The good, the bad, and the ugly facets of insulin resistance - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
The good, the bad, and the ugly facets of insulin resistance
K V S Hari Kumar. Med J Armed Forces India. 2020 Jan.
Abstract
Insulin is a potent anabolic hormone, and binding to its receptor activates downstream intracellular signaling pathways that regulate the nutrient metabolism, fluid homeostasis, growth, ionic transport, maintenance of vascular tone, and other functions. Insulin resistance (IR) is a condition characterized by subnormal cellular response to physiological levels of insulin. The IR is divided into three types (prereceptor, receptor, and postreceptor) based on the site of pathology. Beta cells attempt to overcome the IR by increasing the release of insulin, leading to hyperinsulinemia. IR is the predisposing factor for many metabolic and cardiovascular disorders. From the evolutionary perspective, the presence of IR offers a survival advantage in the face of starvation or stress. In this brief review, we discuss the different facets of insulin resistance and appraise the readers about the hitherto neglected beneficial advantages.
Keywords: Diabetes; Insulin resistance; Lifestyle disease; Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; Polycystic ovarian disease.
© 2019 Director General, Armed Forces Medical Services. Published by Elsevier, a division of RELX India Pvt. Ltd.
Figures
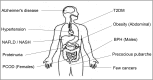
Fig. 1
Spectrum of insulin resistance. PCOD, polycystic ovarian disease; T2DM, type 2 diabetes mellitus; BPH, benign prostatic hyperplasia; NAFLD, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; NASH, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.
Fig. 2
Facets of insulin resistance. PCOD, polycystic ovarian disease; BPH, benign prostatic hyperplasia; NAFLD, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; NASH, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.
Similar articles
- Insulin resistance - "the good or the bad and ugly".
Szosland K, Lewinski A. Szosland K, et al. Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 2018 Dec;39(5):355-362. Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 2018. PMID: 30664340 Review. - Insulin resistance is a two-sided mechanism acting under opposite catabolic and anabolic conditions.
Schwartsburd P. Schwartsburd P. Med Hypotheses. 2016 Apr;89:8-10. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2016.01.007. Epub 2016 Jan 23. Med Hypotheses. 2016. PMID: 26968899 - Thiazolidinediones--tools for the research of metabolic syndrome X.
Komers R, Vrána A. Komers R, et al. Physiol Res. 1998;47(4):215-25. Physiol Res. 1998. PMID: 9803467 Review. - Growth hormone-induced alterations in the insulin-signaling system.
Dominici FP, Turyn D. Dominici FP, et al. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2002 Mar;227(3):149-57. doi: 10.1177/153537020222700301. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2002. PMID: 11856812 Review.
Cited by
- Associations between the serum triglyceride-glucose index and pericoronary adipose tissue attenuation and plaque features using dual-layer spectral detector computed tomography: a cross-sectional study.
Ma Y, Zhen Y, Wang M, Gao L, Dang Y, Shang J, Chen X, Ma S, Zhou K, Feng K, Xin Y, Hou Y, Guo C. Ma Y, et al. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 May 10;14:1166117. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1166117. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37234808 Free PMC article. - Liver Steatosis: A Marker of Metabolic Risk in Children.
Neri CR, Scapaticci S, Chiarelli F, Giannini C. Neri CR, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 27;23(9):4822. doi: 10.3390/ijms23094822. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35563210 Free PMC article. Review. - Therapeutic effect of metformin in the treatment of endometrial cancer.
Mu N, Xu T, Gao M, Dong M, Tang Q, Hao L, Wang G, Li Z, Wang W, Yang Y, Hou J. Mu N, et al. Oncol Lett. 2020 Nov;20(5):156. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.12017. Epub 2020 Aug 24. Oncol Lett. 2020. PMID: 32934724 Free PMC article. Review. - The Intricate Relationship between Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM), Insulin Resistance (IR), and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD).
Tanase DM, Gosav EM, Costea CF, Ciocoiu M, Lacatusu CM, Maranduca MA, Ouatu A, Floria M. Tanase DM, et al. J Diabetes Res. 2020 Jul 31;2020:3920196. doi: 10.1155/2020/3920196. eCollection 2020. J Diabetes Res. 2020. PMID: 32832560 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Moller D.E., Flier J.S. Insulin resistance – mechanisms, syndromes, and implications. N Engl J Med. 1991;325:938–948. - PubMed
- DeFronzo R.A., Ferrannini E. Insulin resistance. A multifaceted syndrome responsible for NIDDM, obesity, hypertension, dyslipidemia, and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Diabetes Care. 1991 Mar;14(3):173–194. - PubMed
- Semple R.K., Savage D.B., Cochran E.K., Gorden P., O'Rahilly S. Genetic syndromes of severe insulin resistance. Endocr Rev. 2011;32:498–514. - PubMed
- Kahn S.E., Hull R.L., Utzschneider K.M. Mechanisms linking obesity to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nature. 2006;444(7121):840–846. - PubMed
- LeRoith D. Beta-cell dysfunction and insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes: role of metabolic and genetic abnormalities. Am J Med. 2002 Oct 28;113(Suppl 6A):3S–11S. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials