Thiazolidinediones: the Forgotten Diabetes Medications - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Thiazolidinediones: the Forgotten Diabetes Medications
Harold E Lebovitz. Curr Diab Rep. 2019.
Abstract
Purpose of review: Thiazolidinediones (TZDs) are the only pharmacologic agents that specifically treat insulin resistance. The beneficial effects of TZDs on the cardiovascular risk factors associated with insulin resistance have been well documented. TZD use has been limited because of concern about safety issues and side effects.
Recent findings: Recent studies indicate that cardiovascular toxicity with rosiglitazone and increase in bladder cancer with pioglitazone are no longer significant issues. There are new data which show that pioglitazone treatment reduces myocardial infarctions and ischemic strokes. New data concerning TZD-mediated edema, congestive heart failure, and bone fractures improves the clinician's ability to select patients that will have minimal significant side effects. Thiazolidinediones are now generic and less costly than pharmaceutical company-promoted therapies. Better understanding of the side effects coupled with clear benefits on the components of the insulin resistance syndrome should promote TZD use in treating patients with type 2 diabetes.
Keywords: Bone fractures; CV outcomes; Heart failure; Insulin resistance; PPARγ agonists; Type 2 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
Harold E. Lebovitz declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Figures
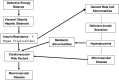
Fig. 1
Insulin-resistant type 2 diabetes is the co-existence of two separate metabolic abnormalities: a primary beta-cell disease: diabetes mellitus and a lipid distribution abnormality which creates insulin resistance, the metabolic syndrome, and increased cardiovascular disease. These abnormalities can be separate or co-exist. These abnormalities can interact in susceptible populations leading to an increase in the prevalence of diabetes and an increase in atherosclerotic disease
Similar articles
- Rosiglitazone and pioglitazone utilization from January 2007 through May 2008 associated with five risk-warning events.
Starner CI, Schafer JA, Heaton AH, Gleason PP. Starner CI, et al. J Manag Care Pharm. 2008 Jul-Aug;14(6):523-31. doi: 10.18553/jmcp.2008.14.6.523. J Manag Care Pharm. 2008. PMID: 18693776 Free PMC article. - Risk of stroke with thiazolidinediones: a ten-year nationwide population-based cohort study.
Lu CJ, Sun Y, Muo CH, Chen RC, Chen PC, Hsu CY. Lu CJ, et al. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2013;36(2):145-51. doi: 10.1159/000353679. Epub 2013 Sep 11. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2013. PMID: 24029780 - Thiazolidinediones in type 2 diabetes: a cardiology perspective.
Khanderia U, Pop-Busui R, Eagle KA. Khanderia U, et al. Ann Pharmacother. 2008 Oct;42(10):1466-74. doi: 10.1345/aph.1K666. Epub 2008 Sep 2. Ann Pharmacother. 2008. PMID: 18698014 Review. - Thiazolidinediones, cardiovascular disease and cardiovascular mortality: translating research into action for diabetes (TRIAD).
Bilik D, McEwen LN, Brown MB, Selby JV, Karter AJ, Marrero DG, Hsiao VC, Tseng CW, Mangione CM, Lasser NL, Crosson JC, Herman WH. Bilik D, et al. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2010 Jul;19(7):715-21. doi: 10.1002/pds.1954. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2010. PMID: 20583206 Free PMC article. - The safety of thiazolidinediones.
Tolman KG. Tolman KG. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2011 May;10(3):419-28. doi: 10.1517/14740338.2011.534982. Epub 2011 Mar 3. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2011. PMID: 21366501 Review.
Cited by
- A critical review on diabetes mellitus type 1 and type 2 management approaches: from lifestyle modification to current and novel targets and therapeutic agents.
Tegegne BA, Adugna A, Yenet A, Yihunie Belay W, Yibeltal Y, Dagne A, Hibstu Teffera Z, Amare GA, Abebaw D, Tewabe H, Abebe RB, Zeleke TK. Tegegne BA, et al. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Oct 18;15:1440456. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1440456. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39493778 Free PMC article. Review. - Retinoid X receptor heterodimers in hepatic function: structural insights and therapeutic potential.
Xu R, Zhang L, Pan H, Zhang Y. Xu R, et al. Front Pharmacol. 2024 Oct 16;15:1464655. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1464655. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39478961 Free PMC article. Review. - Identification of Novel PPARγ Partial Agonists Based on Virtual Screening Strategy: In Silico and In Vitro Experimental Validation.
Lian YE, Wang M, Ma L, Yi W, Liao S, Gao H, Zhou Z. Lian YE, et al. Molecules. 2024 Oct 15;29(20):4881. doi: 10.3390/molecules29204881. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39459249 Free PMC article. - Mesoporous silica and alumina nanoparticles to improve drug delivery of pioglitazone on diabetic type 1 nephropathy in rats.
Varshosaz J, Ahmadipour S, Dezhangfard A. Varshosaz J, et al. Res Pharm Sci. 2024 Aug 19;19(4):459-474. doi: 10.4103/RPS.RPS_65_23. eCollection 2024 Aug. Res Pharm Sci. 2024. PMID: 39399726 Free PMC article. - Computational Drug Design Approaches for the Identification of Novel Antidiabetic Compounds from Natural Resources through Molecular Docking, ADMET, and Toxicological Studies.
Akter B, Uddin MS, Islam MR, Ahamed KU, Aktar MN, Hossain MK, Salamatullah AM, Bourhia M. Akter B, et al. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2024 Oct 8. doi: 10.1007/s12013-024-01540-1. Online ahead of print. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2024. PMID: 39377980
References
- • Weyer C, Bogardus C, Mott DM, Pratley RE. The natural history of insulin secretory dysfunction and insulin resistance in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus. 1999;104:787–94. This is the classic study that documents the relationship between insulin resistance and insulin secretion. - PMC - PubMed
- Lebovitz HE, Banerji MA. Treatment of insulin resistance in diabetes mellitus. Eur J Pharmacol. 2004;490:135–146. - PubMed
- Lebovitz HE. In: The metabolic syndrome chapter 13.36 in Oxford textbook of endocrinology and diabetes 2nd Edition. Wass JAH, Stewart PM, editors. Oxford: OXFORD University Press; 2011.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials