Relationship between fluoroquinolones and the risk of aortic diseases: a meta-analysis of observational studies - PubMed (original) (raw)
Meta-Analysis
Relationship between fluoroquinolones and the risk of aortic diseases: a meta-analysis of observational studies
Xiao-Ce Dai et al. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2020.
Abstract
Background: Our aim was to determine the relationship between the use of fluoroquinolones and the risk of aortic diseases.
Methods: PubMed, EMBASE and the Web of Science were searched from inception to July 6, 2019, to identify observational studies that evaluated the risk of aortic diseases associated in users of fluoroquinolones compared with nonusers or users of other antibiotics. The primary outcome was the first occurrence of aortic diseases. We used the GRADE approach to rate the strength of evidence. We used the inverse variance method random-effect model to estimate the odds ratios (ORs) with 95% CIs, and statistical heterogeneity was assessed by the I2 statistic.
Results: This meta-analysis enrolled 2,829,385 patients reported the relationship between fluoroquinolones and the risk of aortic diseases. Compared with nonusers or users of other antibiotics, users of fluoroquinolone had a significantly increased risk of aortic diseases (adjusted OR, 2.10; 95% CI, 1.65-2.68; P = .000, I2 = 16.4%). The quality of evidence was moderate, and the number needed to harm (NNH) for aortic diseases among patients was estimated to be 1301.
Conclusions: The fluoroquinolone use in patients significantly increases the risk of new-onset aortic diseases. Clinicians need to pay attention to these severe adverse events when considering fluoroquinolone use.
Keywords: Aortic aneurysm; Aortic dissection; Fluoroquinolones; Meta-analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
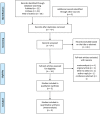
Fig. 1
Selection of observational studies for the meta-analysis
Fig. 2
The Risk of Aortic Diseases among Fluoroquinolone Users in Comparison to Nonusers or Users of Other Antibiotics
Fig. 3
The Sensitive Analysis for the Risk of Aortic Diseases
Similar articles
- Risk of aortic aneurysm and aortic dissection with the use of fluoroquinolones in Korea: a nested case-control study.
Son N, Choi E, Chung SY, Han SY, Kim B. Son N, et al. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2022 Feb 13;22(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s12872-022-02488-x. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2022. PMID: 35152888 Free PMC article. - Fluoroquinolones and the risk of aortopathy: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Noman AT, Qazi AH, Alqasrawi M, Ayinde H, Tleyjeh IM, Lindower P, Bin Abdulhak AA. Noman AT, et al. Int J Cardiol. 2019 Jan 1;274:299-302. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2018.09.067. Epub 2018 Sep 21. Int J Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 30309682 - Fluoroquinolones and the risk of aortic aneurysm or aortic dissection: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis including 53,651,283 patients.
Fatima K, Uzair SU, Salman A, Jawed A, Husain MA, Shah MG, Hasnain MA, Jawed A, Vohra LI, Lal PM. Fatima K, et al. Minerva Cardiol Angiol. 2023 Oct;71(5):485-493. doi: 10.23736/S2724-5683.22.06124-5. Epub 2022 Dec 5. Minerva Cardiol Angiol. 2023. PMID: 36468763 - Fluoroquinolones and the Risk of Aortic Aneurysm or Aortic Dissection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.
Rawla P, El Helou ML, Vellipuram AR. Rawla P, et al. Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med Chem. 2019;17(1):3-10. doi: 10.2174/1871525717666190402121958. Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 30947680 Free PMC article. - Fluoroquinolones and the Risk of Aortopathy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.
Latif A, Ahsan MJ, Kapoor V, Lateef N, Malik SU, Patel AD, Khan BA, Bittner M, Holmberg M. Latif A, et al. WMJ. 2020 Sep;119(3):185-189. WMJ. 2020. PMID: 33091293
Cited by
- Impact of the US Food and Drug Administration warning regarding increased risk of aortic aneurysms or aortic dissections on fluoroquinolone prescribing trends.
Rizk JG, Slejko JF, Heil EL, Seo D, Qato DM. Rizk JG, et al. BMJ Open Qual. 2024 Jul 24;13(3):e002925. doi: 10.1136/bmjoq-2024-002925. BMJ Open Qual. 2024. PMID: 39053916 Free PMC article. - Do fluoroquinolones increase aortic aneurysm or dissection incidence and mortality? A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Chen C, Patterson B, Simpson R, Li Y, Chen Z, Lv Q, Guo D, Li X, Fu W, Guo B. Chen C, et al. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Aug 9;9:949538. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.949538. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 36017083 Free PMC article. - Association Between Previous or Active Cancer and Clinical Outcomes in TAVR Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 255,840 Patients.
Diaz-Arocutipa C, Torres-Valencia J, Zavaleta-Camacho G, Vicent L. Diaz-Arocutipa C, et al. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Nov 2;8:763557. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.763557. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 34796218 Free PMC article. - Current progress of fluoroquinolones-increased risk of aortic aneurysm and dissection.
Jun C, Fang B. Jun C, et al. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2021 Sep 28;21(1):470. doi: 10.1186/s12872-021-02258-1. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2021. PMID: 34583637 Free PMC article. Review. - Safety of fluoroquinolones.
Barberán J, de la Cuerda A, Tejeda González MI, López Aparicio A, Monfort Vinuesa C, Ramos Sánchez A, Barberán LC. Barberán J, et al. Rev Esp Quimioter. 2024 Apr;37(2):127-133. doi: 10.37201/req/143.2023. Epub 2023 Dec 22. Rev Esp Quimioter. 2024. PMID: 38140798 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical