Biological Properties and Bioactive Components of Mentha spicata L. Essential Oil: Focus on Potential Benefits in the Treatment of Obesity, Alzheimer's Disease, Dermatophytosis, and Drug-Resistant Infections - PubMed (original) (raw)
Biological Properties and Bioactive Components of Mentha spicata L. Essential Oil: Focus on Potential Benefits in the Treatment of Obesity, Alzheimer's Disease, Dermatophytosis, and Drug-Resistant Infections
Mohammed S Ali-Shtayeh et al. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019.
Abstract
In the present study, the medicinal aromatic plant Mentha spicata has been investigated as a source of essential oil (EO) and pharmaceuticals. The quantity and composition of EO from M. spicata cultivated in Palestine were analyzed seasonally over a three-year period. A significantly higher EO content was produced in summer and fall months (2.54-2.79%). Chemical analysis of EO revealed 31 compounds with oxygenated monoterpenes (90%) as the most abundant components followed by sesquiterpene and monoterpene hydrocarbons (6 and 3%, respectively). M spicata can be characterized as a carvone chemotype (65%). EO and carvone have shown strong inhibitory activities against the principal enzymes associated with Alzheimer's disease (AD) and overweight diseases (cholinesterase and porcine pancreatic lipase) and also shown strong antidermatophytic activity against Microsporum canis, Trichophyton rubrum, T. mentagrophytes, and Epidermophyton floccosum. The pancreatic lipase inhibition and the synergism showed the potential activity of M. spicata EO and carvone and that their combinations with standard drugs can be useful for the treatment of obesity and overweight. The results also demonstrated that, in addition to their significant inhibitory activity against biofilm formation of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), M. spicata EO and carvone had a strong inhibitory effect on metabolic activity and biomass of the preformed biofilm. The current study supports the utilization of M. spicata EO as a traditional medicine and opens perceptions to find more potent substances in the EO for the management of obesity, AD, and dermatophytosis and for combating drug-resistant bacterial infections.
Copyright © 2019 Mohammed S. Ali-Shtayeh et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
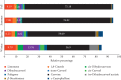
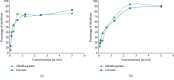
Figure 1
Seasonal variation of percentage of M. spicata EO major compounds over a 3-year study period.
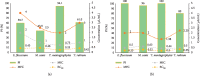
Figure 2
Percentage of mycelial growth inhibition (PI) of (a) M. spicata EO and (b) carvone against the test dermatophytes with MIC, MFC, and EC50 values.
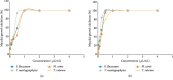
Figure 3
Mycelial growth inhibition activity of (a) M. spicata EO and (b) carvone against the test dermatophytes.
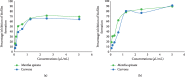
Figure 4
Effects of various doses M. spicata EO and carvone on biofilm formation indicated as % of inhibition, evaluated by the (a) crystal violet (CV) assay and (b) TTC assay.
Figure 5
Effects of various doses of M. spicata EO and carvone on the preformed biofilm presented as % of inhibition, evaluated by the (a) crystal violet (CV) assay and (b) TTC assay.
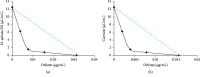
Figure 6
Isobologram curve of double combinations of EO or carvone with orlistat against porcine pancreatic lipase.
Similar articles
- Downy Lavender Oil: A Promising Source of Antimicrobial, Antiobesity, and Anti-Alzheimer's Disease Agents.
Ali-Shtayeh MS, Abu-Zaitoun SY, Dudai N, Jamous RM. Ali-Shtayeh MS, et al. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020 Feb 7;2020:5679408. doi: 10.1155/2020/5679408. eCollection 2020. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020. PMID: 32089724 Free PMC article. - Mentha spicata L. essential oil, phytochemistry and its effectiveness in flatulence.
Mahboubi M. Mahboubi M. J Tradit Complement Med. 2018 Sep 28;11(2):75-81. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcme.2017.08.011. eCollection 2021 Mar. J Tradit Complement Med. 2018. PMID: 33728265 Free PMC article. Review. - Mentha spicata as natural analgesia for treatment of pain in osteoarthritis patients.
Mahboubi M. Mahboubi M. Complement Ther Clin Pract. 2017 Feb;26:1-4. doi: 10.1016/j.ctcp.2016.11.001. Epub 2016 Nov 2. Complement Ther Clin Pract. 2017. PMID: 28107842 Review.
Cited by
- Chemical Characterization of the Essential Oil Compositions of Mentha spicata and M. longifolia ssp. cyprica from the Mediterranean Basin and Multivariate Statistical Analyses.
İsfendiyaroğlu H, Hanoğlu A, Yiğit Hanoğlu D, Alkaş FB, Başer KHC, Özkum Yavuz D. İsfendiyaroğlu H, et al. Molecules. 2024 Apr 25;29(9):1970. doi: 10.3390/molecules29091970. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38731461 Free PMC article. - The Beneficial Effects of Essential Oils in Anti-Obesity Treatment.
De Blasio A, D'Anneo A, Lauricella M, Emanuele S, Giuliano M, Pratelli G, Calvaruso G, Carlisi D. De Blasio A, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 31;22(21):11832. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111832. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34769261 Free PMC article. Review. - Enhancement of the anti-microbial activity of Mentha spicata essential oil on storage by glycerosomes.
Taheri SL, Varshosaz J. Taheri SL, et al. Food Sci Biotechnol. 2023 Apr 15;32(14):2145-2152. doi: 10.1007/s10068-023-01301-5. eCollection 2023 Dec. Food Sci Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37860731 Free PMC article. - Antioxidative, anticancer, and antibacterial activities of a nanogel containing Mentha spicata L. essential oil and electrospun nanofibers of polycaprolactone-hydroxypropyl methylcellulose.
Rasti F, Yousefpoor Y, Abdollahi A, Safari M, Roozitalab G, Osanloo M. Rasti F, et al. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022 Oct 7;22(1):261. doi: 10.1186/s12906-022-03741-8. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022. PMID: 36207726 Free PMC article. - Aphidicidal activity of nano-emulsions of spearmint oil and carvone against Rhopalosiphum maidis and Sitobion avenae.
Mondal PC, Salim R, Kumar V, Kaushik P, Shakil NA, Pankaj, Rana VS. Mondal PC, et al. Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 16;14(1):24226. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-74149-2. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39414889 Free PMC article.
References
- Lawrence B. M. Mint : The Genus Mentha. Boca Raton, FL, USA: CRC Press; 2007.
- Topalov V. D. Mentha. In: Topalov M. S., Dechev V. D., Pehlivanov I. I., editors. Crop Production. Sofia, Bulgaria: Zemizdat Press; 1989. pp. 372–381.
- Ali-Shtayeh M. S., Jamous R. M., Abu-Zaitoun S. Y., Qasem I. B. In-vitro screening of acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activity of extracts from Palestinian indigenous flora in relation to the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Functional Foods in Health and Disease. 2014;4(9):381–400.
- Bernstein N., Chaimovitch D., Dudai N. Effect of irrigation with secondary treated effluent on essential oil, antioxidant activity, and phenolic compounds in oregano and rosemary. Agronomy Journal. 2009;101(1):1–10. doi: 10.2134/agronj2007.0144. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources