New Insights into the Biological and Pharmaceutical Properties of Royal Jelly - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
New Insights into the Biological and Pharmaceutical Properties of Royal Jelly
Saboor Ahmad et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2020.
Abstract
Royal jelly (RJ) is a yellowish-white and acidic secretion of hypopharyngeal and mandibular glands of nurse bees used to feed young worker larvae during the first three days and the entire life of queen bees. RJ is one of the most appreciated and valued natural product which has been mainly used in traditional medicines, health foods, and cosmetics for a long time in different parts of the world. It is also the most studied bee product, aimed at unravelling its bioactivities, such as antimicrobial, antioxidant, anti-aging, immunomodulatory, and general tonic action against laboratory animals, microbial organisms, farm animals, and clinical trials. It is commonly used to supplement various diseases, including cancer, diabetes, cardiovascular, and Alzheimer's disease. Here, we highlight the recent research advances on the main bioactive compounds of RJ, such as proteins, peptides, fatty acids, and phenolics, for a comprehensive understanding of the biochemistry, biological, and pharmaceutical responses to human health promotion and life benefits. This is potentially important to gain novel insight into the biological and pharmaceutical properties of RJ.
Keywords: bioactive compounds; fatty acids; functional properties; phenolics; proteins; royal jelly.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Figure 1
Forager bees transport pollens in their hind leg corbiculae to which they add nectar to form pollen pellets. Forager bees deposit and pack the pollen pellets into cell surrounding the brood area and forming bee bread. Nurse bees develop enlarged food glands and produce RJ by consuming honey and bee bread (Photos taken by Prof. Dr. Jianke Li).
Figure 2
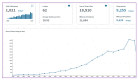
Numbers of publications on RJ that appear from international journals are increasing every year (data from the core collection of the Web of Science).
Figure 3
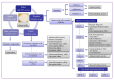
A schematic representation of the main biological substances in RJ and their functional activities. For detailed information refer to Table 1.
Figure 4
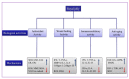
The biological activities of RJ and their mechanism. SOD (superoxide dismutase); GSH (glutathione); CAT (catalase); GR (glutathione reductase); GPx (glutathione peroxidase); ROS (reactive oxygen species); MMP (matrix metallopeptidases); MDA (malondialdehyde); NO (nitric oxide); IFN-ϒ (interferon-gamma); IL-4 (interleukin-4); TNF-α (tumor necrosis factor); IFN-α (Interferon-α); EGF (epidermal growth factor); AMPK (5′ AMP-activated protein kinase); MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinase); IGF-1 (insulin-like growth factor-1), and TOR (target of rapamycin).
Figure 5
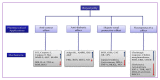
The pharmaceutical effects of RJ and their mechanism. Bax (bcl-2-like protein X); MMP-9 (matrix metallopeptidases-9); AKT (protein kinase B); MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinase); IRS (insulin receptor substrate 1); IL-4 (interleukin-4); TNF-α (tumor necrosis factor); ROS (reactive oxygen species); AMPK (5′ AMP-activated protein kinase); SOD (superoxide dismutase); GSH (glutathione); CAT (catalase); GR(Glutathione reductase); GPx (glutathione peroxidase); MDA (malondialdehyde); NO (nitric oxide); MAKL (mixed lineage kinase domain-like); ERK (extracellular signal-regulated kinases); CREB (cAMP Response Element-Binding Protein); IGF-1 (insulin-like growth factor-1); TOR (target of rapamycin), and BACE1 (β-site amyloid precursor protein cleaving enzymes).
Similar articles
- Royal Jelly: An ancient remedy with remarkable antibacterial properties.
Fratini F, Cilia G, Mancini S, Felicioli A. Fratini F, et al. Microbiol Res. 2016 Nov;192:130-141. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2016.06.007. Epub 2016 Jun 23. Microbiol Res. 2016. PMID: 27664731 Review. - Royal Jelly-A Traditional and Natural Remedy for Postmenopausal Symptoms and Aging-Related Pathologies.
Bălan A, Moga MA, Dima L, Toma S, Elena Neculau A, Anastasiu CV. Bălan A, et al. Molecules. 2020 Jul 20;25(14):3291. doi: 10.3390/molecules25143291. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32698461 Free PMC article. Review. - Queen cells acceptance rate and royal jelly production in worker honey bees of two Apis mellifera races.
Khan KA, Ghramh HA, Ahmad Z, El-Niweiri MAA, Ahamed Mohammed ME. Khan KA, et al. PLoS One. 2021 Apr 13;16(4):e0248593. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0248593. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33848292 Free PMC article. Retracted. - Antioxidant properties of royal jelly associated with larval age and time of harvest.
Liu JR, Yang YC, Shi LS, Peng CC. Liu JR, et al. J Agric Food Chem. 2008 Dec 10;56(23):11447-52. doi: 10.1021/jf802494e. J Agric Food Chem. 2008. PMID: 19007163 - Growth stimulating effect on queen bee larvae of histone deacetylase inhibitors.
Huang CY, Chi LL, Huang WJ, Chen YW, Chen WJ, Kuo YC, Yuan CM, Chen CN. Huang CY, et al. J Agric Food Chem. 2012 Jun 20;60(24):6139-49. doi: 10.1021/jf300815b. Epub 2012 Jun 7. J Agric Food Chem. 2012. PMID: 22642680
Cited by
- Potential application of bee products in food industry: An exploratory review.
Maicelo-Quintana JL, Reyna-Gonzales K, Balcázar-Zumaeta CR, Auquiñivin-Silva EA, Castro-Alayo EM, Medina-Mendoza M, Cayo-Colca IS, Maldonado-Ramirez I, Silva-Zuta MZ. Maicelo-Quintana JL, et al. Heliyon. 2024 Jan 6;10(1):e24056. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e24056. eCollection 2024 Jan 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38268589 Free PMC article. Review. - Royal Jelly: Beneficial Properties and Synergistic Effects with Chemotherapeutic Drugs with Particular Emphasis in Anticancer Strategies.
Salama S, Shou Q, Abd El-Wahed AA, Elias N, Xiao J, Swillam A, Umair M, Guo Z, Daglia M, Wang K, Khalifa SAM, El-Seedi HR. Salama S, et al. Nutrients. 2022 Oct 7;14(19):4166. doi: 10.3390/nu14194166. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36235818 Free PMC article. Review. - The effects of royal jelly supplementation on oxidative stress, inflammatory mediators, mental health, cognitive function, quality of life, and clinical outcomes of patients with ischemic stroke: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial.
Karimi E, Khorvash F, Arab A, Sepidarkish M, Saadatnia M, Amani R. Karimi E, et al. BMC Nutr. 2023 Feb 16;9(1):32. doi: 10.1186/s40795-023-00690-4. BMC Nutr. 2023. PMID: 36797768 Free PMC article. - Royal Jelly Increases Hematopoietic Stem Cells in Peripheral Blood: A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Randomized Trial in Healthy Subjects.
Okamoto H, Ohkuma A, Kawaguchi M, Shigematsu N, Okumura N. Okamoto H, et al. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023 Jan 13;2023:7665515. doi: 10.1155/2023/7665515. eCollection 2023. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023. PMID: 36686976 Free PMC article. - Royal jelly: a predictive, preventive and personalised strategy for novel treatment options in non-communicable diseases.
Baptista BG, Lima LS, Ribeiro M, Britto IK, Alvarenga L, Kemp JA, Cardozo LF, Berretta AA, Mafra D. Baptista BG, et al. EPMA J. 2023 Jul 18;14(3):381-404. doi: 10.1007/s13167-023-00330-8. eCollection 2023 Sep. EPMA J. 2023. PMID: 37605655 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Knecht D., Kaatz H. Patterns of larval food production by hypopharyngeal glands in adult worker honey bees. Apidologie. 1990;21:457–468. doi: 10.1051/apido:19900507. - DOI
- Melliou E., Chinou I. Studies in Natural Products Chemistry. Volume 43. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2014. Chemistry and bioactivities of royal jelly; pp. 261–290.
- Ramadan M.F., Al-Ghamdi A. Bioactive compounds and health-promoting properties of royal jelly: A review. J. Funct. Foods. 2012;4:39–52. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2011.12.007. - DOI
- Sabatini A.G., Marcazzan G.L., Caboni M.F., Bogdanov S., Almeida-Muradian L. Quality and standardisation of royal jelly. J. ApiProd. ApiMed. Sci. 2009;1:1–6. doi: 10.3896/IBRA.4.01.1.04. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- CARS-44/Modern Agro-Industry Technology Research System
- CAAS-ASTIP-2015-IAR/Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Program
- -/National project for upgrading overall bee-product quality of beekeeping industry of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical