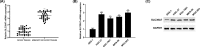SLC39A7, regulated by miR-139-5p, induces cell proliferation, migration and inhibits apoptosis in gastric cancer via Akt/mTOR signaling pathway - PubMed (original) (raw)
SLC39A7, regulated by miR-139-5p, induces cell proliferation, migration and inhibits apoptosis in gastric cancer via Akt/mTOR signaling pathway
Yanting Zhang et al. Biosci Rep. 2020.
Abstract
As a zinc transporter, SLC39A7 (zip7) is vital in intestinal epithelial self-renewal, and recent studies suggested that SLC39A7 was related to cancer progression. Whereas, little is known about the role of SLC39A7 in gastric cancer (GC). In the present study, qRT-PCR analysis demonstrated that SLC39A7 mRNA level was increased in both GC tissues and cell lines. Overexpressing SLC39A7 boosted cell proliferation and migration, while inhibited apoptosis in GC. It was also found that si-SLC39A7 suppressed Akt/mTOR pathway and activation of Akt/mTOR pathway reversed the effects of si-SLC39A7 on GC development. Through prediction website, we found that SLC39A7 was directly regulated by miR-139-5p. miR-139-5p mimic had adverse effects on SLC39A7 expression and influence in the GC cell proliferation, migration and apoptosis by Akt/mTOR signaling pathway, while miR-139-5p inhibitor showed opposite effects. To conclude, our studies showed that SLC39A7 was negatively regulated by miR-139-5p. Besides, SLC39A7 positively regulated GC development through Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. These results indicate that SLC39A7 may be a candidate target gene for GC treatment.
Keywords: SLC39A7; gastric cancer; miR-139-5p; proliferation.
© 2020 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures
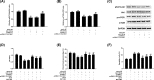
Figure 1. SLC39A7 is highly expressed in GC
(A) qRT-PCR was used to detect SLC39A7 mRNA expression in GC tissues. (B) SLC39A7 mRNA and (C) protein level in GC cells were analyzed via qRT-PCR and Western blot. **P<0.01 vs normal tissues or GES-1 cells.
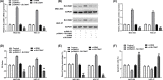
Figure 2. SLC39A7 promoted GC cell proliferation and migration while inhibiting cell apoptosis
MGC-803 and HGC-27 cells were cultured and transfected with si-RNA, si-SLC39A7, pcDNA3.1 or pcDNA3.1-SCL39A7. (A–C) Transfection efficiency of pcDNA3.1-SLC39A7 and si-SLC39A7 were evaluated by qRT-PCR and Western blot. (D,E) Cell proliferation and migration were evaluated by MTT assay and wound-healing assay. (F) Cell apoptosis was evaluated by apoptosis analysis. **P<0.01 vs pcDNA3.1 and ##P<0.01 vs si-RNA.
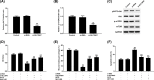
Figure 3. SLC39A7 affects GC cells proliferation, migration and apoptosis through Akt/mTOR pathway
HGC-27 cells were transfected with si-RNA or si-SLC39A7 and treated with SC79 or MHY1485. pS473-Akt/Akt (A,C) and p-mTOR/mTOR (B,C) protein expression in HGC-27 cells was assessed by Western blot. (D) MTT assay, (E) wound-healing assay and (F) apoptosis assay were recruited to analyze the proliferation, migration and apoptosis of HGC-27 cells with si-SLC39A7 or si-RNA transfection and SC79 or MHY1485 treatment. ##P<0.01 vs si-RNA and &&P<0.01 vs si-SLC39A7.
Figure 4. miR-139-5p targets SLC39A7 directly
(A) The putative binding sequence of miR-139-5p in wild-type and mutant SLC39A7-3′UTR. (B) The relative luciferase activity with wild-type or mutant SLC39A7-3′UTR in HGC-27 cells transfected with the miR-139-5p or miR-NC were analyzed. (C) qRT-PCR was applied to assess SLC39A7 mRNA expression in miR-139-5p or miR-139-5p inhibitor transfected group and respective NC group. (D,E) mRNA levels of miR-139-5p in gastric tissues and cell lines were detected via qRT-PCR. (F) Spearman’s correlation analysis was recruited to explore the correlation between miR-139-5p and SLC39A7 mRNA level. **P<0.01 vs miR-139-5p and ##P<0.01 vs miR-139-5p inhibitor.
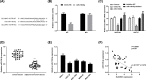
Figure 5. SLC39A7 mediated-Akt/mTOR pathway is involved in the miR-139-5p regulated cell proliferation, migration and apoptosis of GC
HGC-27 cells were co-transfected with mimic inhibitor or miR-139-5p mimic and pcDNA3.1 or pcDNA3.1-SLC39A7 with SC79 or MHY1485 treatment. (A–C) The protein expression of pS473-Akt and p-mTOR was evaluated by Western blot. The cell proliferation (D), migration (E) and apoptosis (F) were analyzed via MTT assay, wound-healing assay and apoptosis assay. **P<0.01 vs mimic NC, ##P<0.01 vs miR-139-5p or miR-139-5p + pcDNA-3.1.
Similar articles
- Mechanism of miR-122-5p regulating the activation of PI3K-Akt-mTOR signaling pathway on the cell proliferation and apoptosis of osteosarcoma cells through targeting TP53 gene.
Li KW, Wang SH, Wei X, Hou YZ, Li ZH. Li KW, et al. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020 Dec;24(24):12655-12666. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202012_24163. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33378012 - miR-101-2, miR-125b-2 and miR-451a act as potential tumor suppressors in gastric cancer through regulation of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway.
Riquelme I, Tapia O, Leal P, Sandoval A, Varga MG, Letelier P, Buchegger K, Bizama C, Espinoza JA, Peek RM, Araya JC, Roa JC. Riquelme I, et al. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2016 Feb;39(1):23-33. doi: 10.1007/s13402-015-0247-3. Epub 2015 Oct 12. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2016. PMID: 26458815 Free PMC article. - miR-188-5p emerges as an oncomiRNA to promote gastric cancer cell proliferation and migration via upregulation of SALL4.
Wang M, Qiu R, Gong Z, Zhao X, Wang T, Zhou L, Lu W, Shen B, Zhu W, Xu W. Wang M, et al. J Cell Biochem. 2019 Sep;120(9):15027-15037. doi: 10.1002/jcb.28764. Epub 2019 Apr 22. J Cell Biochem. 2019. PMID: 31009138 - MicroRNA-99b suppresses human cervical cancer cell activity by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway.
Li YJ, Wang Y, Wang YY. Li YJ, et al. J Cell Physiol. 2019 Jun;234(6):9577-9591. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27645. Epub 2018 Nov 27. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30480801 Retracted. - Mir-20a-5p induced WTX deficiency promotes gastric cancer progressions through regulating PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.
Li J, Ye D, Shen P, Liu X, Zhou P, Zhu G, Xu Y, Fu Y, Li X, Sun J, Xu J, Zhang Q. Li J, et al. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020 Oct 8;39(1):212. doi: 10.1186/s13046-020-01718-4. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 33032635 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Effects of in utero exposure to Δ-9-tetrahydrocannabinol on cardiac extracellular matrix expression and vascular transcriptome in rhesus macaques.
Le HH, Shorey-Kendrick LE, Hinds MT, McCarty OJT, Lo JO, Anderson DEJ. Le HH, et al. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2024 Sep 1;327(3):H701-H714. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00181.2024. Epub 2024 Jul 19. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39028280 - Cellular zinc metabolism and zinc signaling: from biological functions to diseases and therapeutic targets.
Chen B, Yu P, Chan WN, Xie F, Zhang Y, Liang L, Leung KT, Lo KW, Yu J, Tse GMK, Kang W, To KF. Chen B, et al. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024 Jan 3;9(1):6. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01679-y. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024. PMID: 38169461 Free PMC article. Review. - NVS-ZP7-4 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma tumorigenesis and promotes apoptosis via PI3K/AKT signaling.
Tong Q, Yan D, Cao Y, Dong X, Abula Y, Yang H, Kong P, Yi M. Tong Q, et al. Sci Rep. 2023 Jul 21;13(1):11795. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-38596-7. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37479837 Free PMC article. - Extracellular vesicles derived from umbilical cord mesenchymal stromal cells show enhanced anti-inflammatory properties via upregulation of miRNAs after pro-inflammatory priming.
Hyland M, Mennan C, Davies R, Wilson E, Tonge DP, Clayton A, Kehoe O. Hyland M, et al. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2023 Oct;19(7):2391-2406. doi: 10.1007/s12015-023-10586-2. Epub 2023 Jul 20. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2023. PMID: 37474869 Free PMC article. - Long Noncoding RNA, MicroRNA, Zn Transporter Zip14 (Slc39a14) and Inflammation in Mice.
Jimenez-Rondan FR, Ruggiero CH, Cousins RJ. Jimenez-Rondan FR, et al. Nutrients. 2022 Dec 1;14(23):5114. doi: 10.3390/nu14235114. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36501144 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous