; Podo, podocyte; PT, proximal tubule.
Comment in
- Biologic Underpinnings of Type 1 Diabetic Kidney Disease.
Sedor JR, Freedman BI. Sedor JR, et al. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2019 Oct;30(10):1782-1783. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2019080803. Epub 2019 Sep 19. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 31570541 Free PMC article. No abstract available. - Type IV collagen and diabetic kidney disease.
Miner JH. Miner JH. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2020 Jan;16(1):3-4. doi: 10.1038/s41581-019-0229-1. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 31728033 No abstract available. - Hypothesis as to How a Common Missense Mutation in COL4A3 May Confer Protection against Diabetic Kidney Disease.
Pieri M. Pieri M. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020 Mar;31(3):663-664. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2019090966. Epub 2020 Jan 27. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 31988270 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
- COL4A3 Gene Variants and Diabetic Kidney Disease in MODY.
Wang Y, Zhang J, Zhao Y, Wang S, Zhang J, Han Q, Zhang R, Guo R, Li H, Li L, Wang T, Tang X, He C, Teng G, Gu W, Liu F. Wang Y, et al. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2018 Aug 7;13(8):1162-1171. doi: 10.2215/CJN.09100817. Epub 2018 Jul 16. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2018. PMID: 30012629 Free PMC article. - Association of kidney structure-related gene variants with type 2 diabetes-attributed end-stage kidney disease in African Americans.
Guan M, Ma J, Keaton JM, Dimitrov L, Mudgal P, Stromberg M, Bonomo JA, Hicks PJ, Freedman BI, Bowden DW, Ng MC. Guan M, et al. Hum Genet. 2016 Nov;135(11):1251-1262. doi: 10.1007/s00439-016-1714-2. Epub 2016 Jul 26. Hum Genet. 2016. PMID: 27461219 Free PMC article. - Association between COL4A3 variant rs55703767 and susceptibility to diabetic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: results from the INDEED cohort study.
Li Z, Sun Z, Chang D, Zhu L, Chen M, Zhao M. Li Z, et al. Chin Med J (Engl). 2022 May 5;135(9):1129-1130. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000001955. Chin Med J (Engl). 2022. PMID: 35170513 Free PMC article. No abstract available. - Genetic predisposition to nephropathy and associated cardiovascular disease in people with type 1 diabetes: role of the angiotensinI-converting enzyme (ACE), and beyond; a narrative review.
Mohammedi K, Marre M, Alhenc-Gelas F. Mohammedi K, et al. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024 Dec 21;23(1):453. doi: 10.1186/s12933-024-02544-0. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024. PMID: 39709470 Free PMC article. Review. - Effects of a Novel COL4A3 Homozygous/Heterozygous Splicing Mutation on the Mild Phenotype in a Family With Autosomal Recessive Alport Syndrome and a Literature Review.
Chen D, Zhang L, Rao J, Zhou Y, Dai L, Huang S, Yang C, Bian Q, Zhang T, Yang X. Chen D, et al. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2025 Feb;13(2):e70053. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.70053. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2025. PMID: 39924725 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Whole-exome sequencing identifies novel protein-altering variants associated with serum apolipoprotein and lipid concentrations.
Sandholm N, Hotakainen R, Haukka JK, Jansson Sigfrids F, Dahlström EH, Antikainen AA, Valo E, Syreeni A, Kilpeläinen E, Kytölä A, Palotie A, Harjutsalo V, Forsblom C, Groop PH; FinnDiane Study Group. Sandholm N, et al. Genome Med. 2022 Nov 23;14(1):132. doi: 10.1186/s13073-022-01135-6. Genome Med. 2022. PMID: 36419110 Free PMC article. - Prioritization of Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers for Lupus Nephritis Based on Integrated Bioinformatics Analyses.
Chen Z, Lan R, Ye K, Chen H, Chen C, Xu Y. Chen Z, et al. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021 Oct 8;9:717234. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.717234. eCollection 2021. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34692653 Free PMC article. - Epigenetic regulation of core genes linking to diabetic nephropathy progression: Lesson from FinnDiane type 1 diabetes study.
Makino H, Kanasaki K. Makino H, et al. J Diabetes Investig. 2023 Dec;14(12):1341-1343. doi: 10.1111/jdi.14083. Epub 2023 Sep 29. J Diabetes Investig. 2023. PMID: 37772980 Free PMC article. - Impacts of SARS-CoV-2 on diabetes mellitus: A pre and post pandemic evaluation.
Nabi AHMN, Ebihara A, Shekhar HU. Nabi AHMN, et al. World J Virol. 2023 Jun 25;12(3):151-171. doi: 10.5501/wjv.v12.i3.151. World J Virol. 2023. PMID: 37396707 Free PMC article. Review. - Gaining insight into metabolic diseases from human genetic discoveries.
Claussnitzer M, Susztak K. Claussnitzer M, et al. Trends Genet. 2021 Dec;37(12):1081-1094. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2021.07.005. Epub 2021 Jul 24. Trends Genet. 2021. PMID: 34315631 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention : National Diabetes Statistics Report, 2017 Estimates of Diabetes and its Burden in the United States Background, Atlanta, GA, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, US Department of Health and Human Services, 2017
- Tuttle KR, Bakris GL, Bilous RW, Chiang JL, de Boer IH, Goldstein-Fuchs J, et al. .: Diabetic kidney disease: A report from an ADA Consensus conference. Am J Kidney Dis 64: 510–533, 2014 - PubMed
- Krolewski M, Eggers PW, Warram JH: Magnitude of end-stage renal disease in IDDM: A 35 year follow-up study. Kidney Int 50: 2041–2046, 1996 - PubMed
- Harjutsalo V, Katoh S, Sarti C, Tajima N, Tuomilehto J: Population-based assessment of familial clustering of diabetic nephropathy in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 53: 2449–2454, 2004 - PubMed
- Quinn M, Angelico MC, Warram JH, Krolewski AS: Familial factors determine the development of diabetic nephropathy in patients with IDDM. Diabetologia 39: 940–945, 1996 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 EY016379/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_PC_15025/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- K12 DK094721/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK036836/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK110919/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 090532/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R37 DK034818/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 098381/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 DK034818/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK017047/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K24 DK110550/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK094176/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK105154/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK094157/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK081943/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R00 HL122515/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous