PhoH2 proteins couple RNA helicase and RNAse activities - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
. 2020 Apr;29(4):883-892.
doi: 10.1002/pro.3814. Epub 2020 Jan 7.
Affiliations
- PMID: 31886915
- PMCID: PMC7096712
- DOI: 10.1002/pro.3814
Review
PhoH2 proteins couple RNA helicase and RNAse activities
Emma S V Andrews et al. Protein Sci. 2020 Apr.
Abstract
PhoH2 proteins are found in a very diverse range of microorganisms that span bacteria and archaea. These proteins are composed of two domains: an N-terminal PIN-domain fused with a C-terminal PhoH domain. Collectively this fusion functions as an RNA helicase and ribonuclease. In other genomic contexts, PINdomains and PhoHdomains are separate but adjacent suggesting association to achieve similar function. Exclusively among the mycobacteria, PhoH2 proteins are encoded in the genome with an upstream gene, phoAT, which is thought to play the role of an antitoxin (in place of the traditional VapB antitoxin that lies upstream of the 47 other PINdomains in the mycobacterial genome). This review examines PhoH2 proteins as a whole and describes the bioinformatics, biochemical, structural, and biological properties of the two domains that make up PhoH2: PIN and PhoH. We review the transcriptional regulators of phoH2 from two mycobacterial species and speculate on the function of PhoH2 proteins in the context of a Type II toxin-antitoxin system which are thought to play a role in the stress response in bacteria.
Keywords: AAA+ helicase; PIN-PhoH; PIN-domain; PhoH domain; PhoH2; RNAse; ribonuclease; toxin-antitoxin.
© 2019 The Protein Society.
Figures
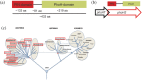
Figure 1
Domain organization, schematic of phoATphoH2 and phylogeny of PhoH2 proteins. (a) PhoH2 proteins are composed of a fusion between a PIN‐domain and a PhoHdomain separated by a flexible linker region. (b) phoAT overlaps the start of phoH2 similar to vapB of vapBC toxin–antitoxin systems. (c) Schematic of universal tree4 indicating phylum in which Ylak, COG1875 proteins can be found (red boxes). Last universal common ancestor (LUCA) and circular nodes correspond to last common ancestors
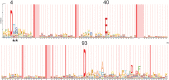
Figure 2
Conservation of PhoAT among closely related mycobacteria. (a) PhoAT sequence from members of the
M. tuberculosis
complex. (b) PhoAT sequence from more distantly related mycobacteria. Image was created using Geneious version 7.1 (Biomatters)
Figure 3
Hidden Markov model that defines PIN‐domain proteins. Based on a multiple sequence alignment the height of each letter defines the significance of the amino acid at that position within the PIN‐domain family. The width of each letter defines the significance of this position in the identification of the PIN‐domain family. The dark and light pink regions are where insertions have occurred. The three conserved amino acids (D, E, D) at Positions 4, 40, and 93 characterize the PIN‐domain protein family along with polar residues located after the first conserved aspartic acid as shown by asterisks. Generated using Pfam1
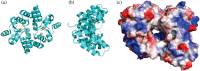
Figure 4
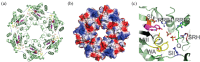
VapC PIN‐domain dimer and tetramer. (a) Ribbon diagram of VapCPAE2754 dimer. The three conserved acidic residues are labeled shown as sticks. (b) Ribbon diagram of VapCPAE2754 dimer rotated 90°. (c) Electrostatic surface diagram of PAE2754 tetramer. Negative (red) and Positive (blue) charges show where ssRNA may bind to positively charged residues at the entrance of the tunnel. Images were made in PyMOL V1.3 using PDB IV8P
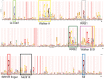
Figure 5
Hidden Markov model that defines PhoHdomain proteins. Based on a multiple sequence alignment, the height of each letter defines the significance of the amino acid at that position within the PhoH‐domain family. The width of each letter defines the significance of this position in the identification of the PhoH‐domain family. The dark and light pink regions are where insertions have occurred. Conserved regions are comparable to motifs for ATPase activity found across each of the helicase families and two motifs unique to PhoH involved with nucleic interactions (RRB 1 and 2). Generated using Pfam1
Figure 6
Structures of the PhoHdomain of PhoH2 from C. glutamicum. (a) Active hexameric conformation of PhoH. (b) Electrostatic map of PhoH hexamer (blue positive charge and red negative charge) showing the positive charges present at the predicted entrance of the tunnel. (c) Magnified view of the PhoH‐domain active site showing each of the conserved residues and motifs labeled and colored as positions from HMM (Q, WA, RRB1, RRB2, WB, SI, SRH, Motif III, and SII). Sulfate ions were identified in the structure (shown as yellow and orange sticks) and show the position where the γ and β phosphate of ATP binds in the active site. Motifs Q, W A/B, RRB1, Motif III, SI, and SII interact with RRB2 and the SRH from the neighboring monomer. Images were made in PyMol V 1.3 using PDB 3B85
Figure 7
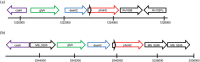
Genomic context of phoH2 genes from M. tuberculosis and M. smegmatis. Genomic context of phoH2 genes from (a) M. tuberculosis and (b) M. smegmatis. phoAT is indicated by the short black arrow directly upstream of phoH2. Rv1096 encodes a glycosyl hydrolase, Rv1097c a putative glycine and proline rich membrane protein and MS_5250 encodes a hypothetical protein of unknown function, CalR9, MS_5246 encodes a nitroreductase and MS_5245 a universal stress protein. Adapted from Xbase (
) and BLAST (
http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi
)
Figure 8
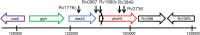
Genomic positions of predicted transcription factor binding sites. Arrows indicate the position of the five predicted transcription factor binding sites. phoAT is indicated by the black block arrow upstream of phoH2. Adapted from the Tuberculosis Database (TBDB;
)
Figure 9
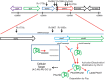
Model of the proposed phoH2 regulation and PhoH2 activity
Similar articles
- The mycobacterial PhoH2 proteins are type II toxin antitoxins coupled to RNA helicase domains.
Andrews ES, Arcus VL. Andrews ES, et al. Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2015 Jul;95(4):385-94. doi: 10.1016/j.tube.2015.03.013. Epub 2015 Apr 16. Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2015. PMID: 25999286 - The PIN-domain ribonucleases and the prokaryotic VapBC toxin-antitoxin array.
Arcus VL, McKenzie JL, Robson J, Cook GM. Arcus VL, et al. Protein Eng Des Sel. 2011 Jan;24(1-2):33-40. doi: 10.1093/protein/gzq081. Epub 2010 Oct 29. Protein Eng Des Sel. 2011. PMID: 21036780 Review. - Post-transcriptional modulation of the SigF regulon in Mycobacterium smegmatis by the PhoH2 toxin-antitoxin.
Andrews ESV, Rzoska-Smith E, Arcus VL. Andrews ESV, et al. PLoS One. 2020 Jul 29;15(7):e0236551. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0236551. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32726339 Free PMC article. - Crystal structure of the VapBC-15 complex from Mycobacterium tuberculosis reveals a two-metal ion dependent PIN-domain ribonuclease and a variable mode of toxin-antitoxin assembly.
Das U, Pogenberg V, Subhramanyam UK, Wilmanns M, Gourinath S, Srinivasan A. Das U, et al. J Struct Biol. 2014 Dec;188(3):249-58. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2014.10.002. Epub 2014 Oct 22. J Struct Biol. 2014. PMID: 25450593 - The PIN-domain toxin-antitoxin array in mycobacteria.
Arcus VL, Rainey PB, Turner SJ. Arcus VL, et al. Trends Microbiol. 2005 Aug;13(8):360-5. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2005.06.008. Trends Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 15993073 Review.
Cited by
- Jumbo Phages: A Comparative Genomic Overview of Core Functions and Adaptions for Biological Conflicts.
M Iyer L, Anantharaman V, Krishnan A, Burroughs AM, Aravind L. M Iyer L, et al. Viruses. 2021 Jan 5;13(1):63. doi: 10.3390/v13010063. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 33466489 Free PMC article. - The Caulobacter NtrB-NtrC two-component system bridges nitrogen assimilation and cell development.
North H, McLaughlin M, Fiebig A, Crosson S. North H, et al. J Bacteriol. 2023 Oct 26;205(10):e0018123. doi: 10.1128/jb.00181-23. Epub 2023 Oct 4. J Bacteriol. 2023. PMID: 37791753 Free PMC article. - Comparative Analysis on Proteomics Profiles of Intracellular and Extracellular M.tb and BCG From Infected Human Macrophages.
Liu H, Su L, Zhu T, Zhu X, Zhu Y, Peng Y, Zhang K, Wang L, Hu C, Chen H, Chen Y, Guo A. Liu H, et al. Front Genet. 2022 Mar 28;13:847838. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.847838. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35419023 Free PMC article. - The Caulobacter NtrB-NtrC two-component system bridges nitrogen assimilation and cell development.
North H, McLaughlin M, Fiebig A, Crosson S. North H, et al. bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Aug 31:2023.06.06.543975. doi: 10.1101/2023.06.06.543975. bioRxiv. 2023. PMID: 37333394 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint. - Identification of Genes Encoded Toxin-Antitoxin System in Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Strains from Clinical Sample.
Sundaram K, Vajravelu LK, Velayutham R, Mohan U. Sundaram K, et al. Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2024;24(8):e140324227967. doi: 10.2174/0118715265274164240117104534. Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2024. PMID: 38486387
References
- Parte AC. LPSN—List of prokaryotic names with standing in nomenclature (http://bacterio.net), 20 years on. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2018;68:1825–1829. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources