Cognitive rehabilitation for attention deficits following stroke - PubMed (original) (raw)
Meta-Analysis
Cognitive rehabilitation for attention deficits following stroke
Tobias Loetscher et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019.
Abstract
Background: Many survivors of stroke report attentional impairments, such as diminished concentration and distractibility. However, the effectiveness of cognitive rehabilitation for improving these impairments is uncertain.This is an update of the Cochrane Review first published in 2000 and previously updated in 2013.
Objectives: To determine whether people receiving cognitive rehabilitation for attention problems 1. show better outcomes in their attentional functions than those given no treatment or treatment as usual, and 2. have a better functional recovery, in terms of independence in activities of daily living, mood, and quality of life, than those given no treatment or treatment as usual.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Stroke Group Trials Register, CENTRAL, MEDLINE, Embase, CINAHL, PsycINFO, PsycBITE, REHABDATA and ongoing trials registers up to February 2019. We screened reference lists and tracked citations using Scopus.
Selection criteria: We included controlled clinical trials (CCTs) and randomised controlled trials (RCTs) of cognitive rehabilitation for impairments of attention for people with stroke. We did not consider listening to music, meditation, yoga, or mindfulness to be a form of cognitive rehabilitation. We only considered trials that selected people with demonstrable or self-reported attentional deficits. The primary outcomes were measures of global attentional functions, and secondary outcomes were measures of attentional domains (i.e. alertness, selective attention, sustained attention, divided attention), functional abilities, mood, and quality of life.
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently selected trials, extracted data, and assessed the risk of bias. We used the GRADE approach to assess the certainty of evidence for each outcome.
Main results: We included no new trials in this update. The results are unchanged from the previous review and are based on the data of six RCTs with 223 participants. All six RCTs compared cognitive rehabilitation with a usual care control. Meta-analyses demonstrated no convincing effect of cognitive rehabilitation on subjective measures of attention either immediately after treatment (standardised mean difference (SMD) 0.53, 95% confidence interval (CI) -0.03 to 1.08; P = 0.06; 2 studies, 53 participants; very low-quality evidence) or at follow-up (SMD 0.16, 95% CI -0.23 to 0.56; P = 0.41; 2 studies, 99 participants; very low-quality evidence). People receiving cognitive rehabilitation (when compared with control) showed that measures of divided attention recorded immediately after treatment may improve (SMD 0.67, 95% CI 0.35 to 0.98; P < 0.0001; 4 studies, 165 participants; low-quality evidence), but it is uncertain that these effects persisted (SMD 0.36, 95% CI -0.04 to 0.76; P = 0.08; 2 studies, 99 participants; very low-quality evidence). There was no evidence for immediate or persistent effects of cognitive rehabilitation on alertness, selective attention, and sustained attention. There was no convincing evidence for immediate or long-term effects of cognitive rehabilitation for attentional problems on functional abilities, mood, and quality of life after stroke.
Authors' conclusions: The effectiveness of cognitive rehabilitation for attention deficits following stroke remains unconfirmed. The results suggest there may be an immediate effect after treatment on attentional abilities, but future studies need to assess what helps this effect persist and generalise to attentional skills in daily life. Trials also need to have higher methodological quality and better reporting.
Copyright © 2019 The Cochrane Collaboration. Published by John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
TL: none.
KJM: none.
DW: none.
RdN: none.
Figures
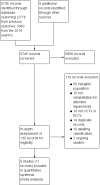
1
Study flow diagram. CCT: controlled clinical trial; RCT: randomised controlled trial.
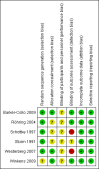
2
Risk of bias summary: review authors' judgements about each risk of bias item for each included study.
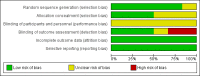
3
Risk of bias graph: review authors' judgements about each risk of bias item presented as percentages across all included studies.
Update of
- Cognitive rehabilitation for attention deficits following stroke.
Loetscher T, Lincoln NB. Loetscher T, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 May 31;2013(5):CD002842. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002842.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. PMID: 23728639 Free PMC article. Updated. Review.
Similar articles
- Cognitive rehabilitation for attention deficits following stroke.
Loetscher T, Lincoln NB. Loetscher T, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 May 31;2013(5):CD002842. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002842.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. PMID: 23728639 Free PMC article. Updated. Review. - Occupational therapy for cognitive impairment in stroke patients.
Gibson E, Koh CL, Eames S, Bennett S, Scott AM, Hoffmann TC. Gibson E, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Mar 29;3(3):CD006430. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006430.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35349186 Free PMC article. Review. - Non-pharmacological interventions for spatial neglect or inattention following stroke and other non-progressive brain injury.
Longley V, Hazelton C, Heal C, Pollock A, Woodward-Nutt K, Mitchell C, Pobric G, Vail A, Bowen A. Longley V, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Jul 1;7(7):CD003586. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003586.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34196963 Free PMC article. - Cognitive rehabilitation for spatial neglect following stroke.
Bowen A, Hazelton C, Pollock A, Lincoln NB. Bowen A, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Jul 1;2013(7):CD003586. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003586.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. PMID: 23813503 Free PMC article. Updated. Review. - Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) for improving activities of daily living, and physical and cognitive functioning, in people after stroke.
Elsner B, Kugler J, Pohl M, Mehrholz J. Elsner B, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Nov 11;11(11):CD009645. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009645.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33175411 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Psychological interventions for mood and cognition after stroke and transient ischaemic attack: A protocol for an umbrella review.
Kontou E, Shokraneh F, das Nair R, Quinn T, Leonardi-Bee J, Thorpe N, Clifford N, Williams M, Wydera S, Drummond A. Kontou E, et al. F1000Res. 2024 May 17;13:199. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.146343.2. eCollection 2024. F1000Res. 2024. PMID: 38817735 Free PMC article. - Inconclusive results of slow cortical potential neurofeedback for the treatment of chronic post-stroke attention deficits.
Kleih SC, Botrel L. Kleih SC, et al. Front Hum Neurosci. 2024 Apr 5;18:1301622. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2024.1301622. eCollection 2024. Front Hum Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38646162 Free PMC article. - Efficacy of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation with different application parameters for post-stroke cognitive impairment: a systematic review.
Wang Y, Wang L, Ni X, Jiang M, Zhao L. Wang Y, et al. Front Neurosci. 2024 Mar 19;18:1309736. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1309736. eCollection 2024. Front Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38567284 Free PMC article. Review.
References
References to studies included in this review
Barker‐Collo 2009 {published and unpublished data}
- Barker‐Collo SL, Feigin VL, Lawes CM, Parag V, Senior H, Rodgers A. Reducing attention deficits after stroke using attention process training: a randomized controlled trial. Stroke 2009;40:3293‐8. - PubMed
Röhring 2004 {published and unpublished data}
- Röhring S, Kulke H, Reulbach U, Peetz H, Schupp W. Effectivity of a neuropsychological training in attention functions by a teletherapeutic setting. Neurologie und Rehabilitation 2004;10(5):239‐46.
Schottke 1997 {published and unpublished data}
- Schottke H. Rehabilitation of attention deficits after stroke – efficacy of a Neuropsychological training program for attention deficits [Rehabilitation von Aufmerksamkeitsstörungen nach einem Schlaganfall – Effektivität eines verhaltensmedizinisch‐neuropsychologischen Aufmerksamkeitstrainings]. Verhaltenstherapie 1997;7:21‐3.
Sturm 1991 {published and unpublished data}
- Sturm W, Willmes K. Efficacy of a reaction training on various attentional and cognitive functions in stroke patients. Neuropsychological Rehabilitation 1991;1:259‐80.
Westerberg 2007 {published and unpublished data}
- Westerberg H, Jacobaeus H, Hirvikoski T, Clevberger P, Ostensson ML, Bartfai A, et al. Computerized working memory training after stroke – a pilot study. Brain Injury 2007;21(1):21‐9. - PubMed
Winkens 2009 {published and unpublished data}
- Winkens I, Heugten CM, Wade DT, Habets EJ, Fasotti L. Efficacy of time pressure management in stroke patients with slowed information processing: a randomized controlled trial. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2009;90(10):1672‐9. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Aben 2013 {published data only}
- Aben L, Heijenbrok‐Kal MH, Loon EM, Groet E, Ponds RW, Busschbach JJ, et al. Training memory self‐efficacy in the chronic stage after stroke: a randomized controlled trial. Neurorehabilitation and Neural Repair 2013;27(2):110‐7. - PubMed
Aivazian 1994 {published data only}
- Aivazian TA, Zaitsev VP, Taravkova IA, Gorbunov FE, Maslovskaia SG, Strelnikov AV. The relaxation psychotherapy of patients with cerebrovascular diseases: its efficacy and predictors. Voprosy Kurortologii, Fizioterapii, i Lechebnoi Fizicheskoi Kultury 1994;2:2‐4. - PubMed
Akinwuntan 2010 {published data only}
- Akinwuntan AE, Devos H, Verheyden G, Baten G, Kiekens C, Feys H, et al. Retraining moderately impaired stroke survivors in driving‐related visual attention skills. Topics in Stroke Rehabilitation 2010;17:328‐36. - PubMed
Albrittain‐Ross 2017 {published data only}
- Albrittain‐Ross N, Ross K, Gilmore N, Kiran S. Intensive cognitive communication rehabilitation (ICCR) program for young adults with acquired brain injury. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2017;98(10):e76.
Alexopoulos 2012 {published data only}
Arnemann 2015 {published data only}
Bergquist 2012 {published data only}
- Bergquist T, Yutsis M. The effect of cognitive rehabilitation delivered via instant messaging on functional independence in persons with acquired brain injury. Brain Injury 2012; Vol. 26, issue 4‐5:700‐1.
Bertens 2015 {published data only}
- Bertens D, Kessels RP, Fiorenzato E, Boelen DH, Fasotti L. Do old errors always lead to new truths? A randomized controlled trial of errorless goal management training in brain‐injured patients. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society 2015;21(8):639‐49. - PubMed
Bezdenezhnykh 2015 {published data only}
- Bezdenezhnykh A, Prokopenko S, Mozheiko E, Petrova M, Grippa E, Lipatnikova S, et al. Neuropsychological computer training versus entertaining computer games in patients with post‐stroke cognitive impairments: randomized clinical study. International Journal of Stroke 2015; Vol. 10 Suppl 2:412.
Blanchet 2016 {published data only}
- Blanchet S, Richards CL, Leblond J, Olivier C, Maltais DB. Cardiorespiratory fitness and cognitive functioning following short‐term interventions in chronic stroke survivors with cognitive impairment: a pilot study. International Journal of Rehabilitation Research 2016;39(2):153‐9. - PubMed
Bo 2019 {published data only}
- Bo W, Lei M, Tao S, Jie LT, Qian L, Lin FQ, et al. Effects of combined intervention of physical exercise and cognitive training on cognitive function in stroke survivors with vascular cognitive impairment: a randomized controlled trial. Clinical Rehabilitation 2019;33(1):54‐63. - PubMed
Boman 2004 {published data only}
- Boman IL, Lindstedt M, Hemmingsson H, Bartfai A. Cognitive training in home environment. Brain Injury 2004;18(10):985‐95. - PubMed
Carelli 2009 {published data only}
- Carelli L, Morganti F, Poletti B, Corra B, Weiss PL, Kizony R, et al. A NeuroVR based tool for cognitive assessment and rehabilitation of post‐stroke patients: two case studies. Annual Review of CyberTherapy and Telemedicine 2009;7(1):243‐7. - PubMed
Carr 2012 {published data only}
- Carr B, Allaous J, Lannin N, MacKenzie B, Falcon A, Tate R, et al. Efficacy of using handheld computers plus occupational therapy training to compensate for memory and planning difficulties after brain injury: a randomised control trial. Neurorehabilitation and Neural Repair 2012; Vol. 26, issue 6:687.
Chen 2011 {published data only}
Chen 2015 {published data only}
- Chen C‐X, Mao R‐H, Li S‐X, Zhao Y‐N, Zhang M. Effect of visual training on cognitive function in stroke patients. International Journal of Nursing Sciences 2015;2(4):329‐33.
Cho 2016 {published data only}
Chung 2013 {published data only}
- Chung C, Pollock A, Campbell T, Durward B, Hagen S. Cognitive rehabilitation for executive dysfunction in adults with stroke or other adult nonprogressive acquired brain damage. Stroke 2013;44:e77‐8. - PubMed
Crotty 2009 {published data only}
- Crotty M, George S. Retraining visual processing skills to improve driving ability after stroke. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2009;90:2096‐102. - PubMed
De Luca 2014 {published data only}
- Luca R, Calabro RS, Gervasi G, Salvo S, Bonanno L, Corallo F, et al. Is computer‐assisted training effective in improving rehabilitative outcomes after brain injury? A case‐control hospital‐based study. Disability and Health Journal 2014;7(3):356‐60. - PubMed
De Luca 2018a {published data only}
- Luca R, Leonardi S, Spadaro L, Russo M, Aragona B, Torrisi M, et al. Improving cognitive function in patients with stroke: can computerized training be the future?. Journal of Stroke and Cerebrovascular Diseases 2018;27(4):1055‐60. - PubMed
De Luca 2018b {published data only}
- Luca R, Russo M, Naro A, Tomasello P, Leonardi S, Santamaria F, et al. Effects of virtual reality‐based training with BTs‐Nirvana on functional recovery in stroke patients: preliminary considerations. International Journal of Neuroscience 2018;128(9):791‐6. - PubMed
Dirette 2004 {published data only}
- Dirette D. A comparison of attention, processing and strategy use by adults with and without acquired brain injuries. Brain Injury 2004;12:1219‐27. - PubMed
Edmans 2009 {published data only}
- Edmans J, Gladman J, Hilton D, Walker M, Sunderland A, Cobb S, et al. Clinical evaluation of a non‐immersive virtual environment in stroke rehabilitation. Clinical Rehabilitation 2009;23(2):106‐16. - PubMed
Faria 2016 {published data only}
Gates 2011 {published data only}
Gauggel 1996 {published data only}
- Gauggel S, Niemann T. Evaluation of a short‐term computer‐assisted training programme for the remediation of attentional deficits after brain injury: a preliminary study. International Journal of Rehabilitation Research 1996;19(3):229‐39. - PubMed
Giaquinto 2003 {published data only}
- Giaquinto S, Fraioli L. Enhancement of the somatosensory N140 component during attentional training after stroke. Clinical Neurophysiology 2003;114(2):329‐35. - PubMed
Gracey 2017 {published data only}
- Gracey F, Fish JE, Greenfield E, Bateman A, Malley D, Hardy G, et al. A randomized controlled trial of assisted intention monitoring for the rehabilitation of executive impairments following acquired brain injury. Neurorehabilitation and Neural Repair 2017;31(4):323‐33. - PubMed
Graf 2011 {published data only}
- Graf J, Kulke H, Sous‐Kulke C, Schupp W, Lautenbacher S. Effects of an attention training on the aphasic symptomatology in stroke patients. Zeitschrift fur Neuropsychologie 2011;22(1):21‐32.
Gray 1992 {published data only}
- Gray JM, Robertson I, Pentland B, Anderson S. Microcomputer‐based attentional retraining after brain damage: a randomised group controlled trial. Neuropsychological Rehabilitation 1992;2(2):97‐115.
Hashimoto 2006 {published data only}
- Hashimoto K, Okamoto T, Watanabe S, Ohashi M. Effectiveness of a comprehensive day treatment program for rehabilitation of patients with acquired brain injury in Japan. Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine 2006;38(1):20‐5. - PubMed
Jiang 2016 {published data only}
- Jiang C, Yang S, Tao J, Huang J, Li Y, Ye H, et al. Clinical efficacy of acupuncture treatment in combination with RehaCom cognitive training for improving cognitive function in stroke: a 2 × 2 factorial design randomized controlled trial. Journal of the American Directors Association 2016;17(12):1114‐22. - PubMed
Kang 2008 {published data only}
- Kang YJ, Ku J, Han K, Kim SI, Yu TW, Lee JH, et al. Development and clinical trial of virtual reality‐based cognitive assessment in people with stroke: preliminary study. Cyberpsychology & Behavior 2008;11(3):329‐39. - PubMed
Kang 2009 {published data only}
- Kang EK, Baek MJ, Kim S, Paik NJ. Non‐invasive cortical stimulation improves post‐stroke attention decline. Restorative Neurology and Neuroscience 2009;27(6):645‐50. - PubMed
Kaur 2018 {published data only}
- Kaur H, Kumaran S, Bhatia R, Pandey RM, Chopra S, Nehra A. Non‐linguistic cognitive impairment and its relationship with language recovery post aphasia rehabilitation: a neuropsychological and fMRI study. International Journal of Stroke 2018;13 Suppl 2:61.
Kim 2008 {published data only}
- Kim YK, Seo CH, Park JW, Lee HJ, Shin SH. Effects of cognitive rehabilitative treatment using computerized program (RehaCom) in stroke patients. Neurorehabilitation and Neural Repair 2008;22(5):569.
Kim 2013 {published data only}
Klonoff 2010 {published data only}
- Klonoff PS, Olson KC, Talley MC, Husk KL, Myles SM, Gehrels JA, et al. The relationship of cognitive retraining to neurological patients' driving status: the role of process variables and compensation training. Brain Injury 2010;24(2):63‐73. - PubMed
Levine 2011 {published data only}
Mazer 2003 {published data only}
- Mazer BL, Sofer S, Korner‐Bitensky N, Gelinas I, Hanley J, Wood‐Dauphinee S. Effectiveness of a visual attention retraining program on the driving performance of clients with stroke. Archives Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2003;84:541‐50. - PubMed
McDonnell 2007 {published data only}
- McDonnell MN, Hillier SL, Miles TS, Thompson PD, Ridding MC. Influence of combined afferent stimulation and task‐specific training following stroke: a pilot randomized controlled trial. Neurorehabilitation & Neural Repair 2007;21(5):435‐43. - PubMed
Mead 2007 {published data only}
- Mead GE, Greig CA, Cunningham I, Lewis SJ, Dinn S, Saunders DH, et al. Stroke: a randomized trial of exercise or relaxation. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2007;55(6):892‐9. - PubMed
Middleton 1991 {published data only}
- Middleton DK, Lambert MJ, Seggar LB. Neuropsychological rehabilitation: microcomputer‐assisted treatment of brain‐injured adults. Perceptual and Motor Skills 1991;72(2):527‐30. - PubMed
Miotto 2009 {published data only}
- Miotto EC, Evans JJ, Lucia MC, Scaff M. Rehabilitation of executive dysfunction: a controlled trial of an attention and problem solving treatment group. Neuropsychological Rehabilitation 2009;19(4):517‐40. - PubMed
NCT00298558 {published data only}
- NCT00298558. ACTIVE: advanced cognitive training for independent and vital elderly. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00298558 (first received 2 March 2006).
NCT01109836 {published data only}
- NCT01109836. Austrian Polyintervention Study to Prevent Cognitive Decline After Ischemic Stroke (ASPIS). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01109836 (first received 23 April 2010).
NCT01365858 {published data only}
- NCT01365858. Virtual Action Planning in Stroke: a control rehabilitation study (VAPS REHAB). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01365858 (first received 3 June 2011).
NCT01372059 {published data only}
- NCT01372059. The effects of a rhythm and music‐based therapy program and therapeutic riding in late recovery phase following stroke. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01372059 (first received 13 June 2011).
NCT01886183 {published data only}
- NCT01886183. Effects of training in a virtual environment in chronic stroke patients. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01886183 (first received 25 June 2013).
NCT02482688 {published data only}
- NCT02482688. A new rehabilitation treatment following stroke. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02482688 (first received 26 June 2015).
Otfinowski 2006 {published data only}
- Otfinowski J, Jasiak‐Tyrkalska B, Starowicz A, Regula K. Computer‐based rehabilitation of cognitive impairments and motor arm function of patients with hemiparesis after stroke. Neurologia i Neurochirurgia Polska 2006;40:112‐8. - PubMed
Park 2015 {published data only}
Park 2018 {published data only}
Piccardi 2006 {published data only}
- Piccardi L, Nico D, Bureca I, Matano A, Guariglia C. Efficacy of visuo‐spatial training in right‐brain damaged patients with spatial hemineglect and attention disorders. Cortex 2006;42(7):973‐82. - PubMed
Ploughman 2008 {published data only}
- Ploughman M, McCarthy J, Bosse M, Sullivan HJ, Corbett D. Does treadmill exercise improve performance of cognitive or upper‐extremity tasks in people with chronic stroke? A randomized cross‐over trial. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2008;89(11):2041‐7. - PubMed
Ploughman 2017 {published data only}
- Ploughman M, Eskes GA, Kelly LP, Kirkland MC, Devasayaham AJ, Wallack EM, et al. Aerobic exercise enhances the beneficial effects of cognitive training and reopens the 'window of recovery' in chronic stroke via neurotrophins. International Journal of Stroke 2017; Vol. 12 Suppl 4:18‐9.
Prokopenko 2013 {published data only}
- Prokopenko SV, Mozheyko EY, Petrova MM, Koryagina TD, Kaskaeva DS, Chernykh TV, et al. Correction of post‐stroke cognitive impairments using computer programs. Journal of the Neurological Sciences 2013;325:148‐53. - PubMed
Pulin 2017 {published data only}
- Pulin V, Korner‐Bitensky N, Bherer L, Lussier M, Dawson DR. Comparison of two cognitive interventions for adults experiencing executive dysfunction post‐stroke: a pilot study. Disability and Rehabilitation 2017;39(1):1‐13. - PubMed
Pyoria 2007 {published data only}
- Pyoria O, Talvitie U, Nyrkko H, Kautiainen H, Pohjolainen T, Kasper V. The effect of two physiotherapy approaches on physical and cognitive functions and independent coping at home in stroke rehabilitation. A preliminary follow‐up study. Disability & Rehabilitation 2007;29(6):503‐11. - PubMed
Pyun 2009 {published data only}
- Pyun SB, Yang H, Lee S, Yook J, Kwon J, Byun EM. A home programme for patients with cognitive dysfunction: a pilot study. Brain Injury 2009;23:686‐92. - PubMed
Quaney 2009 {published data only}
Ressner 2018 {published data only}
- Ressner P, Krulová P, Beránková D, Nilius P, Bártová P, Zapletalová J, et al. Effect of a combined approach to cognitive rehabilitation in post‐stroke patients. Česká a Slovenská Neurologie a Neurochirurgie 2018;81(3):314‐9.
Rizkalla 2011 {published data only}
- Rizkalla MN, Tippett WJ. Examining a visuospatial/visuomotor training program as an intervention to induce a cognitive change during acute post‐stroke recovery. Stroke 2011;42(11):e618.
Särkämö 2008 {published data only}
- Särkämö T, Tervaniemi M, Laitinen S, Forsblom A, Soinila S, Mikkonen M, et al. Music listening enhances cognitive recovery and mood after middle cerebral artery stroke. Brain 2008;131:866‐76. - PubMed
Särkämö 2010 {published data only}
- Särkämö T, Pihko E, Laitinen S, Forsblom A, Soinila S, Mikkonen M, et al. Music and speech listening enhance the recovery of early sensory processing after stroke. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience 2010;22:2716‐27. - PubMed
Shi 2017 {published data only}
- Shi Y, Zhang Z. Effect of comprehensive rehabilitation training on prevention of post‐stroke dementia: a randomized controlled trial. International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Medicine 2017;10(5):7760‐6.
Shiflett 2002 {published data only}
- Shiflett SC, Nayak S, Bid C, Miles P, Agostinelli S. Effect of Reiki treatments on functional recovery in patients in poststroke rehabilitation: a pilot study. Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine 2002;8(6):755‐63. - PubMed
Skidmore 2014 {published data only}
Skidmore 2015 {published data only}
Sohlberg 2000 {published data only}
- Sohlberg MM, McLaughlin KA, Pavese A, Heidrich A, Posner MI. Evaluation of attention process training and brain injury education in persons with acquired brain injury. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology 2000;22(5):656‐76. - PubMed
Spahn 2010 {published data only}
- Spahn V, Kulke H, Kunz M, Thone‐Otto A, Schupp W, Lautenbacher S. Is the neuropsychological treatment of memory specific or unspecific? Comparing treatment effects on memory and attention. Zeitschrift fur Neuropsychologie 2010;21(4):239‐45.
Spikman 2010 {published data only}
- Spikman JM, Boelen DH, Lamberts KF, Brouwer WH, Fasotti L. Effects of a multifaceted treatment program for executive dysfunction after acquired brain injury on indications of executive functioning in daily life. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society 2010;16:118‐29. - PubMed
Stapleton 2001 {published data only}
- Stapleton T, Ashburn A, Stack E. A pilot study of attention deficits, balance control and falls in the subacute stage following stroke. Clinical Rehabilitation 2001;15(4):437‐44. - PubMed
Sturm 1997 {published data only}
- Sturm W, Willmes K, Orgass B, Hartje W. Do specific attention deficits need specific training?. Neuropsychological Rehabilitation 1997;7(2):81‐103.
Sturm 2006 {published data only}
- Sturm W, Thimm A, Küst J, Karbe H, Fink GR. Alertness‐training in neglect: behavioral and imaging results. Restorative Neurology and Neuroscience 2006;24:371‐84. - PubMed
Thimm 2006 {published data only}
- Thimm M, Fink GR, Küst J, Karbe H, Sturm W. Impact of alertness training on spatial neglect: a behavioural and fMRI study. Neuropsychologia 2006;44(7):1230‐46. - PubMed
Tornas 2014 {published data only}
- Tornas S, Lovstad M, Solbakk A‐K, Host K, Schanke A‐K, Stubberud J. Goal management training in patients with acquired brain injury – preliminary results. Brain Injury 2014;28(5‐6):569‐70.
Van de Ven 2017 {published data only}
Villalobos 2018 {published data only}
- Villalobos D, Bilbao Á, Espejo A, García‐Pacios J. Efficacy of an intervention programme for rehabilitation of awareness of deficit after acquired brain injury: a pilot study. Brain Injury 2018;32(2):158‐66. - PubMed
Von Koch 2000 {published data only}
- Koch L, Holmqvist LW, Wottrich AW, Tham K, Pedro‐Cuesta J. Rehabilitation at home after stroke: a descriptive study of an individualized intervention. Clinical Rehabilitation 2000;14(6):574‐83. - PubMed
Wagenaar 1992 {published data only}
- Wagenaar RC, Wieringen PC, Netelenbos JB, Meijer OG, Kuik DJ. The transfer of scanning training effects in visual inattention after stroke: five single‐case studies. Disability & Rehabilitation 1992;14(1):51‐60. - PubMed
Wentink 2016 {published data only}
- Wentink MM, Berger MA, Kloet AJ, Meesters J, Band GP, Wolterbeek R, et al. The effects of an 8‐week computer‐based brain training programme on cognitive functioning, QoL and self‐efficacy after stroke. Neuropsychological Rehabilitation 2016;26:847‐65. - PubMed
Yamamoto‐Mitani 2007 {published data only}
- Yamamoto‐Mitani N, Matsuoka K, Fujii M. Home‐based rehabilitation program for older adults with cognitive impairment: preliminary results. Psychogeriatrics 2007;7(1):14‐20.
Zucchella 2014 {published data only}
References to studies awaiting assessment
Bartfai 2014 {published data only}
Bayat 2014 {published data only}
- Bayat G, Dastgheib S, Shoeibi A. The impact of program based computer software versus Mozart's music on hemiparetic patients using magnetic resonance spectroscopy: a randomized control trial study. International Journal of Stroke 2014; Vol. 9 Suppl 3:218.
Bushnick 2010 {published data only}
- Bushnick T, Englander J, Oggins J, Levinson R, Halper D. A randomized clinical trial of a cognitive orthotic with executive planning capability in individuals with cognitive dysfunction. Brain Injury 2010;24(3):392‐3.
Chen 2018 {published data only}
- Chen BY, Aldhukair H, Cote J, Flinois J, Hoang T, Shen HC, et al. Early tablet‐assisted cognitive rehabilitation for aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: feasibility of a single‐center randomized controlled trial. Neurology 2018;90 Suppl 1:P3.227.
Dawson 2017 {published data only}
- Dawson D, Bar Y, McEwen S, Skidmore E, Nalder E, Anderson N, et al. Enhancing participation in everyday life for people with stroke via telerehabilitation: a randomized controlled trial. International Journal of Stroke 2017; Vol. 12 Suppl 4:87.
Flynn 2000 {published data only}
- Flynn A. Investigation into whether psychology led cognitive rehabilitation of attentional and visio‐spatial skills improves performance in these areas beyond spontaneous recovery. National Research Register (N0280012930).
Frommelt 2003 {published data only}
- Frommelt P. Neurophysiological rehabilitation: modular cognitive retraining versus compensatory skills. www.isrctn.com/ISRCTN45171788 (first received 1 August 2003). [ISRCTN45171788]
Gil‐Pages 2018 {published data only}
Holleman 2012 {published data only}
- Holleman M, Vink M, Horst R, Luijpen M, Rienstra A, Schmand B. Effects of a holistic neuropsychological rehabilitation programme (Intensive NeuroRehabilitation, INR) on emotional well‐being, coping, and quality of life after acquired brain injury. Brain Impairment 2012;13(1):136‐7.
Huang 2015 {published data only}
Kaur 2016 {published data only}
- Kaur H, Bhatia R, Pandey RM, Chopra S, Nehra A. Effectiveness of using a home‐based comprehensive neuropsychological rehabilitation with aphasia therapy in patients with post stroke aphasia: a preliminary study. International Journal of Stroke 2016;11 Suppl 3:228.
Matz 2007 {published data only}
- Matz K, Teuschl Y, Eckhardt R, Herbst A, Dachenhausen A, Brainin M. Cognitive training in patients with first lacunar stroke – a randomized pilot trial for the prevention of post‐stroke cognitive decline. Cerebrovascular Diseases 2007;23 Suppl 2:42.
Oh 2017 {published data only}
- Oh EY, Jung MS. Effects of a cognitive training program on cognitive function and activities of daily living in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2017;47(1):1‐13. - PubMed
Peers 2018 {published data only}
- Peers PV, Bishop S, Murphy F, Duncan J, Astle DE, Watson P, et al. Home‐based cognitive training in stroke: implications for cognition and everyday functioning. International Journal of Stroke 2018;13 Suppl 3:51.
Zhang 2016 {published data only}
- Zhang H, Yun X, Zhang X, Shen M, Pan H, Zhang Y, et al. Efficacy of rehabilitation for impairments of attention. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2016;97(10):e131‐2.
Zhu 2011 {published data only}
- Zhu L, Song WQ, Yue YH, Liu L. Effect of computer‐assisted cognitive training on the cognitive function and depression in patients with brain injury. Chinese Journal of Cerebrovascular Diseases 2011;8(10):508‐12.
References to ongoing studies
Donnellan 2014 {published data only}
- Donnellan C. REsources And LIfe Strategy Management (REALISM) trial: protocol for a stroke rehabilitation intervention using a goal setting and attainment framework. International Journal of Stroke 2014; Vol. 9 Suppl 3:221.
NCT02925637 {published data only}
- NCT02925637. Effectiveness of FACoT for individuals post stroke. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02925637 (first received 6 October 2016).
Additional references
Barker‐Collo 2006
- Barker‐Collo S, Feigin V. The impact of neuropsychological deficits on functional stroke outcomes. Neuropsychology Review 2006;16:53‐64. - PubMed
Barker‐Collo 2010
- Barker‐Collo S, Feigin VL, Parag V, Lawes CMM, Senior H. Auckland Stroke Outcomes Study Part 2: cognition and functional outcomes 5 years poststroke. Neurology 2010;75:1608‐18. - PubMed
Ben‐Yishay 1990
- Ben‐Yishay Y, Prigatano GP. Cognitive remediation. In: Rosenthal M, Griffith ER, Bond MR, Miller JD editor(s). Rehabilitation of the Adult and Child with Traumatic Brain Injury. 2nd Edition. Philadelphia (PA): F.A. Davis, 1990:393‐409.
Bernhardt 2019
- Bernhardt J, Borschmann KN, Kwakkel G, Burridge JH, Eng JJ, Walker MF, et al. Setting the scene for the Second Stroke Recovery and Rehabilitation Roundtable. International Journal of Stroke 2019;14(5):450‐6. - PubMed
Bogdanova 2016
Bowen 2013
Broadbent 1982
- Broadbent DE, Cooper PF, FitzGerald P, Parkes KR. The Cognitive Failures Questionnaire (CFQ) and its correlates. British Journal of Clinical Psychology 1982;21:1‐16. - PubMed
Cappa 2005
- Cappa SF, Benke T, Clarke S, Rossi B, Stemmer B, Heugten CM. EFNS guidelines on cognitive rehabilitation: report of an EFNS task force. European Journal of Neurology 2005;12:665‐80. - PubMed
Cicerone 2000
- Cicerone KD, Dahlberg C, Kalmar K, Langenbahn DM, Malec JF, Bergquist TF, et al. Evidence‐based cognitive rehabilitation: recommendations for clinical practice. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2000;81:1596‐615. - PubMed
Cicerone 2002
- Cicerone KD. Remediation of "working attention" in mild traumatic brain injury. Brain Injury 2002;16:185‐95. - PubMed
Cicerone 2005
- Cicerone KD, Dahlberg C, Malec JF, Langenbahn DM, Felicetti T, Kneipp S, et al. Evidence‐based cognitive rehabilitation: updated review of the literature from 1998 through 2002. Archives of Physical and Medical Rehabilitation 2005;86:1681‐92. - PubMed
Cicerone 2011
- Cicerone KD, Langenbahn DM, Braden C, Malec JF, Kalmar K, Fraas M, et al. Evidence‐based cognitive rehabilitation: updated review of the literature from 2003 through 2008. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2011;92:519‐30. - PubMed
Cicerone 2019
- Cicerone KD, Goldin Y, Ganci K, Rosenbaum A, Wethe JV, Langenbahn DM, et al. Evidence‐based cognitive rehabilitation: systematic review of the literature from 2009 through 2014. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2019;100(8):1515‐33. - PubMed
Covidence [Computer program]
- Veritas Health Innovation. Covidence. Version accessed 23 January 2019. Melbourne, Australia: Veritas Health Innovation.
Duncan 2003
- Duncan PW, Bode RK, Lai SM, Perera S, Glycine Antagonist in Neuroprotection Americas Investigators. Rasch analysis of a new stroke‐specific outcome scale: the Stroke Impact Scale. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2003;84(7):950‐63. - PubMed
Goldberg 1972
- Goldberg DP. The Detection of Psychiatric Illness by Questionnaire. London (UK): Oxford University Press, 1972.
GRADEpro GDT 2015 [Computer program]
- McMaster University (developed by Evidence Prime). GRADEpro GDT. Version accessed 19 July 2019. Hamilton (ON): McMaster University (developed by Evidence Prime).
Granger 1994
- Granger CV, Hamilton BB. The uniform data system for medical rehabilitation. Report of first admissions for 1992. American Journal of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 1994;73:51‐5. - PubMed
Guyatt 2008
Higgins 2011
- Higgins JP, Green S, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org.
Hochstenbach 1998
- Hochstenbach J, Mulder T, Limbeek J, Donders R, Schoonderwaldt H. Cognitive decline following stroke: a comprehensive study of cognitive decline following stroke. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology 1998;20:503‐17. - PubMed
Hochstenbach 2003
- Hochstenbach JB, Otter R, Mulder TW. Cognitive recovery after stroke: a 2‐year follow‐up. Archives of Physical and Medical Rehabilitation 2003;84:1499‐504. - PubMed
Hoffmann 2014
- Hoffmann TC, Glasziou PP, Boutron I, Milne R, Perera R, Moher D, et al. Better reporting of interventions: template for intervention description and replication (TIDieR) checklist and guide. BMJ 2014;348:g1687. - PubMed
Hyndman 2003
- Hyndman D, Ashburn A. People with stroke living in the community: attention deficits, balance, ADL ability and falls. Disability and Rehabilitation 2003;25:817‐22. - PubMed
Hyndman 2008
- Hyndman D, Pickering RM, Ashburn A. The influence of attention deficits on functional recovery post stroke during the first 12 months after discharge from hospital. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry 2008;79:656‐63. - PubMed
Kwa 1996
- Kwa VIH, Limburg M, deHaan RJ. The role of cognitive impairment in the quality of life after ischaemic stroke. Journal of Neurology 1996;243:599‐604. - PubMed
Lefebvre 2011
- Lefebvre C, Manheimer E, Glanville J. Chapter 6: Searching for studies. In: Higgins JP, Green S, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org.
Lezak 2004
- Lezak MD, Howieson DB, Loring DW, Hannay HJ, Fischer JS. Neuropsychological Assessment. Oxford (UK): Oxford University Press, 2004.
Mahoney 1965
- Mahoney FI, Barthel D. Functional evaluation: the Barthel Index. Maryland State Medical Journal 1965;14:56‐65. - PubMed
McKevitt 2010
- McKevitt C, Fudge N, Redfern J, Sheldenkar A, Crichton S, Wolfe C. UK Stroke Survivor Needs Survey. London (UK): The Stroke Association, 2010.
Merriman 2019
Mitchell 2010
- Mitchell AJ, Kemp S, Benito‐Leon J, Reuber M. The influence of cognitive impairment on health‐related quality of life in neurological disease. Acta Neuropsychiatrica 2010;22:2‐13.
Nouri 1987
- Nouri FM, Lincoln NB. An extended activities of daily living scale for stroke patients. Clinical Rehabilitation 1987;1:301‐5.
Nys 2006
- Nys GM, Zandvoort MJ, Worp HB, Haan EH, Kort PL, Jansen BP, et al. Early cognitive impairment predicts long‐term depressive symptoms and quality of life after stroke. Journal of the Neurological Sciences 2006;247:149‐56. - PubMed
Park 2001
- Park NW, Ingles JL. Effectiveness of attention rehabilitation after an acquired brain injury: a meta‐analysis. Neuropsychology 2001;15(2):199‐210. - PubMed
Pollock 2012
- Pollock A, George B, Fenton M, Firkins L. Top ten research priorities relating to life after stroke. Lancet Neurology 2012;11:209. - PubMed
Ponsford 1991
- Ponsford J, Kinsella G. The use of a rating scale of attentional behaviour. Neuropsychological Rehabilitation 1991;1:241‐57. - PubMed
Rasquin 2004
- Rasquin SM, Lodder J, Ponds R, Winkens I, Jolles J, Verhey FR. Cognitive functioning after stroke: a one‐year follow‐up study. Dementia and Geriatric Cognitive Disorders 2004;18:138‐44. - PubMed
Review Manager 2014 [Computer program]
- Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager 5 (RevMan 5). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Robertson 1994
- Robertson IH, Ridgeway V, Nimmo‐Smith I. Test of Everyday Attention. Bury St Edmunds (UK): Thames Valley Test Company, 1994.
Robertson 1997
- Robertson IH, Ridgeway V, Greenfield E, Parr A. Motor recovery after stroke depends on intact sustained attention: a 2‐year follow‐up study. Neuropsychology 1997;11:290‐5. - PubMed
Rogers 2018
- Rogers JM, Foord R, Stolwyk RJ, Wong D, Wilson PH. General and domain‐specific effectiveness of cognitive remediation after stroke: systematic literature review and meta‐analysis. Neuropsychology Review 2018;28(3):285‐309. - PubMed
Sohlberg 1989
- Sohlberg M, Mateer C. Introduction to Cognitive Rehabilitation: Theory and Practice. New York (NY): The Guilford Press, 1989.
Strauss 2006
- Strauss E, Sherman EM, Spreen O. A Compendium of Neuropsychological Tests. 3rd Edition. Oxford (UK): Oxford Press, 2006.
Virk 2015
- Virk S, Williams T, Brunsdon R, Suh F, Morrow A. Cognitive remediation of attention deficits following acquired brain injury: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. NeuroRehabilitation 2015;36(3):367‐77. - PubMed
Ware 1992
- Ware JE, Sherbourne CD. The MOS 36‐item short‐form health survey (SF‐36). I. Conceptual framework and item selection. Medical Care 1992;30:473‐83. - PubMed
Weicker 2016
- Weicker J, Villringer A, Thöne‐Otto A. Can impaired working memory functioning be improved by training? A meta‐analysis with a special focus on brain injured patients. Neuropsychology 2016;30(2):190. - PubMed
WHOQOL Group 1998
- WHOQOL Group. The World Health Organization Quality of Life Assessment (WHOQOL): development and general psychometric properties. Social Science & Medicine 1998;46:1569‐85. - PubMed
Whyte 2003
- Whyte J, Hart T, Bode RK, Malec JF. The Moss Attention Rating Scale for traumatic brain injury: initial psychometric assessment. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2003;84:268‐76. - PubMed
Zeidan 2010
- Zeidan F, Johnson SK, Diamond BJ, David Z, Goolkasian P. Mindfulness meditation improves cognition: evidence of brief mental training. Consciousness and Cognition 2010;19(2):597‐605. - PubMed
Zigmond 1983
- Zigmond AS, Snaith RP. The Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 1983;67:361‐70. - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Lincoln 2000
Loetscher 2013
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical