The New Biology of Diabetic Kidney Disease-Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
The New Biology of Diabetic Kidney Disease-Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications
Yuliya Lytvyn et al. Endocr Rev. 2020.
Abstract
Diabetic kidney disease remains the most common cause of end-stage kidney disease in the world. Despite reductions in incidence rates of myocardial infarction and stroke in people with diabetes over the past 3 decades, the risk of diabetic kidney disease has remained unchanged, and may even be increasing in younger individuals afflicted with this disease. Accordingly, changes in public health policy have to be implemented to address the root causes of diabetic kidney disease, including the rise of obesity and diabetes, in addition to the use of safe and effective pharmacological agents to prevent cardiorenal complications in people with diabetes. The aim of this article is to review the mechanisms of pathogenesis and therapies that are either in clinical practice or that are emerging in clinical development programs for potential use to treat diabetic kidney disease.
© Endocrine Society 2019. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
Graphical Abstract
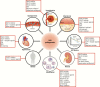
Figure 1.
Proposed anti-inflammatory mechanisms in the kidney mediated by SGLT2 inhibition in diabetes. SGLT2, sodium glucose co-transporter 2.
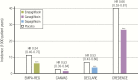
Figure 2.
Summary of renal composite outcomes with SGLT2 inhibition in EMPA-REG OUTCOME, CANVAS, DECLARE, and CREDENCE Trials. The renal composite outcome shown for EMPA-REG, CANVAS, and CREDENCE is incident or worsening nephropathy, defined as progression to macroalbuminuria; a doubling of the serum creatinine level; the initiation of renal-replacement therapy; or death from renal disease. For DECLARE, the renal composite outcome shown is sustained decline of at least 40% in estimated glomerular filtration rate to <60 mL/min/1.73 m2, end-stage renal disease, or death from renal causes. CANVAS, Canagliflozin Cardiovascular Assessment Study; CREDENCE, Evaluation of the Effects of Canagliflozin on Renal and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Participants with Diabetic Nephropathy; DECLARE, Dapagliflozin Effect on Cardiovascular Events; EMPA-REG, Empagliflozin, Cardiovascular Outcomes, and Mortality in Type 2 Diabetes; HR, hazard ratio.
Figure 3.
Forest plot of hazard ratios for the primary and secondary outcomes of the SONAR Trial. Composite renal outcome: composite of doubling of serum creatinine (sustained for ≥30 days) or end-stage kidney disease (eGFR <15 mL/min/1.73 m2 sustained for ≥90 days, chronic dialysis for ≥90 days, kidney transplantation, or death from kidney failure. Cardiorenal composite endpoint: doubling serum creatinine, end-stage kidney disease, cardiovascular death, nonfatal myocardial infarction, or non-fatal stroke. Primary outcome in all patients (responders and nonresponders combined). Cardiovascular composite endpoint: cardiovascular death, nonfatal myocardial infarction, or non-fatal stroke. Abbreviations: CI, confidence interval; eGFR, glomerular filtration rate; SONAR, Study of Diabetic Nephropathy with Atrasentan.
Similar articles
- New Glucose-Lowering Agents for Diabetic Kidney Disease.
de Vos LC, Hettige TS, Cooper ME. de Vos LC, et al. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2018 Mar;25(2):149-157. doi: 10.1053/j.ackd.2018.01.002. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2018. PMID: 29580579 Review. - Effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists on kidney function and safety in type 2 diabetes patients.
Kim MK, Kim DM. Kim MK, et al. J Diabetes Investig. 2021 Jun;12(6):914-916. doi: 10.1111/jdi.13552. Epub 2021 May 7. J Diabetes Investig. 2021. PMID: 33759351 Free PMC article. Review. - Combination therapy for kidney disease in people with diabetes mellitus.
van Raalte DH, Bjornstad P, Cherney DZI, de Boer IH, Fioretto P, Gordin D, Persson F, Rosas SE, Rossing P, Schaub JA, Tuttle K, Waikar SS, Heerspink HJL. van Raalte DH, et al. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2024 Jul;20(7):433-446. doi: 10.1038/s41581-024-00827-z. Epub 2024 Apr 3. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 38570632 Review. - New strategies to tackle diabetic kidney disease.
Batu Demir D, Cooper ME. Batu Demir D, et al. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2016 Jul;25(4):348-54. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0000000000000234. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2016. PMID: 27138228 Review. - Novel therapeutic agents for the treatment of diabetic kidney disease.
Hartman RE, Rao PSS, Churchwell MD, Lewis SJ. Hartman RE, et al. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2020 Nov;29(11):1277-1293. doi: 10.1080/13543784.2020.1811231. Epub 2020 Sep 14. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2020. PMID: 32799584 Review.
Cited by
- Recent Advances in the Emerging Therapeutic Strategies for Diabetic Kidney Diseases.
Huang W, Chen YY, Li ZQ, He FF, Zhang C. Huang W, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 17;23(18):10882. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810882. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36142794 Free PMC article. Review. - Renal Proximal Tubular Cells: A New Site for Targeted Delivery Therapy of Diabetic Kidney Disease.
Li H, Dai W, Liu Z, He L. Li H, et al. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Nov 30;15(12):1494. doi: 10.3390/ph15121494. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36558944 Free PMC article. Review. - Regeneration of glomerular metabolism and function by podocyte pyruvate kinase M2 in diabetic nephropathy.
Fu J, Shinjo T, Li Q, St-Louis R, Park K, Yu MG, Yokomizo H, Simao F, Huang Q, Wu IH, King GL. Fu J, et al. JCI Insight. 2022 Mar 8;7(5):e155260. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.155260. JCI Insight. 2022. PMID: 35133981 Free PMC article. - Recent Advances in the Management of Diabetic Kidney Disease: Slowing Progression.
Wang N, Zhang C. Wang N, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 7;25(6):3086. doi: 10.3390/ijms25063086. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38542060 Free PMC article. Review. - Exploring the relations of NLR, hsCRP and MCP-1 with type 2 diabetic kidney disease: a cross-sectional study.
Fang Y, Wang B, Pang B, Zhou Z, Xing Y, Pang P, Zheng D, Zhang G, Yang B. Fang Y, et al. Sci Rep. 2024 Feb 8;14(1):3211. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-53567-2. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38332001 Free PMC article.
References
- Collins AJ, Foley RN, Herzog C, et al. US renal data system 2010 annual data report. Am J Kidney Dis. 2011;57(1 Suppl 1):A8, e1-526. - PubMed
- Ziyadeh FN. Mediators of diabetic renal disease: the case for tgf-Beta as the major mediator. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004;15 Suppl 1:S55–S57. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous