Risky decision making and cognitive flexibility among online sports bettors in Nigeria - PubMed (original) (raw)
Risky decision making and cognitive flexibility among online sports bettors in Nigeria
Tochukwu Nweze et al. Int J Psychol. 2020 Dec.
Abstract
Online sports betting is a popular recreational activity in Nigeria. Like other forms of gambling, risk of pathological progression exists for gamblers who continue betting despite severe financial and psychosocial consequences. In the present study, we examined whether this population of gamblers shows deficits in decision making and cognitive flexibility that have been documented in Western gambling populations. Thirty-six online sports bettors and 42 non-gambling participants completed a version of the Iowa gambling task (IGT) and an established set-shifting task for the assessment of cognitive flexibility. The two groups did not differ significantly in the selection of disadvantageous decks on the IGT. In contrast, sports bettors committed significantly more errors on the set-shifting task than non-gambling control participants. As this performance deficit was not specific to trials requiring a set shift, it most likely resulted from gambling-related changes in general cognitive or motivational abilities that are required to successfully complete challenging mental tasks. While our results illustrate that findings from Western populations cannot automatically be generalised to other contexts, it should be noted that we focused on only one particular type of gambling and included mostly participants with mild gambling-related problems.
Keywords: Cognitive flexibility; Gamblers; Impulsivity; Iowa gambling task; Risky decision making.
© 2020 The Authors. International Journal of Psychology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of International Union of Psychological Science.
Figures
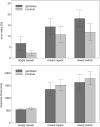
Figure 1
Accuracy and latency of participants' responses to repeat trials in single‐task blocks (single repeat), repeat trials in mixed‐task blocks (mixed repeat) and switch trials in mixed‐task blocks (mixed switch) of the set‐shifting task. Error bars indicate 95% confidence intervals.
Similar articles
- Conceptualising emotional and cognitive dysregulation amongst sports bettors; an exploratory study of 'tilting' in a new context.
Torrance J, Roderique-Davies G, Greville J, O'Hanrahan M, Davies N, Sabolova K, John B. Torrance J, et al. PLoS One. 2022 Feb 17;17(2):e0264000. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0264000. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35176068 Free PMC article. - Predicting Risky Decision Making (Odds Selection) in Regular Soccer Gamblers from Nigeria using Cognitive Tasks Combined with Non-Cognitive Measures.
Ucheagwu VA, Ogbogu UC, Patrick UU, Ossai JP. Ucheagwu VA, et al. J Gambl Stud. 2023 Mar;39(1):103-117. doi: 10.1007/s10899-022-10159-x. Epub 2022 Sep 24. J Gambl Stud. 2023. PMID: 36152112 - Risk Factors for Gambling Problems Specifically Associated with Sports Betting.
Russell AMT, Hing N, Browne M. Russell AMT, et al. J Gambl Stud. 2019 Dec;35(4):1211-1228. doi: 10.1007/s10899-019-09848-x. J Gambl Stud. 2019. PMID: 30924002 - [Decision making and the Iowa Gambling Task: relevance to dependence study].
Takano Y, Takahashi N, Hironaka N. Takano Y, et al. Nihon Arukoru Yakubutsu Igakkai Zasshi. 2010 Oct;45(5):420-9. Nihon Arukoru Yakubutsu Igakkai Zasshi. 2010. PMID: 21226340 Review. Japanese. - Youth Sports Betting and Problem Gambling in the Global and Nigerian Context: A Review.
Daniel FM, Ukoaka BM, Essien EA, Emeruwa VE, Obo GE, Ugorji WC, Essiet RN, Ike WI, Emirene NI, Bachi FS, Udofia IA, Eyo AA. Daniel FM, et al. Niger Med J. 2024 Nov 6;65(5):547-556. doi: 10.60787/nmj.v65i3.469. eCollection 2024 Sep-Oct. Niger Med J. 2024. PMID: 39633692 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Contributions of Working Memory and Inhibition to Cognitive Flexibility in Nigerian Adolescents.
Nweze T, Nwani W. Nweze T, et al. Dev Neuropsychol. 2020 Apr-Jun;45(3):118-128. doi: 10.1080/87565641.2020.1765169. Epub 2020 May 15. Dev Neuropsychol. 2020. PMID: 32412307 Free PMC article. - Clinical Correlates of Sports Betting: A Systematic Review.
Valenciano-Mendoza E, Mora-Maltas B, Mestre-Bach G, Munguía L, Richard J, Derevensky JL, Potenza MN, Jiménez-Murcia S. Valenciano-Mendoza E, et al. J Gambl Stud. 2023 Jun;39(2):579-624. doi: 10.1007/s10899-023-10196-0. Epub 2023 Apr 1. J Gambl Stud. 2023. PMID: 37004597 Free PMC article. - Gambling in Sub-Saharan Africa: Traditional Forms and Emerging Technologies.
Bitanihirwe BKY, Adebisi T, Bunn C, Ssewanyana D, Darby P, Kitchin P. Bitanihirwe BKY, et al. Curr Addict Rep. 2022;9(4):373-384. doi: 10.1007/s40429-022-00449-0. Epub 2022 Oct 25. Curr Addict Rep. 2022. PMID: 36312763 Free PMC article. Review. - Psychometric Study of the Cognitive Flexibility Inventory in a Colombian Sample.
Navarro MC, Quiroz Molinares N, Mebarak M. Navarro MC, et al. Int J Psychol Res (Medellin). 2022 Jan-Jun;15(1):42-54. doi: 10.21500/20112084.5371. Int J Psychol Res (Medellin). 2022. PMID: 36199527 Free PMC article. - The Interest in Betting, Smoking, Alcohol, and Drugs in Malawi: Changing Trends between 2012-2022.
Demir G, Bandawe C. Demir G, et al. Malawi Med J. 2024 Mar 20;36(1):30-37. doi: 10.4314/mmj.v36i1.5. eCollection 2024 Mar. Malawi Med J. 2024. PMID: 39086368 Free PMC article.
References
- Armstrong, A. , & Carroll, M. (2017). Sports betting in Australia. Melbourne, Australia: Australian Gambling Research Centre; Retrieved from https://aids.gov.au/agrc/publications/sports‐betting‐australia
- Bechara, A. (2003). Risky business: Emotion, decision making and addiction. Journal of Gambling Studies, 19, 23–51. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials