Effects of Leucine-Enriched Whey Protein Supplementation on Physical Function in Post-Hospitalized Older Adults Participating in 12-Weeks of Resistance Training Program: A Randomized Controlled Trial - PubMed (original) (raw)
Randomized Controlled Trial
. 2019 Oct 1;11(10):2337.
doi: 10.3390/nu11102337.
Affiliations
- PMID: 31581591
- PMCID: PMC6835698
- DOI: 10.3390/nu11102337
Randomized Controlled Trial
Effects of Leucine-Enriched Whey Protein Supplementation on Physical Function in Post-Hospitalized Older Adults Participating in 12-Weeks of Resistance Training Program: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Maria Amasene et al. Nutrients. 2019.
Abstract
Age-related strength and muscle mass loss is further increased after acute periods of inactivity. To avoid this, resistance training has been proposed as an effective countermeasure, but the additional effect of a protein supplement is not so clear. The aim of this study was to examine the effect of a whey protein supplement enriched with leucine after resistance training on muscle mass and strength gains in a post-hospitalized elderly population. A total of 28 participants were included and allocated to either protein supplementation or placebo supplementation following resistance training for 12 weeks (2 days/week). Physical function (lower and upper body strength, aerobic capacity and the Short Physical Performance Battery (SPPB) test), mini nutritional assessment (MNA) and body composition (Dual X-ray Absorptiometry) were assessed at baseline and after 12 weeks of resistance training. Both groups showed improvements in physical function after the intervention (p < 0.01), but there were no further effects for the protein group (_p_ > 0.05). Muscle mass did not improve after resistance training in either group (p > 0.05). In conclusion, 12 weeks of resistance training are enough to improve physical function in a post-hospitalized elderly population with no further benefits for the protein-supplemented group.
Keywords: aging; elderly; leucine; muscle mass; protein supplementation; resistance training; strength; whey protein.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study, in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data, in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
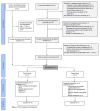
Figure 1
Flow Diagram of participants.
Similar articles
- Effects of Whey, Soy or Leucine Supplementation with 12 Weeks of Resistance Training on Strength, Body Composition, and Skeletal Muscle and Adipose Tissue Histological Attributes in College-Aged Males.
Mobley CB, Haun CT, Roberson PA, Mumford PW, Romero MA, Kephart WC, Anderson RG, Vann CG, Osburn SC, Pledge CD, Martin JS, Young KC, Goodlett MD, Pascoe DD, Lockwood CM, Roberts MD. Mobley CB, et al. Nutrients. 2017 Sep 4;9(9):972. doi: 10.3390/nu9090972. Nutrients. 2017. PMID: 28869573 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - A high whey protein-, leucine-, and vitamin D-enriched supplement preserves muscle mass during intentional weight loss in obese older adults: a double-blind randomized controlled trial.
Verreijen AM, Verlaan S, Engberink MF, Swinkels S, de Vogel-van den Bosch J, Weijs PJ. Verreijen AM, et al. Am J Clin Nutr. 2015 Feb;101(2):279-86. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.114.090290. Epub 2014 Nov 26. Am J Clin Nutr. 2015. PMID: 25646324 Clinical Trial. - Supplement-based nutritional strategies to tackle frailty: A multifactorial, double-blind, randomized placebo-controlled trial.
Roschel H, Hayashi AP, Fernandes AL, Jambassi-Filho JC, Hevia-Larraín V, de Capitani M, Santana DA, Gonçalves LS, de Sá-Pinto AL, Lima FR, Sapienza MT, Duarte AJS, Pereira RMR, Phillips SM, Gualano B. Roschel H, et al. Clin Nutr. 2021 Aug;40(8):4849-4858. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2021.06.024. Epub 2021 Jul 3. Clin Nutr. 2021. PMID: 34358827 Clinical Trial. - Whey Protein, Leucine- and Vitamin-D-Enriched Oral Nutritional Supplementation for the Treatment of Sarcopenia.
Cereda E, Pisati R, Rondanelli M, Caccialanza R. Cereda E, et al. Nutrients. 2022 Apr 6;14(7):1524. doi: 10.3390/nu14071524. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 35406137 Free PMC article. Review. - Effects of Whey Protein, Leucine, and Vitamin D Supplementation in Patients with Sarcopenia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.
Chang MC, Choo YJ. Chang MC, et al. Nutrients. 2023 Jan 19;15(3):521. doi: 10.3390/nu15030521. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 36771225 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- The Effects of Graded Protein Intake in Conjunction with Progressive Resistance Training on Skeletal Muscle Outcomes in Older Adults: A Preliminary Trial.
Michel JM, Lievense KK, Norton SC, Costa JV, Alphin KH, Bailey LA, Miller GD. Michel JM, et al. Nutrients. 2022 Jun 30;14(13):2739. doi: 10.3390/nu14132739. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 35807922 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Effects of Resistance Training Intervention along with Leucine-Enriched Whey Protein Supplementation on Sarcopenia and Frailty in Post-Hospitalized Older Adults: Preliminary Findings of a Randomized Controlled Trial.
Amasene M, Cadenas-Sanchez C, Echeverria I, Sanz B, Alonso C, Tobalina I, Irazusta J, Labayen I, Besga A. Amasene M, et al. J Clin Med. 2021 Dec 24;11(1):97. doi: 10.3390/jcm11010097. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 35011838 Free PMC article. - Delivery of a telehealth supported home exercise program with dietary advice to increase plant-based protein intake in people with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a 12-week randomised controlled feasibility trial.
Freer CL, George ES, Tan SY, Abbott G, Daly RM. Freer CL, et al. Br J Nutr. 2024 May 28;131(10):1709-1719. doi: 10.1017/S0007114524000242. Epub 2024 Jan 25. Br J Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38268105 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Effectiveness of Protein Supplementation Combined with Resistance Training on Muscle Strength and Physical Performance in Elderly: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.
Labata-Lezaun N, Llurda-Almuzara L, López-de-Celis C, Rodríguez-Sanz J, González-Rueda V, Hidalgo-García C, Muniz-Pardos B, Pérez-Bellmunt A. Labata-Lezaun N, et al. Nutrients. 2020 Aug 27;12(9):2607. doi: 10.3390/nu12092607. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32867103 Free PMC article. - Systematic review and meta-analysis of protein intake to support muscle mass and function in healthy adults.
Nunes EA, Colenso-Semple L, McKellar SR, Yau T, Ali MU, Fitzpatrick-Lewis D, Sherifali D, Gaudichon C, Tomé D, Atherton PJ, Robles MC, Naranjo-Modad S, Braun M, Landi F, Phillips SM. Nunes EA, et al. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2022 Apr;13(2):795-810. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.12922. Epub 2022 Feb 20. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2022. PMID: 35187864 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Fielding R.A., Vellas B., Evans W.J., Bhasin S., Morley J.E., Newman A.B., Abellan van Kan G., Andrieu S., Bauer J., Breuille D., et al. Sarcopenia: An undiagnosed condition in older adults. Current consensus definition: Prevalence, etiology, and consequences. International working group on sarcopenia. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2011;12:249–256. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2011.01.003. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical